El Cerrito, California
El Cerrito (Spanish for "The Little Hill") is a city in Contra Costa County, California, United States, and forms part of the San Francisco Bay Area. It has a population of 25,962 according to the 2020 census. El Cerrito was founded by refugees from the 1906 San Francisco earthquake. It was incorporated in 1917 as a village with 1,500 residents. As of the census in 2000, there were 23,171 people, 10,208 households and 5,971 families in the city.
El Cerrito, California | |
|---|---|
.jpg.webp) Cerrito Theater on San Pablo Avenue | |
 Seal | |
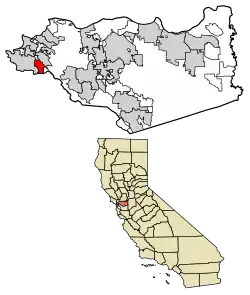 Location of El Cerrito in Contra Costa County, California | |
 El Cerrito, California Location in the United States | |
| Coordinates: 37°54′57″N 122°18′42″W | |
| Country | United States |
| State | California |
| County | Contra Costa |
| Incorporated | August 23, 1917[1] |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Lisa Motoyama[2] |
| • State Senator | Nancy Skinner (D)[3] |
| • State Assembly | Buffy Wicks (D)[4] |
| • U. S. Congress | John Garamendi (D)[5] |
| • County Board | District 1: John Gioia |
| Area | |
| • Total | 3.67 sq mi (9.51 km2) |
| • Land | 3.67 sq mi (9.51 km2) |
| • Water | 0.00 sq mi (0.00 km2) 0% |
| Elevation | 69 ft (21 m) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 25,962 |
| • Density | 7,100/sq mi (2,700/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC-8 (PST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-7 (PDT) |
| ZIP code | 94530 |
| Area code(s) | 510, 341 |
| FIPS code | 06-21796 |
| GNIS feature IDs | 277504, 2410410 |
| Website | www |
History
.jpg.webp)
El Cerrito was founded by refugees from the 1906 San Francisco earthquake. They settled in what was then Don Víctor Castro's Rancho San Pablo, and adjacent to the ranch owned by the family of Luís María Peralta, the Rancho San Antonio.[8] A post office opened at the settlement in 1909 and the refugee camp became known as Rust, after Wilhelm F. Rust, its first postmaster.[9][10] The village's residents did not care for the name and changed it to El Cerrito (meaning "little hill" or "knoll") in 1916, in reference to nearby Albany Hill.[9][11][12] A year later, El Cerrito was incorporated as a village with 1,500 residents.[8]
El Cerrito was incorporated in August 1917. The communities of Stege Junction, Rust, Schmidtville, and Schindler, were all included in the new city.[13][14][15][16] The 1920 census shows that the Schmidtville community had many Italian immigrants.[17] A post office operated at Schmidtville from 1900 to 1901.[9]
Geography

According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 3.7 square miles (9.6 km2), all of it land. The city ranges in elevation from 20 to 934 feet, with an average elevation of 69 feet (21 m).[10]
El Cerrito is located on the eastern shore of San Francisco Bay in the extreme south-west corner of Contra Costa County. The hilly areas of El Cerrito provide views of its San Francisco, and of the Golden Gate Bridge. El Cerrito is located along Interstate 80, and nearby Interstate 580. El Cerrito is bordered by Albany and Kensington to the south, the Richmond annex to the west, East Richmond Heights to the north, and Wildcat Canyon Regional Park to the east. Local landmark Albany Hill is in Albany, just across the border with El Cerrito. (El Cerrito—Spanish, "the little hill"—takes its name from Albany Hill.)[18][19] The Hayward Fault runs through El Cerrito. In addition, El Cerrito is within 490 feet (150 meters) of Berkeley to the southeast, and approximately 5 miles (8.0 km) from the University of California Berkeley campus.
Demographics
| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1920 | 1,505 | — | |
| 1930 | 3,870 | 157.1% | |
| 1940 | 6,137 | 58.6% | |
| 1950 | 18,011 | 193.5% | |
| 1960 | 25,437 | 41.2% | |
| 1970 | 25,190 | −1.0% | |
| 1980 | 22,731 | −9.8% | |
| 1990 | 22,869 | 0.6% | |
| 2000 | 23,171 | 1.3% | |
| 2010 | 23,549 | 1.6% | |
| 2020 | 25,962 | 10.2% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census[20] | |||
2010
At the 2010 census El Cerrito had a population of 23,549. The population density was 6,385.3 inhabitants per square mile (2,465.4/km2). The 2010 racial makeup of El Cerrito was:[21]
- 12,543 (53.3%) White,
- 6,439 (27.3%) Asian,
- 1,819 (7.7%) African American,
- 107 (0.5%) Native American,
- 37 (0.2%) Pacific Islander,
- 1,079 (4.6%) from other races, and
- 1,525 (6.5%) from two or more races.
