Duke of Silesia
The Duke of Silesia was the sons and descendants of the Polish Duke Bolesław III Wrymouth. In accordance with the last will and testament of Bolesław, upon his death his lands were divided into four or five hereditary provinces distributed among his sons, and a royal province of Kraków reserved for the eldest, who was to be High Duke of all Poland. This was known as the fragmentation of Poland. Subsequent developments lead to further splintering of the duchies.
At the beginning of the 14th century, fourteen independent Duchies existed in Silesia: Brzeg, Wrocław, Świdnica, Jawor, Ziębice, Głogów, Ścinawa, Żagan and Oleśnica in Lower Silesia; Koźle, Cieszyn, Bytom, Niemodlin, Opole, Strzelce, Racibórz and Opava in Upper Silesia and the ecclesiastical Duchy of Nysa. Between 1327 and 1329 most dukes accepted the overlordship of Bohemian king John of Bohemia, who acquired the right of succession for all of these duchies. In the coming centuries all branches of the Silesian Piasts died out, and with the death of George William, Duke of Liegnitz the dynasty ceased to exist.
Duchy of Silesia

The Duchy of Silesia, one of the hereditary provinces of Poland, Silesia, was granted to Bolesław III's eldest son, Władysław II the Exile, and was subsequently divided among his sons Bolesław I the Tall (Wrocław/Lower Silesia), Mieszko I Tanglefoot (Racibórz/Upper Silesia) and Konrad Spindleshanks (Głogów). After Konrad's death Głogów was again united with the Duchy of Wrocław/Lower Silesia.
Piast Dynasty
| Ruler | Born | Reign | Death | Ruling Part | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ladislaus II the Exile | .jpg.webp) | 1105 | 1138–1146 | 30 May 1159 | Silesia | also monarch of Poland exiled by his half-brothers |
| Boleslaus IV the Curly |  | 1125 | 1146–1163 | 5 January 1173 | Silesia | half-brother of Ladislaus II also Duke of Masovia and monarch of Poland |
Partitions of Silesia
In 1173 Bolesław returned and he agreed to let Mieszko and Bolesław rule in their own Duchies, separated from the Duchy of Silesia. This led to the creation of the Duchy of Racibórz for Mieszko I and the Duchy of Opole for Jarosław, beginning the fragmentation of the Duchy of Silesia. The territories controlled by Mieszko I and Jarosław roughly corresponded to what is known as Upper Silesia, while the territories remaining with Bolesław I roughly corresponded to Lower Silesia.
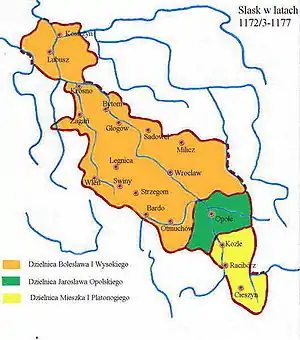
Lower Silesia
Duchy of Lower Silesia was a direct continuation of the Duchy of Silesia, but without the territories roughly corresponding to Upper Silesia; hence it was composed of the territories roughly corresponding to Lower Silesia. Some sources refer to it as the Duchy of Silesia; some as Duchy of Lower Silesia; others yet as the Duchy of Wrocław (Breslau). Wrocław was the capital of the Duchy of Silesia, yet this early (1172–1248) Duchy of Silesia should not be confused with the smaller Duchy of Wrocław that was created with further fragmentation in 1248. The Duchy went through various border changes in the coming years, sometimes losing and sometimes gaining territory. In 1248 Lower Silesia was divided when Bolesław II had to cede the Duchy of Wrocław to his younger brother Henry III.

Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia was divided into the Duchies of Cieszyn, and Opole-Racibórz. In 1340 the Duchy of Racibórz was united with Opava, a Bohemian fief.

Partitions of Polish Silesia under Piast dynasty
Below follows a simplified table of Silesia's partitions:
| Duchy of Silesia (1138–1163) | ||||||||||||||
| Lower Silesia (1163–1241) |
Opole-Racibórz, Upper Silesia (1st creation) (1163–1282) | |||||||||||||
| Wrocław (1241–1335) |
Legnica (1st creation) (1241–1449) |
Opole (1282–1521) |
Bytom (1282–1357) |
Racibórz (1282–1336) |
||||||||||
| Oleśnica (1312–1492) |
Żagań (1309–1504) |
Głogów (1st creation) (1274–1331) |
Świdnica-Jawor (divided into Świdnica and Jawor 1312–1346) (1274–1392) |
Ziębice (1312–1442) |
Oświęcim (1315–1457) | |||||||||
| Cieszyn (1281–1653) | ||||||||||||||
| Annexed to Bohemia | Annexed to Bohemia (1331) Recovered by Jawor (1337) Annexed to Bohemia (1346) |
Annexed to Bohemia Recovered by Opole (1521) | ||||||||||||
Shared inheritance:
Both parts reunited by Żagań line (1480) |
Lubin (1348–1446) |
Brzeg (1st creation) (1342–1450) (divided (1358–68) in halves, one of them part of Świdnica-Jawor; Olawa split 1400–54 and joined Legnica) |
Shared inheritance: - Half A: Part of Oleśnica inheritance (1357–1498) - Half B: Part of Cieszyn (1357–1459), and then Oleśnica inheritances (1459–98) Both parts recovered by Opole (1498) | |||||||||||
| Annexed to Bohemia | ||||||||||||||
| Annexed to Bohemia | Annexed to Bohemia | Part of Głogów Half A inheritance (1446–1482) |
Opole (1282–1521) |
Zator (1445–1513) | ||||||||||
| Annexed to Poland | ||||||||||||||
| Annexed to Poland (1488) | Legnica (2nd creation) (1454–1672) (bought Brzeg from Opole (1481), and regained Lubin from Głogów (1482)) |
|||||||||||||
| Annexed to Bohemia | Brzeg (2nd creation) (1488–1672) (Lubin recreated as dowry 1521–50; Olawa split 1586–95, 1602–05, 1672–80) |
|||||||||||||
| Annexed to Saxony | Opole-Racibórz (1521–1532) |
Annexed to Poland | ||||||||||||
| Annexed to Brandenburg-Ansbach | ||||||||||||||
| Annexed to the Holy Roman Empire | Annexed to the Holy Roman Empire | |||||||||||||
A quick reminder avoiding confusion:
| Lower Silesia | Upper Silesia |
|---|---|
|
Table of rulers
| Ruler | Born | Reign | Death | Ruling part | Consort | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boleslaus I the Tall |  | 1127 | 1163–1201 | 8 December 1201 | Lower Silesia | Zvenislava of Kiev 1142 two children Christina 1157 seven children | |
| Mieszko III Tanglefoot |  | 1130 | 1163–1211 | 6 May 1211 | Upper Silesia | Ludmila of Bohemia between 1170 and 1178 five children | First Duke of Upper Silesia, emerged from Silesia with the Duchy of Lower Silesia. |
| Henry I the Bearded |  | 1165 | 1201–1238 | 19 March 1238 | Lower Silesia | Hedwig of Merania 1188 seven children | Also monarch of Poland. |
| Casimir II |  | 1179/80 | 1211–1230 | 13 May 1230 | Opole-Racibórz (Upper Silesia) | Viola of Bulgaria between 1212 and 1220 four children | |
| Henry II the Pious |  | 1196 | 1238–1241 | 9 April 1241 | Lower Silesia | Anna of Bohemia 1216 ten children | Also monarch of Poland. |
| Regencies of Henry I the Bearded (1230–1238) and Henry II the Pious (1238–1239) | |||||||
| Mieszko II the Fat |  | 1220 | 1230–1246 | 22 October 1246 | Opole-Racibórz (Upper Silesia) | Judith of Masovia c. 1239–1240 no children | |
| Regency of Anna of Bohemia (1241–1242) | Sons of Henry II, made partitions in 1248: Henry got the duchy of Wrocław, and Boleslaus the duchy of Legnica. | ||||||
| Henry III the White[1] |  | 1227 or 1230 | 1242–1266 | 3 December 1266 | Wrocław | Judith of Masovia 2 June 1252 two children Helena of Saxony before 1266 no children | |
