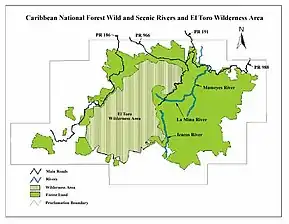
El Toro Wilderness
El Toro Wilderness (Spanish: Selva El Toro) is a 10,254-acre (41.5 km2) federally designated National Wilderness Preservation System unit located within El Yunque National Forest (formerly known as the Caribbean National Forest) on the Sierra de Luquillo in eastern Puerto Rico. El Toro, named after the highest peak in the forest at 3,524 feet (1,074 m), is the only tropical wilderness in the United States National Forest System.[2] It was created in 2005 by the Caribbean National Forest Act of 2005.[3]
| El Toro Wilderness | |
|---|---|
 | |
 Location in Puerto Rico | |
| Location | El Yunque National Forest |
| Nearest city | Canovanas, Puerto Rico |
| Coordinates | 18°16′13″N 65°49′44″W |
| Area | 10,254 acres (41.5 km2) |
| Established | December 2005 |
| Governing body | United States Forest Service |
In descending order of land area, the wilderness is located in parts of the municipalities of Río Grande, Naguabo, Las Piedras, and Canóvanas. El Toro Wilderness, along with the Luquillo Experimental Forest (LEF), is part of the Luquillo Biosphere Reserve, a designated UNESCO biosphere reserve, which emphasizes the site’s importance in the global protection of biodiversity through conservation action.[4]
Features
El Toro Wilderness has dense vegetation with mixed evergreen plants ranging from 3 meters to 30 meters in height at the highest and lowest mountain elevations, respectively. The forest protects all four major forest types found throughout the national forest: the tabonuco forest, the palo colorado forest, the Sierra palm tree forest and the dwarf forest (also known as the elfin forest or cloud forest).[5]
The wilderness is home to a number of plant and animal species found nowhere else in the world, such as the endangered Puerto Rican parrot and the rare elfin woods warbler. The forest is home to 42 native and 35 migratory bird species, a number of bat species, and high numbers of amphibian and reptile species, such as the Puerto Rican boa. Some of the rare plant species found in the area include the endangered miniature orchid Lepanthes eltoroensis and the critically endangered palo de jazmín (Styrax portoricensis).[5]
The area also contains important archaeological sites and Taino petroglyphs, such as the Icacos Petroglyph Group (also known as the Rio Blanco Petroglyphs), listed on the National Register of Historic Places since 2015.[6]
Recreation
Recreational opportunities in the wilderness include hiking, birdwatching and primitive or dispersed camping. Two hiking trails cross the wilderness area: El Toro Trail, which starts from Cubuy in Canóvanas and leads to the summit of El Toro, and the Sabana Trail which begins at the Sabana Recreation Area in Naguabo and loops through the dense jungle. Additionally, the Tradewinds Trail traverses El Toro Wilderness and connects these two trails with the rest of the national forest.[5]
References
- Protected Planet Website- Retrieved April 13, 2023
- El Toro Wilderness fact sheet - U.S. Forest Service
- "Caribbean National Forest Act of 2005 (2005 - H.R. 539)". GovTrack.us. Retrieved 2020-05-22.
- IUCN WCPA Wilderness Specialist Group. "Wilderness Protected Areas: Management guidelines for IUCN Category 1b protected areas" (PDF).
- USDA, Forest Service. "El Toro Wilderness".
- United States Department of the Interior, National Park Service. "National Register of Historic Places Registration Form, Icacos Petroglyph Group" (PDF).
External links
- El Toro Wilderness - USDA Forest Service
- El Toro Wilderness - Wilderness.net
- U.S. Geological Survey Map at the U.S. Geological Survey Map Website. Retrieved April 13, 2023.