Hispanic or Latino of any race were 2,621 persons (11.1%).
The census reported that 23,456 people (99.6% of the population) lived in households, 48 (0.2%) lived in non-institutionalized group quarters, and 45 (0.2%) were institutionalized.
There were 10,142 households, 2,394 (23.6%) had children under the age of 18 living in them, 4,703 (46.4%) were opposite-sex married couples living together, 1,047 (10.3%) had a female householder with no husband present, and 416 (4.1%) had a male householder with no wife present. There were 509 (5.0%) unmarried opposite-sex partnerships, and 189 (1.9%) same-sex married couples or partnerships. 2,953 (29.1%) were one person and 1188 (11.7%) had someone living alone who was 65 or older. The average household size was 2.31. There were 6,166 families (60.8% of households); the average family size was 2.84.
The age distribution was 4,087 people (17.4%) under the age of 18, 1,281 people (5.4%) aged 18 to 24, 6,918 people (29.4%) aged 25 to 44, 7,036 people (29.9%) aged 45 to 64, and 4,227 people (17.9%) who were 65 or older. The median age was 43.5 years. For every 100 females, there were 92.3 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 89.1 males.
There were 10,716 housing units at an average density of 2,905.6 per square mile (1,121.9/km2),of which 10,142 were occupied, 6,145 (60.6%) by the owners and 3,997 (39.4%) by renters. The homeowner vacancy rate was 1.1%; the rental vacancy rate was 5.4%. 14,474 people (61.5% of the population) lived in owner-occupied housing units and 8,982 people (38.1%) lived in rental housing units.
2000
As of the census[22] of 2000, there were 23,171 people in 10,208 households, including 5,971 families, in the city. The population density was 6,356.5 inhabitants per square mile (2,454.3/km2). There were 10,462 housing units at an average density of 2,870.1 per square mile (1,108.2/km2). The racial makeup of the city was 57.79% White, 8.54% Black or African American, 0.50% Native American, 24.38% Asian, 0.25% Pacific Islander, 3.06% from other races, and 5.48% from two or more races. 7.93% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race.
Of the 10,208 households 20.7% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 45.4% were married couples living together, 9.7% had a female householder with no husband present, and 41.5% were non-families. 30.4% of households were one person and 12.8% were one person aged 65 or older. The average household size was 2.25 and the average family size was 2.81.
The age distribution was 15.9% under the age of 18, 6.7% from 18 to 24, 31.2% from 25 to 44, 25.7% from 45 to 64, and 20.4% 65 or older. The median age was 43 years. For every 100 females, there were 89.7 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 86.6 males.
The median income for a household in the city was $57,253, and the median family income was $69,397 (these figures had risen to $77,650 and $97,488 respectively as of a 2007 estimate[23]). Males had a median income of $50,316 versus $40,866 for females. The per capita income for the city was $32,593. About 3.5% of families and 6.7% of the population were below the poverty line, including 7.9% of those under age 18 and 3.9% of those age 65 or over.
At home the percentages of the languages residents speak are English 70.47%, Spanish 6.26%, Chinese 5.96%, Japanese 2.70%, Mandarin 1.80%, Cantonese 1.57%, Persian 1.43%, Tagalog 1.30%, Korean 1.08%, French 0.90%, German 0.83%, Formosan 0.73%, Italian 0.66%, Vietnamese 0.57%, Urdu 0.50%, and 3.23% of people spoke some other language which represented less than 0.50% of the population.[24]
Economy
.jpg.webp)
San Pablo Avenue stretches the length of El Cerrito and is the primary commercial and retail corridor of the city, though there is a segment in which the businesses on the west side of the avenue are actually in Richmond Annex but have an El Cerrito postal address.
El Cerrito is home to El Cerrito Plaza, a large, regional mall, served by public transit at the adjacent El Cerrito Plaza station. The shopping center is further surrounded by other commercial and retail businesses along San Pablo Avenue and Fairmount Avenue, including the Cerrito Theater, a restored two-screen movie theater known for offering beer, wine, and a full dining menu.
The city is nominally home to Arhoolie Records (actually located in Richmond Annex), part of the Smithsonian Institution. Also located in the city was Playland-Not-At-The-Beach, a now-closed popular amusement park museum.