| Boleslaus II the Bald |  | c. 1220/5 | 1242–1278 | 26–31 December 1278 | Legnica | Hedwig of Anhalt 1242 seven children Euphemia of Pomerelia 1261 (annulled 1277) no children Sophia of Dyhrn (morganatic) 1277 no children | |
| Ladislaus I |  | 1225 | 1246–1282 | 27 August or 13 September 1282 | Opole-Racibórz (Upper Silesia) | Euphemia of Greater Poland 1251 five children | In 1282 Opole-Raciborz was divided in various duchies, to the four sons of Władysław. |
| Conrad I[2] |  | 1228/31 | 1251–1274 | 6 August 1274 | Głogów | Salome of Greater Poland 1249 six children Sophie of Landsberg 1271 no children | First duke of Głogów. Brother of Henry III the White and Boleslaw II the Bald. |
| Henry IV the Just[3] |  | 1257/1258 | 1266–1290 | 23 June 1290 | Wrocław | Constance of Opole March 1280 no children Matilda of Brandenburg-Salzwedel c. 1288 no children | also monarch of Poland. |
| Wroclaw temporarily annexed to Legnica | |||||||
| Henry III[1][4] | 1251/60 | 1274–1309 | 3 December 1309 | Głogów | Matilda of Brunswick-Lüneburg March 1291 nine children |
Children of Conrad I, divided the land. Henry III received Glogow, Przemko ruled Zagan and Conrad inherited Scinawa. Conrad would later inherit his brother Przemko's duchy, but was Henry who reunited the land after Conrasd 's land. After Henry III's won death, the lands were again divided. | |
| Przemko I[5] |  | 1252/65 | 1274–1284 | 26 February 1289 | Głogów (at Żagań) | Unmarried | |
| Conrad II the Hunchback[6] |  | 1252/65 | 1274–1304 | 11 October 1304 | Głogów (at Scinawa until 1284; in Żagań since 1284) | Unmarried | |
| Henry V the Fat[7] |  |
1248 | 1273–1278 | 22 February 1296 | Świdnica-Jawor | Elisabeth of Greater Poland 1277 eight children |
Children of Boleslaus II, divided the land. Henry V had been nominated by his father as duke of Świdnica-Jawor, which he gave to his brothers Bolko and Bernard to inherit the entire Legnica. In 1290, after the death of the childless Henry IV, Henry V also inherited Wrocław. In 1296, after Henry V's death, Bolko was appointed regent for his nephews (sons of Henry V). |
| 1278–1296 | Legnica | ||||||
| Bolko I the Strict[8] |  | 1252/6 | 1278–1301 | 9 November 1301 | Świdnica-Jawor | Beatrice of Brandenburg-Salzwedel 4 October 1284 Berlin ten children | |
| Bernard I the Lightsome |  | 1253/7 | 1278–1286 | 25 April 1286 | Świdnica-Jawor | Unmarried | |
| Premislaus | 12 June 1268 | 1282–1306 | 7 May 1306 | Racibórz | Anna of Masovia between 1289 and 1290 three children |
Sons of Ladislaus I, ruled jointly until 1290, when Mieszko founded his own duchy, Cieszyn. | |
| Mieszko I[9] |  | 1252/6 | 1282–1315 | 27 June 1315 | Cieszyn | Unknown between 1275 and 1280 three children | |
| Bolko [Boleslaus] I[10] |  | before 21 October 1258 | 1282–1313 | 14 May 1313 | Opole | Grimislava? before 1286 Agnes c.1280 three children |
Sons of Ladislaus I, ruled jointly. In 1284, they divided the land: Boleslaus retained Opole and Casimir received Bytom, as its first duke. |
| Casimir[11] | 1253/7 | 1282–1312 | 10 March 1312 | Bytom (in Opole until 1284) | Helena between 1275 and 1278 six children | ||
| Regencies of Bolko I the Strict (1296–1301), Heinrich of Würben (1301–02) and Wenceslaus II of Bohemia (1302–05) | Children of Henry V, under regency until 1305. Freed from regency at fourteen, Boleslaus ruled with his younger brothers, Henry and Ladislaus, until 1311, when they divided the land. He received Legnica, together with Ladislaus. After a year of co-rulership, Boleslaus expelled Ladislaus and excluded him from government. Becoming sole ruler, he created, in 1312, the Duchy of Brzeg, which ruled until his death, Abdicating of Legnica for his son in 1342. Henry received Wrocław, but, in 1327 having no male heirs, signed a contract of inheritance with King John of Bohemia and upon his death the Duchy of Wrocław fell to the Kingdom of Bohemia. | ||||||
| Boleslaus III the Generous |  |
23 September 1291 | 1296–1342 | 21 April 1352 | Legnica | Margaret of Bohemia 1318 three children Katharina of Croatia 1326 no children | |
| 1312–1352 | Brzeg | ||||||
| Ladislaus I | 6 June 1296 | 1296–1312 | after 13 January 1352 | Legnica | Anna of Masovia 1325 (annulled 1329) no children | ||
| Henry VI the Good[12] |  | 18 March 1294 | 1296–1335 | 24 November 1335 | Wrocław (in Legnica until 1311) | Anna of Austria 1310 three children | |
| Annexation to the Kingdom of Bohemia | |||||||
| Leszek | 1292 | 1306–1336 | 1336 | Racibórz | Agnes of Głogów-Żagań 1332 no children | Son of Przemysław I. After his death in 1336, Raciborz was annexed by the Kingdom of Bohemia. | |
| Annexation to the Kingdom of Bohemia (1306–1521) | |||||||
| Matilda of Brunswick-Lüneburg |  | 1276 | 1309–1318 | 26 April 1318 | Głogów | Henry III March 1291 nine children | Widow of Henry III. |
| Henry IV the Faithful[13] |  | 1292 | 1309–1342 | 22 January 1342 | Żagań (in Głogów 1318–21) | Matilda of Brandenburg-Salzwedel 5 January 1310 four children |
Sons of Henry III, inherited, together, Żagań. In 1312, Conrad and Boleslaus created their own duchy with its capital in Oleśnica, becoming the first dukes of Oleśnica. The death of Boleslaus left Conrad as sole ruler of his duchy. Henry and Premislaus continued the joint rule. They reunited again, and as their father did, the two duchies of the paternal inheritance after the death of their mother. In 1321 the two brothers made new partitions. From 1321, Henry ruled Żagań and Premislaus ruled Głogów. After the childless death of Premislaus, his duchy was briefly annexed by the Kingdom of Bohemia. |
| Przemko II[14] | 1305 | 1318–1331 | 11 January 1331 | Głogów (in Żagań 1309–21) | Constance of Świdnica 1326 no children | ||
| John | 1298 | 1318–1365 | 19 May 1365 | Głogów (in Żagań 1309–18; in Ścinawa since 1318) | Constance of Świdnica 1326 no children | ||
| Conrad I[15] |  | 1294 | 1312–1366 | 22 December 1366 | Oleśnica (in Żagań 1309–12) | Elisabeth of Wroclaw 10 January 1322 no children Euphemia of Bytom 2 March 1333 two children | |
| Boleslaus |  | 1295 | 1312–1321 | before 23 April 1321 | Oleśnica (in Żagań 1309–12) | Unmarried | |
| Annexation to the Kingdom of Bohemia (1331–1337) and to the Jawor portion of Świdnica-Jawor (1337–1346); New annexation to the Kingdom of Bohemia (1346–1349/60) In 1349 Henry V of Iron (son of Henry the Fatithful) recovered half of the inheritance of his uncle Przemko in Głogów from Bohemia; the other half was given to Przemko II's widow, Constance, in 1360. | |||||||
| Regency of Herman, Margrave of Brandenburg-Salzwedel (1301–1305) | Henry and Bernard ruled together until 1312, then divided the land between them. Henry kept also Głogów, which he recovered from Bohemia. However, Głogów returns to Bohemian control after Henry's death. | ||||||
| Bernard II the Stable | 1291 | 1301–1326 | 6 May 1326 | Świdnica-Jawor(in Świdnica since 1312) | Kunigunde of Poland 1310 five children | ||
| Henry I[16] |  | 1292/6 | 1301–1346 | before 15 May 1346 | Świdnica-Jawor(in Jawor since 1312) | Agnes of Bohemia 1316 no children | |
| Siemowit | 1292 | 1312–1316 | after 1 July 1342 | Bytom | Unmarried | Son of Casimir. Deposed in 1316. | |
| Bolko [Boleslaus] II[10] |  | before 1300 | 1313–1356 | 21 June 1356 | Opole | Elisabeth of Świdnica 6 May 1326 seven children |
Sons of Bolko I, ruled jointly. |
| Albert | after 1300 | 1313–1323 | 25 September 1373 | Opole | Agnes of Magdeburg 1347 one child | ||
| Casimir I[17] | 1280/90 | 1315–1358 | 29 September 1358 | Cieszyn | Euphemia of Czersk-Warsaw 1321 nine children | ||
| Ladislaus I[18] |  | 1275/80 | 1315–1324 | 15 May 1324 | Oświęcim | Euphrosyne of Masovia c. 1304 two children | First Duke of Oświęcim, which emerged from Cieszyn. |
| Ladislaus I[18] | 1277/83 | 1316–1352 | 8 September 1352 | Bytom | Beatrice of Brandenburg-Salzwedel 21 September 1308 two children Ludgarda of Mecklenburg 6 October 1328 six children | Brother of Siemowit. Ruled jointly with his brother George until 1327. | |
| George I | 1300 | 1316–1327 | 1327 | Bytom | Unmarried | Ruled jointly with his brother Ladislaus. | |
| Bolko II[19] |  | 1 February 1300 | 1322–1341 | 11 June 1341 | Ziębice | Bonne of Savoy-Vaud 21 November 1321 two children | First duke of Ziębice. Son of Bolko the Strict. |
| Regency of Euphrosyne of Masovia (1324–1325) | |||||||
| John I the Scholastic |  | 1308/10 | 1324–1372 | 29 September 1372 | Oświęcim | Unknown one child Salome Reuss von Plauen after 12 July 1359 three children | |
| Nicholas I the Small | 1327 | 1341–1358 | 23 April 1358 | Ziębice | Agnes Krusina zu Lichtemburka 23 October 1343 six children | ||
| Henry V of Iron[20] |  | 1319 | 1342–1369 | After 8 April 1369 | Żagań (with Half A of Głogów from 1349) | Anna of Płock 6 September 1337 five children | Son of Henry IV the Faithful. In 1349 Half A of Głogów reemerges from Bohemia to be annexed by Żagań line of the Piasts. |
| Katharina of Croatia | ? | 1352–1358 | before 5 March 1358 | Brzeg | Boleslaus III the Generous 1326 no children | Widow. After her death the duchy was divided between Louis the Fair (her stepson) and Bolko the Small from Swidnica-Jawor. | |
| Boleslaus I[21] | 1330 | 1352–1355 | 4 October 1355 | Bytom | 14 February 1347 three children |
Son of Ladislaus IV. After his death his widow inherited the duchy. In 1357 the duchy was divided in two parts, being one annexed by the Duchy of Oleśnica, and the other annexed by the Duchy of Cieszyn. | |
| Margareta of Sternberg | ? | 1355–1357 | after 5 June 1365 | Bytom | |||
| Definitive annexation to the duchies of Oleśnica and Cieszyn | |||||||
| Ladislaus II[22] |  | 1332 | 1356–1396 | 18 May 1401 | Opole | Elisabeth of Wallachia c. 1355 three children Euphemia of Masovia 1369 two children |
Sons of Bolko II, ruled jointly. |
| Henry[23] | before 18 August 1338 | 1356–1365 | before 23 October 1365 | Opole | Unmarried | ||
| Bolko III[24] |  | 1337 | 1356–1370 | 21 October 1382 | Opole | Anna of Oświęcim c. 1355 five children | |
| Bolko III[24] | 1348 | 1358–1410 | 13 June 1410 | Ziębice | Euphemia of Bytom 1369 eight children |
Sons of Nicholas I, ruled jointly. | |
| Henry I[25] | 1350 | 1358–1366 | after 8 August 1366 | Ziębice | Unmarried | ||
| Constance of Świdnica | 1313 | 1360–1361 | 21 November 1363 | Głogów (Half B) | Przemko II 1326 no children | In 1360 Half B of Głogów reemerges from Bohemia to be given to Constance, widow of Przemko II. She renounces the title in favour of her brother Bolko II the Small. | |
| Bolko II the Small[26] |  | 1312 | 1326–1368 | 28 July 1368 | Świdnica-Jawor (in Świdnica until 1346; in Half A of Brzeg since 1358, and Half B of Głogów since 1361) | Agnes of Austria 1 June 1338 no children |
Sons of Bernard II, ruled jointly until Henry's death in 1343. In 1346, after his uncle Henry I's death with no male heirs, he reunites Świdnica-Jawor in one duchy. Bolko also bought half of Brzeg in 1358. Brother of Constance, widow duchess of Głogów, inherited part of the duchy from her. After his death in 1368, the half of Głogów returned the Kingdom of Bohemia, and the half of Brzeg to Louis the Fair. |
| Henry II | 1316 | 1334–1343 | 28 June 1345 | Świdnica | Katharina of Hungary 1 June 1338 one child | ||
| Annexation of Half B to the Kingdom of Bohemia (1368–1384) | |||||||
| Reintegration of Half A in Brzeg | |||||||
| Wenceslaus I |  | 1318 | 1342–1364 | 2 June 1364 | Legnica | Anna of Cieszyn c.1338 five children |
Sons of Boleslaus IV, ruled jointly until 1346, when Louis created his own duchy, Lubin, which he ruled until his death. In 1358 inherited half of Brzeg from his stepmother Katharina. Reunited Brzeg after the death of the owner of the other part, Bolko the Small (1368). |
| Louis I the Fair |  |
1321 | 1348–1398 | 6–23 December 1398 | Lubin (in Legnica 1342–1346) |
Agnes of Głogów-Żagań 1341 six children | |
| 1358–1398 | Brzeg (in Half B until 1368) | ||||||
| Henry VII the Courageous[27] | 1343/5 | 1361–1399 | 11 July 1399 | Brzeg (in Half B until 1368; with Lubin since 1398) | Helena of Orlamunde 1369 one child Margaret of Masovia July 1379 one child | Duke of Brzeg jointly with his father Louis I, inherited Lubin from him. | |
| Rupert I | 27 March 1347 | 1364–1409 | before 12 January 1409 | Legnica | Hedwig of Zagan 10 February 1372 two children |
Sons of Wenceslaus I, ruled jointly. | |
| Wenceslaus II |  | 1348 | 1364–1413 | 30 December 1419 | Legnica | Unmarried | |
| Boleslaus IV | 1349 | 1364–1394 | 3/4 March 1394 | Legnica | Unmarried | ||
| Henry VIII[28] |  | 1355 | 1364–1398 | 12 December 1398 | Legnica | Unmarried | |
| Conrad II the Gray[29] |  | 1340 | 1366–1403 | 10 June 1403 | Oleśnica | Agnes of Cieszyn 23 February 1354 one child | Son of Conrad I. |
| Agnes of Austria |  | 1322 | 1368–1392 | 2 February 1392 | Świdnica-Jawor | Bolko II the Small 1 June 1338 no children | Widow, succeeded her husband according to his will. After her death the duchy was annexed to the Kingdom of Bohemia. |
| Annexation to the Kingdom of Bohemia | |||||||
| Henry VI the Elder[30] |  | before 1345 | 1369–1393 | 5 December 1393 | Żagań (in Głogów Half A until 1378) | Hedwig of Legnica 10 February 1372 no children |
Sons of Henry V, ruled jointly until 1378. In that year, they made partitions: Henry VI retained Żagań and Henry VII the half of Głogów. Henry VIII received a few towns, but he eventually succeeded his heirless brother Henry VII in 1395. |
| Henry VII Rumpold[31] | 1350 | 1369–1395 | 24 December 1395 | Głogów (Half A) (in Żagań until 1378) | Unmarried | ||
| Henry VIII the Sparrow[32] |  | 1357 | 1369–1378 1395–1397 | 14 March 1397 | Głogów (Half A) (in Żagań until 1378) | Catherine of Opole 1382 five children | |
| John II | 1344/51 | 1372–1376 | 19 February 1376 | Oświęcim | Hedwig of Brieg 1366 three children | Son of John I. | |
| John III | 1366 | 1376–1405 | 19 August 1405 | Oświęcim | Hedwig of Lithuania 1394 no children | Son of John II. Left no descendants. The duchy went to a son of Premislaus IV. | |
| Premislaus I Noszak |  |
1332/6 | 1358–1410 | 23 May 1410 | Cieszyn | Elisabeth of Bytom 1360 three children |