Parks and recreation
El Cerrito city parks include both recreation/sports parks as well as undeveloped nature areas. Most notable are the 80-acre (320,000 m2) Hillside Natural Area open space, Huber Park (Terrace Drive), Cerrito Vista Park (Moeser Lane and Pomona Avenue), and Arlington Park (Arlington Boulevard), Tassajara Park (Tassajara Avenue and Barrett Avenue), Poinsett Park (Poinsett Avenue), and the Canyon Trail Park and Art Center (Gatto Avenue).
The city is home to a 2.6-mile (4.2 km) segment of the Ohlone Greenway (named after the Native American Ohlone people), a trail that runs the length of the City along a former railroad grade underneath the BART right-of-way that is popular with walkers, runners, and bicyclists, as well as the blind, deaf, and mute population.
Government

In October, 2019, the California State Auditor's High Risk Cities report (which analyzed 2016-17 data) named El Cerrito as the 7th most fiscally at-risk city in California, largely due to having negative general fund reserves, cash flow and liquidity challenges, escalating pension costs, and a variety of other issues.[25] In a letter to the community, the City Manager criticized the State Auditor's analysis for lacking important context and providing inadequate analysis, acknowledged that City budgets are tight, and defended the city's fiscal management practices. After an on-site assessment, the State Auditor received authorization from the California Legislature to conduct a full audit[26] of the City of El Cerrito in order to determine the causes of its fiscal distress,[27] which is expected to be released in March, 2020. Subsequently, in its next two annual High Risk Cities reports, the Auditor listed El Cerrito as 8th most at-risk (2017-18 data) and 6th most at-risk (2018-19 data).[28]
Following the lead of the State Auditor, others have criticized El Cerrito for its excessive reliance on short-term borrowing to paper over growing budget deficits[29] and for having failed to note the significance of, and act upon, multiple going concern warnings from its own financial auditor.[30] The local East Bay Times newspaper dubbed El Cerrito "the worst managed city in the Bay Area."[31]
Education
El Cerrito is in the West Contra Costa Unified School District, a multi-city district that operates three elementary schools, one middle school, and one high school in the city:
- Fairmont Elementary School
- Harding Elementary School
- Madera Elementary School
- Fred T. Korematsu Middle School (opened in 2015 at the site of the former Castro Elementary School, replacing Portola Middle School which was deemed seismically unsafe)
- El Cerrito High School
- Libraries
There is a branch of the Contra Costa County Library system in El Cerrito.[32]
Transportation

Interstate 80 runs north-south through El Cerrito, with San Pablo Avenue serving as the primary surface artery. Bay Area Rapid Transit serves two stations in the city – El Cerrito del Norte and El Cerrito Plaza – while AC Transit operates local bus service. El Cerrito del Norte station is a major hub for AC Transit, as well as North Bay regional bus operators including FAST, Golden Gate Transit, Vallejo Transit, Napa VINE, and WestCat.
The Ohlone Greenway is part of a regional north-south active transportation route, and is a popular path for bike commuters and recreational cyclists and pedestrians.
In popular culture
- El Cerrito has been mentioned in the book ttfn by Lauren Myracle. Character Angela finds out the family is moving to El Cerrito.[33]
- El Cerrito, referred to as "Old El Cerrito", is mentioned in the book Star Trek: The Kobayashi Maru by author Julia Ecklar. While attending Star Fleet Academy in San Francisco, Cadet James T. Kirk, on failing the Kobayashi Maru test for the second time, travels to the World Library annex in Old El Cerrito in hopes of finding a solution to the test.
- El Cerrito is mentioned in the song "Golden Gate Fields" by Rancid.
- Metallica wrote Ride the Lightning and Master of Puppets in a small house in El Cerrito where the band lived for a while. Cliff Burton joined the band only if Metallica would agree to move to El Cerrito.
- Kenny Chesney's song El Cerrito Place on his 2012 album Welcome to the Fishbowl is about someone searching for his lost love in El Cerrito.
- Game Theory's 1988 song "You Drive" mentions El Cerrito in the first line.
- Cracker recorded a song titled "El Cerrito" released on their 2014 album Berkeley to Bakersfield.
Notable people
- Catherine Asaro, science-fiction author, grew up in El Cerrito
- Jeff Atwood, co-founder of Stack Overflow
- Paul Baloff, lead vocalist of metal band Exodus
- Les Blank, documentary filmmaker (1935-2013)
- Ernie Broglio, former Major League Baseball player
- Doug Clifford, musician
- Emily Compagno, television journalist and Fox News host
- Stu Cook, musician
- Drew Gooden, Milwaukee Bucks forward, attended El Cerrito High School; during his tenure, basketball team went to and lost state basketball final
- John C. Dvorak, technology journalist
- John Fogerty and Tom Fogerty, musicians from the band Creedence Clearwater Revival, grew up in El Cerrito; Band reunited to play its last concert during El Cerrito High School reunion at Golden Gate Fields in Albany
- Karen Grassle, actress, Little House on the Prairie, resident of El Cerrito
- Pumpsie Green, first African American to play for the Boston Red Sox
- Larissa Kelly, all-time female Jeopardy! champion
- Tung-Yen Lin, structural engineer who founded T. Y. Lin International
- Thomas Pridgen, former drummer for the band The Mars Volta
- Susan Rasky, journalist
- Maria Remenyi, Miss California USA 1966, Miss USA 1966
- Alice Schwartz, co-founder of Bio-Rad Laboratories, billionaire.[34]
- Marcus Semien, Major League Baseball player
- Adam Sessler, co-host of X-Play on G4.