Upper Duke of Cieszyn, in 1284 recovered part of the Lower Silesian duchy of Głogów from Bohemia. Abdicated of Głogów for his son, Premislaus, in 1404, but recovered it in 1406. |
| 1384–1404 1406–1410 | Głogów (Half B) | ||||||
| Premislaus The Younger[33] | 1362 | 1404–1406 | 1 January 1406 | Głogów (Half B) |
Unknown one child |
Received, in his father's lifetime, the duchy of Głogów. In the next year also inherited Oświęcim from John III. Preceded his father in death, but left descendants to rule in Oświęcim, while Głogów returned to his father. | |
| 1405–1406 | Oświęcim | ||||||
| Hedwig of Legnica | 1351 | 1393–1403 | 1 August 1409 | Żagań | Henry VI the Elder 10 February 1372 no children | Widow of Henry VI. | |
| Bolko IV[34] | 1363/7 | 1396–1437 | 6 May 1437 | Opole | Margaret of Gorizia 1398 five children |
Sons of Bolko III, ruled jointly. In 1422, Bolko V, Bolko IV's son, joined the co-rulership, but abdicated two years after, to rule Niemodlin and Strzelce, vassal towns of Opole. | |
| Bishop Jan Kropidło |  | 1360/4 | 1396–1421 | 3 March 1421 | Opole | Unmarried | |
| Bernard I[35] | 1374/8 | 1396–1400 | 2/4 April 1455 | Opole | Hedwig of Melsztyna two children | ||
| Bolko V the Hussite[34] | c.1400 | 1422–1424 | 29 May 1460 | Opole | Elisabeth Granowski c. 1418 one child | ||
| Catherine of Opole | 16 March 1367 | 1397–1420 | 6 June 1420 | Głogów (Half A) (in Prudnik, Kożuchów and Zielona Góra) | Henry VIII the Sparrow 1382 five children | Ruled in her dowry lands, which reverted to her sons after her death. | |
| John I[36] |  | 1385 | 1403–1439 | 12 April 1439 | Żagań (in Głogów Half A 1397–1412) | Scholastika of Saxe-Wittenberg c.1405 ten children |
Sons of Henry VIII, ruled jointly in the half of Głogów, inherited from their uncle Henry VIII. In 1403 inherited Żagań from their mother Hedwig. In 1412 divided the land between them. After the partition, John ruled alone in Żagań, and the other brothers continued the joint rule in Głogów. With the abdication of Wenceslaus and the death of Henry X, Henry IX became sole ruler from 1423. In 1446 he inherited Lubin. |
| Henry IX the Elder[37] | 1387 | 1397–1467 | 11 November 1467 | Głogów (Half A) (in Żagań 1403–1412) | Hedwig of Oleśnica c. 1432 six children | ||
| Henry X Rumpold[38] | 1390 | 1397–1423 | 18 January 1423 | Głogów (Half A) (in Żagań 1403–1412) | Unmarried | ||
| Wenceslaus I[39] | 1391 | 1397–1417 | before 4 February 1431 | Głogów (Half A) (in Żagań 1403–1412) | Unmarried | ||
| Henry IX[37] | 1369 | 1399–1420 | 10 July 1420 | Lubin | Anna of Cieszyn 20 September 1396 six children |
Reunited for a brief period the regional duchy of Lubin and Brzeg under his rule. In 1400 divided the inherited land with his brother Louis, who received Brzeg. However Henry also retained a part of this duchy, called Oława. | |
| 1399–1420 | Brzeg (only in Oława from 1400) | ||||||
| Louis II |  |
1380/5 | 1400–1436 | 30 May 1436 | Brzeg | Hedwig Zapólya before 14 August 1409 no children Elisabeth of Brandenburg 9 April 1418 Konstanz no children |
Received Brzeg, and reunited it with Legnica in 1413. However, died without descendants. His lands were inherited by his widow. |
| 1413–1436 | Legnica | ||||||
| Conrad III the Old |  | 1359 | 1403–1412 | 28 December 1412 | Oleśnica | Judith (?) c.1380 seven children | Son of Conrad IV. |
| Casimir I[40] | 1396 | 1406–1434 | 7 April 1434 | Oświęcim | Anna of Zagan before 28 May 1417 three children Margareta of Racibórz 1433 no children | Son of Premislaus V. | |
| Boleslaus I | 1363 | 1410–1431 | 6 May 1431 | Cieszyn (with Głogów Half B) | Margareta of Opava-Raciborz 1 January 1406 no children Euphemia of Masovia 20 November 1412 five children | ||
| John I | 1358 | 1410–1428 | 27 August 1428 | Ziębice | Elizabeth Lackfi 19 March 1408 one child |
Sons of Bolko III, ruled jointly. From 1420 ruled alone. After his death the duchy was annexed to the Kingdom of Bohemia, and later mortgaged it to Půta III of Častolovice during 1429–1435. | |
| Henry II | 1396 | 1410–1420 | 11 March 1420 | Ziębice | Unmarried | ||
| Conrad IV the Elder |  | 1384 | 1412–1416 | 9 August 1447 | Oleśnica | Unmarried | Sons of Conrad III, ruled jointly. |
| Conrad V Kantner | 1385 | 1412–1439 | 10 September 1439 | Oleśnica | Margaret (?) 9 October 1411 five children | ||
| Conrad VI the Dean | 1391 | 1416–1427 | 3 September 1427 | Oleśnica | Unmarried | ||
| Conrad VII the White |  | after 1396 | 1416–1427 1439–1450 | 14 February 1452 | Oleśnica | Katharina (?) 2 February 1437 no children Dorothea of Warsaw? 7 March 1450 no children | |
| Conrad VIII the Younger | after 1397 | 1416–1444 | 5 September 1444 | Oleśnica (only in Ścinawa since 1427) | Unmarried | ||
| Wenceslaus III | 1400 | 1420–1423 | 14 January/28 May 1423 | Brzeg (at Oława) | Unmarried | Children of Henry IX, divided their possessions. Wenceslaus kept Olawa (in Brzeg) and Rupert and Louis ruled in Lubin. Louis reunited his father's possessions. After his death his lands were divided between his sons and his widow. | |
| Rupert II | 1396/1402 | 1420–1431 | 24 August 1431 | Lubin | Unmarried | ||
| Louis III | before 1405 | 1420–1441 | before 18 June 1441 | Lubin | Margareta of Opole c.1423 two children | ||
| 1423–1441 | Brzeg (at Oława) | ||||||
| Wenceslaus I[41] | 1418 | 1434–1468 | c.28 July 1368 | Zator (in Oświęcim until 1445) | Maria Kopczowski c. 1450 seven children |
Sons of Casimir I, ruled jointly. In 1445 Wenceslaus created for himself the duchy of Zator. Premislaus abdicated from power, and John became sole ruler over Oświęcim, which was annexed to the Kingdom of Poland in 1457. | |
| Premislaus | 1425 | 1434–1445 | December 1484 | Oświęcim | Margareta of Opole 23 February 1463 one child | ||
| John IV | 1426/30 | 1434–1457 | c.21 February 1497 | Oświęcim | Katharina 30 December 1465 no children Barbara of Karniów c. 1475 one child | ||
| Definitive annexation to the Kingdom of Poland | |||||||
| Ziębice was recovered to the Piasts | |||||||
| Euphemia | 1385 | 1435–1442 | 17 November 1447 | Ziębice | Frederick III of Oettingen 1397 nine children | Daughter of Bolko III. In 1435 she bought the Duchy to the Emperor and Častolovice's heiresses. In 1442 it was sold to the Kingdom of Bohemia. | |
| Annexation to the Kingdom of Bohemia | |||||||
| Elisabeth of Brandenburg | 29 September 1403 | 1436–1449 | 31 October 1449 | Legnica | Louis II 9 April 1418 Konstanz no children Wenceslaus I, Duke of Cieszyn 17 February 1439 (annulled 1445) no children |
Widow of Louis II. In 1443 is forced to give Brzeg to John I and Henry X of Lubin. After her death in 1449, Legnica was annexed by the Kingdom of Bohemia. | |
| 1436–1443 | Brzeg | ||||||
| Annexation to the Kingdom of Bohemia (1449–1454) | |||||||
| Margareta of Opole | 1412/4 | 1441–1454 | 15 January 1454 | Brzeg (at Oława) | Louis III c. 1423 two children | Widow of Louis III. | |
| Olawa annexed to Legnica | |||||||
| John I |  |
1425 | 1441–1446 | after 21 November 1453 | Lubin | Hedwig of Brzeg February 1445 one child |
Sons of Louis III, ruled jointly. In 1443 they inherit Brzeg from Elisabeth of Brandenburg. In 1446, due to the difficult financial situation, Lubin was sold to the Duchy of Głogów. In 1450 Brzeg is sold to Opole. |
| 1443–1450 | Brzeg | ||||||
| Henry X[42] | 1426 | 1441–1446 | before 28 May 1452 | Lubin | Unmarried | ||
| 1443–1450 | Brzeg | ||||||
| Lubin was bought by Henry IX the Elder, duke of Głogów | |||||||
| Brzeg was bought by duke Nicholas I of Opole | |||||||
| Regency of Euphemia of Masovia (1431–1442) | After the partition following the end of the regency of their mother, Ladislaus retained Głogów and Wenceslaus and Premislaus Cieszyn. Boleslaus received only a few towns in Cieszyn (Bielsko and Frysztat). After Ladislaus' death, Premislaus retained co-rulership Cieszyn and Głogów, with his widowed sister-in-law. From 1468 ruled over all Cieszyn. | ||||||
| Ladislaus I[43] | 1420 | 1431–1460 | 14 February 1460 | Głogów (Half B) (in Cieszyn until 1442) | Margareta of Celje December 1444 no children | ||
| Wenceslaus I[44] | 1413/8 | 1431–1468 | 1474 | Cieszyn | Elisabeth of Brandenburg 17 February 1439 (annulled 1445) no children | ||
| Premislaus II | 1422/5 | 1431–1442 1468–1477 |
18 March 1477 | Cieszyn | Anna of Warsaw c.1465 one child | ||
| 1460–1477 | Głogów (Half B) | ||||||
| Boleslaus II | 1425/8 | 1431–1452 | 4 October 1452 | Cieszyn | Anna of Bielsk 28 January 1448 three children | ||
| Nicholas I[45] | 1424 | 1437–1476 | 3 July 1476 | Opole (with Brzeg since 1450) | Magdalena of Brieg February 1442 ten children |
Children of Bolko IV, ruled jointly. After John's death in 1439, Nicholas ruled alone. In 1450 he bought Brzeg. | |
| John I[46] | 1410/3 | 1437–1439 | 5 September 1439 | Opole | Unmarried | ||
| Conrad IX the Black | 1415 | 1450–1471 | 14 August 1471 | Oleśnica | Margareta of Rawa 1453 one child |
Son of Conrad VII. | |
| Henry XI[47] | 1435 | 1467–1476 | 22 February 1476 | Głogów (Half A) | Barbara of Brandenburg 11 October 1472 Berlin no children | Son of Henry IX. | |
| Margareta of Celje |  | 1411 | 1477–1480 | 22 July 1480 | Głogów (Half B) | Herman I of Montfort-Pfannberg-Bregenz 15 March 1430 four children Ladislaus I December 1444 no children | Widow of Ladislaus I, ruled with her brother-in-law Premislaus II since 1460. From 1477 ruled alone. |
| Balthasar | 1415 | 1439–1461 1468–1472 | 15 July 1472 | Żagań | Agnes before 1460 one child Barbara of Cieszyn 11 September 1469 no children |
Sons of John I, ruled jointly. Wenceslaus and John abdicated in 1449, and Balthasar ruled alone, but John came in 1461 and dethroned Balthasar. However the latter dethroned the usurper and ruled again. John put aside his brother in 1472 and ruled once again, but, in that year his duchy was annexed to Saxony. In 1476, John II inherits part of Glogow from his cousin Henry XI, and in 1480 reunites both parts of this duhcy. In 1482 lost Lubin for Legnica. In 1488 Głogów is annexed by the Kingdom of Poland. | |
| Rudolph | 1418 | 1439–1454 | 18 September 1454 | Żagań | Unmarried | ||
| Wenceslaus[48] | 1434 | 1439–1449 | 29 April 1488 | Żagań | Unmarried | ||
| John II the Mad |  |
16 April 1435 | 1439–1449 1461–1468 1472 |
22 September 1504 | Żagań | Katharina of Opava c.1462 five children | |
| 1476/1480–1482 | Głogów (both halves reunited 1480) | ||||||
| Annexation to the Duchy of Saxony | |||||||
| Annexation to the Kingdom of Poland | |||||||
| Lubin, since 1446 part of Głogów, reverted to Legnica | |||||||
| Casimir II | 1450 | 1468–1490 | 8 January/7 July 1490 | Zator | Margaret of Karniów c. 12 August 1482 one child |
Sons of Wenceslaus I, ruled jointly. In 1490 John became sole ruler. In 1513 the Duchy is annexed by the Kingdom of Poland. | |
| Ladislaus | 1455 | 1468–1482 | 28 May or 21 September 1494 | Zator | Anna before 1488 one child | ||
| Wenceslaus II[49] | 1450/55 | 1468–1487 | before 5 October 1487 | Zator | Unmarried | ||
| John V[50] | before 1455 | 1468–1513 | 17 September 1513 | Zator | |||
| Annexation to the Kingdom of Poland | |||||||
| Margareta of Rawa | 1441 | 1471–1475 | 1 September 1485 | Oleśnica | Conrad IX the Black 1453 one child | Widow of Conrad IX. | |
| Regency of Conrad X, Duke of Oleśnica (1475–78) | Daughter of Conrad IX. Deposed in 1478 by her regent and died in the next year. | ||||||
| Barbara | 1465 | 1475–1478 | 30 November 1479 | Oleśnica | Unmarried | ||
| Nicholas II |  | 1462 | 1476–1497 | 27 June 1497 | Opole (with Brzeg until 1481) | Unmarried | Sons of Nicholas II, ruled jointly. In 1481 they sold Brzeg to Frederick I of Legnica. From 1497 John ruled alone. In 1521 purchased Racibórz from Bohemia, and restored the Duchy of Opole-Racibórz. However, as he left no descendants the duchy reverted to the Margraviate of Brandenburg-Ansbach. |
| John II the Good[51] |  |
1460 | 1476–1521 | 27 March 1532 | Opole (with Brzeg until 1481) |
Unmarried | |
| 1521–1532 | Opole-Racibórz | ||||||
| Annexation to the Margraviate of Brandenburg-Ansbach | |||||||
| Brzeg returned to Legnica | |||||||
| Casimir II | 1449 | 1477–1528 | 13 December 1528 | Cieszyn | Johanna of Opava 6 October 1328 six children |
Father and son, ruled jointly. Wenceslaus predeceased his father and never came to rule alone. | |
| Wenceslaus II[52] |  | 1488/96 | 1518–1524 | 17 November 1524 | Cieszyn | Anna of Brandenburg-Ansbach 1 December 1518 three children | |
| Conrad X the White | 1420 | 1450–1452 1478–1492 | 21 September 1492 | Oleśnica | Dorothea Reynkenberg before 1492 (morganatic) no children | Adicated of co-rulership with his brother Conrad IX in 1452, but in 1478 expelled his niece and ruled alone. In 1492 Oleśnica was annexed by the Kingdom of Bohemia. | |
| Annexation to the Kingdom of Bohemia | |||||||
| Frederick I | 3 May 1446 | 1454–1488 | 9 May 1488 | Legnica (with Oława) |
5 September 1474 three children |
Legnica became independent from Bohemia in 1454. In the same year inherited Brzeg-Olawa from his mother Margareta of Opole. In 1481 Frederick I of Legnica purchased Brzeg from Opole, and recovered Lubin in 1482, from John the Mad. | |
| 1481/2–1488 | Lubin | ||||||
| 1481/2–1488 | Brzeg (reunited with Oława) | ||||||
| Ludmila of Poděbrady |  | 16 October 1446 | 1488–1503 | 20 January 1503 | Brzeg | Widow of Frederick I. Received Brzeg as her dower, but also served as regent for her sons in Legnica. | |
| Regency of Ludmila of Poděbrady (1488–95) | Ruled jointly until the end of regency. John didn't reach adulthood. In 1503, after their mother's death, George inherited Brzeg from their mother, and Frederick became sole ruler of Legnica, which, after the childless death of George in 1521, was reunited with Brzeg. | ||||||
| John II | 1477 | 1488–1495 | 6 March 1495 | Legnica | Unmarried | ||
| George I[53] |  |
1481/3 | 1488–1521 | 30 May 1521 | Brzeg (with Lubin; in Legnica until 1505) | Anna of Pomerania 9 June 1516 no children | |
| Frederick II the Great |  |
12 February 1480 | 1488–1547 | 17 September 1547 | Legnica | Elisabeth of Poland-Lithuania 21 November 1515 one child Sophie of Brandenburg-Ansbach-Kulmbach 14 November 1519 three children | |