- Chris Strachwitz, founder of Arhoolie records
- Maw Shein Win, first Poet Laureate of El Cerrito
- Tess Taylor, poet and CNN contributor
- Gail Tsukiyama, author[35]
- Joyo Velarde, musician
- Matt Young, former Major League Baseball player
Notes
- "California Cities by Incorporation Date". California Association of Local Agency Formation Commissions. Archived from the original (Word) on November 3, 2014. Retrieved March 27, 2013.
- "City Council". El Cerrito, CA. Retrieved March 21, 2013.
- "Senators". State of California. Retrieved March 21, 2013.
- "Members Assembly". State of California. Retrieved March 21, 2013.
- "California's 8th Congressional District - Representatives & District Map". Civic Impulse, LLC. Retrieved March 9, 2013.
- "2019 U.S. Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved July 1, 2020.
- "El Cerrito (city) QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- Contra Costa/Alameda County Line Archived September 27, 2007, at the Wayback Machine, Mervin Belfils/El Cerrito Historical Society, October 1975/June 2006, retrieved 2007-08-01
- Durham, David L. (1998). California's Geographic Names: A Gazetteer of Historic and Modern Names of the State. Clovis, Calif.: Word Dancer Press. p. 628. ISBN 1-884995-14-4.
- "El Cerrito". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior.
- "El Cerrito's History | el Cerrito, CA - Official Website".
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on June 22, 2020. Retrieved January 5, 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - Town Memo (February 2, 2016)
- (7 December 1910). Campaign for Incorporation, Newcastle News
- Radin, Rick and William Love (3 February 2016). El Cerrito begins planning for its centennial, . East Bay Times
- (14 December 1904). Tramp Frightens School Girl, Evening Statesman
- Historic Resource Evaluation: 1715 Elm Street, El Cerrito, California, Ver Planck Historic Preservation Consulting (December 2013)
- "El Cerrito's History | el Cerrito, CA - Official Website".
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on June 22, 2020. Retrieved January 5, 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - "Census of Population and Housing". Census.gov. Retrieved June 4, 2015.
- "2010 Census Interactive Population Search: CA - El Cerrito city". U.S. Census Bureau. Archived from the original on July 15, 2014. Retrieved July 12, 2014.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 31, 2008.
- "American FactFinder". Factfinder.census.gov. Archived from the original on June 8, 2011. Retrieved January 9, 2014.
- El Cerrito entry, MLA Data Center, retrieved October 21, 2007
- Wildermuth, John (October 25, 2019). "These Bay Area cities are in financial trouble, state says". San Francisco Chronicle. Retrieved February 3, 2021.
- Howle, Elaine M. (January 13, 2020). "2020-803 Local High Risk - City of El Cerrito (State Auditor)" (PDF). www.legaudit.assembly.ca.gov. Retrieved June 26, 2023.
- "California State Auditor - 2020-803 Audit Scope and Objectives". www.auditor.ca.gov. Retrieved February 3, 2021.
- "State Auditor's Local Government High-Risk Dashboard". www.auditor.ca.gov. Retrieved February 3, 2021.
- "Crisis shows why El Cerrito needs to heed State Auditor's warning". California Policy Center. March 31, 2020. Retrieved February 3, 2021.
- "10 Things you should know about El Cerrito's financial crisis". El Cerrito Committee for Responsible Government. December 6, 2020. Retrieved February 3, 2021.
- "Editorial: Bay Area's worst-managed city teeters on bankruptcy". East Bay Times. October 26, 2020. Retrieved February 3, 2021.
- "El Cerrito Library Archived 2011-07-19 at the Wayback Machine." Contra Costa County Library. Retrieved on April 1, 2010.
- Lauren Myracle (February 1, 2007). TTFN (Ta-Ta for Now). Harry N. Abrams. ISBN 978-0-8109-9279-5.
- "Alice Schwartz". Forbes. Retrieved March 6, 2018.
- "GAIL TSUKIYAMA". Retrieved July 27, 2020.