| 1503–1505 1521–1547 | Brzeg | ||||||
| Anna of Pomerania |  | 1492 | 1521–1550 | 25 April 1550 | Lubin | George I 9 July 1516 no children | Inherited Lubin from her husband. As she didn't have children, the land passed, at her death, permanently to Legnica. |
| Annexation to Legnica | |||||||
| Regencies of Anna of Brandenburg-Ansbach (1528–1539) and John III of Pernstein (1528–1545) | |||||||
| Wenceslaus III Adam |  | December 1524 | 1528–1579 | 4 November 1579 | Cieszyn | Maria of Pernstein 8 February 1540 three children Sidonia Katharina of Saxe-Lauenburg 25 November 1567 Cieszyn six children | |
| Frederick Casimir |  | December 1541/January 1542 | 1560–1571 | 4 May 1571 | Cieszyn | Katharina of Legnica 28 December 1563 Legnica one child | Son of Wenceslaus, co-ruled with him from 1560 but preceded his father in death. |
| Frederick III |  | 22 February 1520 | 1547–1559 | 15 December 1570 | Legnica (with Lubin) | Catherine of Mecklenburg-Schwerin 3 March 1538 Legnica six children |
Children of Frederick II, divided the land: Frederick III kept Legnica (and absorbed Lubin in 1550), and George II inherited Brzeg. |
| George II the Pious |  | 18 July 1523 | 1547–1586 | 7 May 1586 | Brzeg | Barbara of Brandenburg 15 February 1545 Berlin seven children | Jointly with his brother Frederick II. |
| Henry XI[47] |  | 23 February 1539 | 1559–1581 | 3 March 1588 | Legnica | Sophie of Brandenburg-Ansbach 11 November 1560 Legnica six children | |
| Catherine of Mecklenburg-Schwerin |  | 14 April 1518 | 1570–1581 | 17 November 1581 | Legnica (at Chojnów) | Frederick III 3 March 1538 Legnica six children |
Widow of Frederick III. |
| Regency of Sidonia Katharina of Saxe-Lauenburg (1579–1594) | |||||||
| Adam Wenceslaus |  | 12 December 1574 | 1579–1617 | 13 July 1617 | Cieszyn | Elisabeth of Courland 17 September 1595 five children | |
| Frederick IV |  | 20 April 1552 | 1581–1596 | 27 March 1596 | Legnica | Maria Sidonia of Cieszyn 20 January 1587 no children Dorothea of Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg 23 November 1589 no children Anna of Württemberg 24 October 1594 no children | |
| Barbara of Brandenburg |  | 10 August 1527 | 1586–1595 | 2 January 1595 | Brzeg | George II 15 February 1545 Berlin seven children | Widow, ruled in Brzeg. |
| John George | 17 June 1552 | 1586–1592 | 6 July 1592 | Brzeg (at Oława) | Anna of Württemberg 16 September 1582 Brzeg no children | ||
| Anna of Württemberg |  | 17 June 1552 | 1592–1594 | 7 July 1616 | Brzeg (at Oława) | John George 16 September 1582 Brzeg no children Frederick IV 24 October 1594 no children | She married twice, so in 1594 she was stripped from her duchy. |
| Joachim Frederick |  |
29 September 1550 | 1586–1592 1594–1602 |
25 March 1602 | Brzeg (at Oława; in the entire Brzeg since 1595) |
19 May 1577 Brzeg six children |
Initially co-ruler with his brother, John George, after his death the duchy went to his widow, which was stripped from her when she married again. He reunited Brzeg, and then reunited it with Legnica in 1596. |
| 1596–1602 | Legnica | ||||||
| Anna Maria of Anhalt |  | 29 September 1550 | 1602–1605 | 14 November 1605 | Brzeg (at Oława) | Received Olawa after her husband's death. She also served as regent for her children in the other possessions of her husband. She did not do it by herself. She had co-rulership on her regency. After her death the regency was taken by the sister of Joachim Frederick, Elisabeth Magdalena, and her husband, who ruled until the brothers came of age, in 1609. | |
| Regencies of Anna Maria of Anhalt (1602–05), Elisabeth Magdalena of Brzeg and Charles II of Poděbrady (1602–09) | Sons of Joachim Frederick, ruled jointly until 1612. In that year they made partitions. George Rudolf received Legnica and John Christian Brzeg. George left no descendants, and was succeeded by his nephews. | ||||||
| George Rudolf |  | 12 January 1595 | 1602–1653 | 14 January 1653 | Legnica (in Brzeg until 1612) | Sophia Elisabeth of Anhalt-Dessau 4 November 1614 Dessau no children Elisabeth Magdalena of Munsterberg 5 December 1624 no children | |
| John Christian |  | 28 August 1591 | 1602–1633 | 25 December 1639 | Brzeg (in Legnica until 1612) | Dorothea Sibylle of Brandenburg 12 December 1610 Berlin thirteen children Anna Hedwig Sitzsch (morganatic) 13 September 1626 Brzeg seven children | |
| Regency of Charles of Austria, Bishop of Wroclaw (1617–24) | |||||||
| Frederick William |  | 9 November 1601 | 1617–1625 | 19 August 1625 | Cieszyn | Unmarried | |
| Elizabeth Lucretia |  | 1 June 1599 | 1625–1653 | 19 May 1653 | Cieszyn | Gundakar, Prince of Liechtenstein 23 April 1618 no children | After her death, Cieszyn was annexed by the Holy Roman Empire. |
| Definitive annexation to the Holy Roman Empire | |||||||
| Louis IV |  | 19 April 1616 | 1653–1663 | 24 November 1653 | Legnica | Anna Sophie of Mecklenburg-Güstrow 8 May 1649 Brzeg one child |
Sons of John Christian, ruled jointly in Legnica. George was already duke of Brzeg since his father's death. As George didn't have no descendants he was succeeded in his domains by his brother Christian. The latter, after his own death, left Oława for his widow, and the remaining lands were inherited by his own son. |
| George III |  |
4 September 1611 | 1633–1664 | 4 July 1664 | Brzeg | Sophia Katharina of Munsterberg 23 February 1638 Bernstadt one child Elisabeth Marie Charlotte of Palatinate-Simmern-Kaiserslautern 19 October 1660 Brzeg no children | |
| 1653–1654 1663–1664 | Legnica | ||||||
| Christian |  |
9 April 1618 | 1653–1654 1663–1672 |
28 February 1672 | Legnica | Louise of Anhalt-Dessau 24 November 1648 Dessau four children | |
| 1664–1672 | Brzeg | ||||||
| Regency of Louise of Anhalt-Dessau (1672–1675) | Last male representative of the House of Piast. Died without descendants. | ||||||
| George William |  | 29 September 1660 | 1672–1675 | 21 November 1675 | Legnica and Brzeg | Unmarried | |
| Annexation to the Holy Roman Empire | |||||||
| Louise of Anhalt-Dessau |  | 10 February 1631 | 1672–1680 | 25 April 1680 | Brzeg (at Oława) | Christian 24 November 1648 Dessau four children | Regional duchess in Brzeg, widow of Christian. After her death the Duchy was annexed by the Holy Roman Empire. |
| Annexation to the Holy Roman Empire | |||||||
Partitions of Bohemian Silesia under Přemyslid dynasty
Below follows a simplified table of Silesia's partitions:
| Piast Ráciborz (1282-1336) | |||
| Opava (1269-1456) (brief annexation to Piast Legnica in 1308-11; also in Ziębice 1443-56) |
|||
| Ráciborz (1378-1521) |
Krnov (1424-1493) (brief annexation to Hungary in 1474-90) | ||
| Glubczyce (1433-1485) |
|||
| Pledged to Opole and annexed to Bohemia | |||
| Annexed to Bohemia |
Annexed to Bohemia | ||
| Annexed to Opole | |||
Table of rulers
- The numbering of the Silesian Premyslid rulers is a problematic matter between scholars, as different sources numbers and orders them differently.
| Ruler | Born | Reign | Death | Ruling part | Consort | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nicholas I | 1255 | 1269-1318 | 25 July 1318 | Opava | Adelaide of Habsburg (d.1313) 1283 three children | Natural son of Premysl Ottokar II of Bohemia and Agnes of Kuenring, inherited from his father the Silesian duchy of Opava. | |
| Nicholas II |  | 1288 | 1318-1365 | 8 December 1365 | Opava | Anna of Racibórz 1318 six children Hedwig of Olesnica (d.1359) May 1342 one child Jutta of Opole (d.aft.1378) 1360 three children | |
| John I | 1288 | 1365-1382 | 8 December 1365 | Racibórz (in Opava until 1377) | Anna of Głogów-Żagań (d.1369) 1361 three children |
Children of Nicholas II, divided the land; After Nicholas III's death, Glubczyce returned to Opava. | |
| Nicholas III | 1339 | 1365-1394 | 9 July 1394 | Opava (at Glubczyce; in Opava until 1377) | Unmarried | ||
| Premislaus I |  | 1288 | 1365-1433 | 8 December 1365 | Opava | Anna of Lutz (d.1405) 1395 three children Catherine of Ziebice (d.23 May 1422) c.1405 three children Elena of Bosnia 1425 three cildren | |
| Wenceslaus I | 1361 | 1365-1381 | 1381 | Opava | Unmarried | ||
| John II of Iron | c.1365 | 1382-1424 | 1424 | Racibórz | Helena of Lithuania (d.c.1450) 16 January 1407 three children |
Children of John I, divided the land. John kept the main Ráciborz and Krnov, and Nicholas was given Bruntál. John lost Krnov in 1388, but recovered it in 1422. | |
| Nicholas IV | c.1370 | 1382-1406 | 1406 | Racibórz (at Bruntál) | Unmarried | ||
| Wenceslaus II | 1405 | 1424-1456 | 29 October 1456 | Racibórz | Margaret of Szamotuły (d.5 November 1464) 1437 four children |
Children of John II, divided the land. | |
| Nicholas V | 1409 | 1424-1452 | 22 December 1452 | Racibórz | Margaret Clemm of Ellguth three children Barbara Rockemberg 1451 Kraków two children | ||
| Wenceslaus II | 1397 | 1433-1445 | 1445 | Glubczyce (in Opava until 1435) | Elisabeth of Kravař 1420 two children |
Children of Premislaus I, divided the land. William and Ernest inherited the duchy of Ziebice in succession, alongside Opava, where they ruled together with their half- brother Nicholas IV (and possibly also Premislaus II). In 1452, after William's death, Ernest and his brothers associated William's sons as co-rulers. Wenceslaus II, another half-brother, inherited a part of Opava centered around Glubczyce. In 1464, the duchy of Opava was sold to Bohemia. | |
| William | 1410 | 1433-1452 | 15 August 1452 | Opava | Salome of Častolovice five children | ||
| 1443-1452 | Ziębice | ||||||
| Ernest | 1415 | 1433-1456 | 1464 | Opava | Unmarried | ||
| 1452-1456 | Ziębice | ||||||
| Nicholas IV | 1400 | 1433-1437 | 1437 | Opava | |||
| Premislaus II the Elder |  | c.1425 | 1433-1456 | 16 June 1478 | Opava | ||
| Frederick | 1440 | 1452-1456 | 1470 | Opava | |||
| Wenceslaus III | 1445 | 1474 | Opava | ||||
| Premislaus III the Younger | 1450 | 17 February 1493 | Opava | ||||
| Pledge to Opole by debt; Debt transferred in 1464 to Bohemia: Annexation to Bohemia | |||||||
| John (III) | 1420 | 1445-1454 | 1454 | Glubczyce (in Fulnek) | Unmarried | Children of Wenceslaus II, divided the land, which was reunited shortly by John III. | |
| John III the Pious | 1425 | 1445-1485 | 1485 | Glubczyce (in Fulnek since 1454) | Catherine (d.1485) no children | ||
| Barbara Rockemberg | c.1410? | 1452-1462 | November 1463 | Krnov (at Pszczyna) | Wilhelm Willandt no children Jerzy Orient one child Nicholas V 1451 Kraków two children | Wife of Nicholas V, inherited the town of Pszczyna as widow seat, while ruling as regent in the rest of the duchy for her stepsons. | |
| Regency of Barbara Rockemberg (1452-1462) | Children of Nicholas V, divided the land. In 1474, John lost the duchy, which was then claimed by his sister. | ||||||
| John IV the Elder | 1440 | 1452-1474 1464-1483 | 1483 | Krnov Krnov (at Wodzisław Śląski) | Unmarried | ||
| Wenceslaus V | 1442 | 1452-1478 | 1478 | Krnov (at Rybnik) | Unmarried | ||
| Annexation to Hungary (1474-1490) | |||||||
| Regency of Margaret of Szamotuły (1456-1464) | |||||||
| John V the Younger |  | 1446 | 1456-1493 | 14 April 1493 | Racibórz | Magdalena of Opole (c.1465-May 1501) 13 January 1478 Opole four children | |
| Barbara | 1445 | 1490-1510 | 27 April 1510 | Krnov | John IV, Duke of Oświęcim 1475 one child | Claimed (and ruled, effectively) her family's duchy from 1490, co-ruling with her son-in-law since 1493[54] | |
| Annexation to Bohemia | |||||||
| Regency of Magdalena of Opole (1493-1499) | Children of John V, ruled jointly. In 1521, after the childless brothers' death, the duchy returned to Opole. | ||||||
| Nicholas VI | 1478 | 1493-1506 | 3 November 1506 | Racibórz | Unmarried | ||
| John VI | 1484 | 1493-1506 | November/December 1506 | Racibórz | |||
| Valentin the Hunchback | 1485 | 1493-1521 | 13 November 1521 | Racibórz | |||
| Annexation to Opole | |||||||
The Ecclesiastical Duchy of Nysa
Established in 1290 by High Duke Henry IV Probus, held by the Bishops of Wrocław
- 1302–1319 Henry of Wiebrzno
- 1326–1341 Nankier
- 1342–1376 Przecław of Pogarell
- 1382–1417 Wenceslaus II of Legnica
- 1417–1447 Konrad IV of Oleśnica
- 1447–1456 Peter II Nowak
- 1456–1467 Jošt of Rožmberk
- 1468–1482 Rudolf of Rüdesheim
- 1482–1506 Jan IV Roth
- 1506–1520 Jan V Thurzo
- 1520–1539 Jacob of Salza
- 1539–1562 Balthazar of Promnitz
- 1562–1574 Caspar of Logau
- 1574–1585 Martin Gerstmann
- 1585–1596 Andreas Jerin
- 1596–1599 Bonaventura Hahn
- 1599–1600 Paul Albert of Radolfzell
- 1600–1608 Jan VI of Sitsch
- 1608–1624 Charles of Austria, son of Charles II, Archduke of Austria
- 1625–1655 Karol Ferdynand Vasa, Duke of Opole from 1648
- 1656–1662 Leopold Wilhelm of Habsburg
- 1663–1664 Charles Joseph of Habsburg, also Grand Master of the Teutonic Order from 1662
- 1665–1671 Sebastian von Rostock
- 1671–1682 Frederick of Hesse-Darmstadt
- 1683–1732 Franz Ludwig von Pfalz-Neuburg
- 1732–1747 Philipp Ludwig von Sinzendorf
Major part annexed by the Kingdom of Prussia after the First Silesian War in 1742.
- 1747–1795 Philipp Gotthard von Schaffgotsch
- 1795–1817 Joseph Christian Franz zu Hohenlohe-Waldenburg-Bartenstein
Prussian part secularised in 1810.
- 1823–1832 Emanuel von Schimonsky
- 1835–1840 Leopold von Sedlnitzky
- 1843–1844 Joseph Knauer
- 1845–1850 Melchior von Diepenbrock
Theocracy abolished in 1850.
See also
- List of Polish rulers
- Piast dynasty
- Dukes of Masovia
- Dukes of Greater Poland
- Dukes of Little Poland
- Dukes of Cuiavia
- Dukes of Sieradz-Łęczyca
References
- Avoid confusion between Henry III the White and Henry III, duke of Głogów
- Avoid confusion with the later duke of Oleśnica, Conrad I.
- Avoid confusion with the later duke of Zagan, Henry IV the Faithful
- A new line of dukes started with Conrad I, and Henry was his son. As Henry was, like his uncle Henry III the White, descendant of Henry II, he was numbered, not according to his uncle, but independently as a new line.
- Albeit more known as Przemko, his true name was probably Premislaus
- Avoid confusion with the later duke of Oleśnica, Konrad II the Hunchback.
- Avoid confusion with the later duke of Zagan, Henry V of Iron
- Albeit more known as Bolko, his true name was probably Boleslaus. Avoid confusion with his contemporary, Bolko I of Opole.
- A new line of dukes starts with Mieszko I, who is thereby counted as I.
- Applied for Bolko I and Bolko II of Opole. Albeit more known as Bolko, their true name was probably Boleslaus, name with they are also stated in sources. Bolko I was the first Boleslaus/Bolko in Upper Silesia and he was numbered as such. However, avoid confusion with his Lower Silesian contemporary, Bolko I the Strict. The same can be said to Bolko II of Opole. Avoid confusiom between him and his Lower Silesian contemporaries, Bolko the Small and Bolko II of Ziębice.
- Albeit having co-ruled in Opole, and then started a line of it own, he was never styled II, after Casimir I of Opole.
- Avoid confusion with the later duke of Zagan, Henry VI the Elder
- Avoid confusion with the prior duke of Wrocław, Henry IV the Just
- Albeit more known as Przemko, probably his true name was Premislaus.
- As a starter of a new line of dukes, Conrad ignored his ancestors numberings and styled himself as I. Avoid confusion with the prior duke of Głogów, Conrad I.
- A new line of dukes started with Bolko I, and Henry was his son. However, unlike Głogów line, who followed Henry the Pious, this Henry didn't follow any numbering of his ancestors, and styled himself as the I.
- Styled himself I, ignoring his ancestors' numberings of the united Opole-Racibórz.
- Applied to Władysław of Oświęcim and Władysław of Bytom. They styled themselves I, ignoring the numbering of their ancestor and last duke of the united Opole-Racibórz, Ladislaus I of Opole-Racibórz. Avoid confusion with this two contemporary dukes
- Albeit known as Bolko, his true name was probably Boleslaus. Starter of a new line of dukes, he recognized his father's numbering
- Avoid confusion with the prior duke of Legnica-Wrocław, Henry V the Fat
- Styled I, as he is the first Upper Silesian Boleslaus.
- Ladislaus, as ruler of Opole and a direct descendant of Ladislaus I of Opole-Racibórz, numbered himself II.
- Not counting the regents of Opole-Racibórz, Henry was in fact the first (and only) ruler in Upper Silesia to bear this name, more usual in Lower Silesia. In fact, his mother, Elisabeth of Świdnica, was Lower Silesian.
- Applied to Upper Silesian Bolko III of Strzelce and Lower Silesian Bolko III of Ziębice. Albeit more known as Bolko, their true name must have been Boleslaus. Avoid confusion between these two contemporary dukes.
- Albeit following the numberings of the rulers named Bolko, the same is not applied to the dukes Henry in Ziębice. Henry is styled the I, ignoring the numbering of Henry II the Pious.
- Albeit known as Bolko, his true name was probably Boleslaus. Avoid confusion with his Lower Silesian uncle, Bolko II of Ziębice, and the Upper Silesian Bolko II of Opole.
- Avoid confusion with the contemporary duke of Zagan, Henry VII Rumpold
- Avoid confusion with the contemporary duke of Zagan, Henry VIII the Sparrow
- Avoid confusion with the prior duke of Zagan, Konrad II the Hunchback.
- Avoid confusion with the prior duke of Wrocław, Henry VI the Good
- Avoid confusion with the contemporary duke of Legnica-Brzeg, Henry VII the Courageous
- Avoid confusion with the contemporary duke of Legnica, Henry VIII
- Possibly because he was Upper Silesian, he didn't recognize the numberings of his predecessors, Przemko I and Przemko II
- Albeit more known as Bolko, his true name was probably Boleslaus.
- Bernard was the first Upper Silesian ruler to bear this name.
- He was the first Lower Silesian duke to bear this name. Avoid confusion with the contemporary Upper Silesian duke of Opole, John I
- Avoid confusion between contemporary dukes Henry IX of Lubin and Henry IX the Elder of Zagan. Henry IX the Elder has also the same sobriquet as his father, Henry VI.
- Avoid confusion with the duke of Lubin and Brzeg, Henry X. Besides, Henry X's uncle, Henry VII, was also known as Rumpold
- He was the first Wenceslaus of Głogów-Żagań line
- Ignored the numbering of his ancestor, Casimir I of Opole, as he is usually styled I.
- Avoid confusion with the contemporary duke of Cieszyn, Wenceslaus I
- Avoid confusion with the duke of Lubin and Brzeg, Henry X Rumpold.
- He was the first duke of Głogów to bear this name, but as he was Upper Silesian, he ignored the numbering of his ancestor, Ladislaus I of Opole-Racibórz.
- He was the first Upper Silesian duke to bear this name. Avoid confusion with the contemporary duke of Zator, Wenceslaus I
- He was the first Upper Silesian duke to bear this name
- Avoid confusion with the contemporary Lower Silesian duke of Zagan, John I
- Avoid confusion between Henry XI of Głogów and Henry XI of Legnica.
- Strangely he was not numbered II, when he had an uncle with this name who co-ruled in the same duchy.
- Avoid confusion with the later duke of Cieszyn, Wenceslaus II
- John adopted the numbering V, after his uncle, Jan IV of Oświęcim
- As ruler of the reunited Opole-Racibórz, he did only consider his name bearers in this two duchies: the only one was Jan I of Opole.
- Avoid confusion with the prior duke of Zator, Wenceslaus II
- He was the first in Lower Silesia to bear this name.
- Helena Osvětimská, 2020-03-06
Bibliography
- Neue deutsche Biographie, Berlin 2001, Bd.: 20, p. 403–407
- Meyers Großes Konversations-Lexikon, Leipzig 1905–1909, Bd.: 17, p. 845–847