Emmet County, Michigan
Emmet County is a county located in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is the northernmost county in the Lower Peninsula. As of the 2020 Census, the population was 34,112, making it the second-most populous county in Northern Michigan (behind Grand Traverse County).[2] The county seat is Petoskey, which is also the county's largest city.[3]
Emmet County | |
|---|---|
 Emmet County Building | |
|
Logo | |
 Location within the U.S. state of Michigan | |
 Michigan's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 45°35′N 84°59′W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | April 1, 1840[1] |
| Named for | Robert Emmet |
| Seat | Petoskey |
| Largest city | Petoskey |
| Area | |
| • Total | 882 sq mi (2,280 km2) |
| • Land | 467 sq mi (1,210 km2) |
| • Water | 415 sq mi (1,070 km2) 47% |
| Population (2020) | |
| • Total | 34,112 |
| • Density | 70/sq mi (30/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) |
| Congressional district | 1st |
| Website | www |
Emmet County is located at the top of the Lower Peninsula of Michigan, bounded on the west by Lake Michigan and on the north by the Straits of Mackinac. Its rural areas are habitat for several endangered species. Long a center of occupation by the Odawa people, today the county is the base for the federally recognized Little Traverse Bay Bands of Odawa Indians.
History
Native Americans and New France
Odawa history records that Emmet County was thickly populated by indigenous peoples called the Mush-co-desh, which means "the prairie tribe". They had an agrarian society and were said to have "shaped the land by making the woodland into prairie as they abandoned their old worn out gardens which formed grassy plains". Ottawa tradition claims that they slaughtered from forty to fifty thousand Mush-co-desh and drove the rest from the land after the Mush-co-desh insulted an Ottawa war party.[5]
The Odawa were important prior to European colonization for their trading network throughout the Great Lakes area. The Odawa of nearby L'Arbre Croche fished, hunted, and grew and gathered produce, including corn, squash, onions, cucumbers, turnips, cabbages, melon, and wild strawberries.[6] The Odawa bartered with the French at Mackinac Island, a major fur-trading center where Lake Huron meets Lake Michigan. They traded food, bark, and canoes for goods – like clothing and glass and porcelain beads. The canoes and food, including dried fish and meat and produce, supplied the fur traders who worked in the wilderness of the Great Lakes and the Upper Mississippi regions.[7] They retained this influence into the 18th century, as French traders relied on them to take furs east from tribes they traded with to the north and west. When French explorers first came to this area, they claimed it as part of New France, based in today's Quebec province.
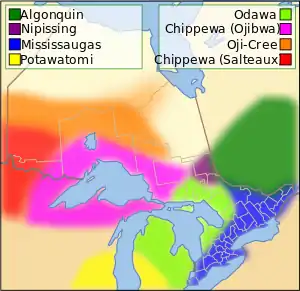
The Ottawa and Ojibwe tribes were the principal inhabitants of this area, extending across to Manitoulin Island and the Bruce Peninsula of Ontario, Canada. The French established Fort Michilimackinac in about 1715. It was a trading post and the basis of a multicultural settlement that developed around it. Seasonally numerous Native Americans of various tribes would come to trade there.
Pierre du Jaunay, a Jesuit priest from France, served as a missionary at Michilimackinac beginning in 1735. From the Sainte-Anne log church, he served the French and later British residents, neighboring Native Americans, and visiting traders and explorers for almost 30 years.[8] Du Jaunay split his time between the Sainte-Anne church and the Saint-Ignace at L’Arbre Croche mission in Cross Village, where he had a farm. He was assisted by several French priests and some Native American slaves.[8]
British Control
During the Seven Years' War (1754–63), British and French forces, together with Indian allies on each side, fought on the North American front in what became known in the British colonies as the French and Indian War. The British took control of Fort Michilimackinac in 1761 and continued to use it as a trading post. In 1763, Ojibwe warriors took the fort as a part of Pontiac's Rebellion and held it for a year before the British retook it. The British abandoned the wooden fort in 1781 after building the limestone Fort Mackinac on nearby Mackinac Island.
US Control and white settlement under the Mormons
An Indian community on the lakeshore in the western part of the county continued to thrive after the British abandoned the fort. After the War of 1812, Mackinac Island and this area became part of the United States.
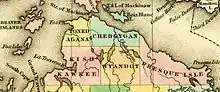
In the 1840s, Odawa villages lined the Lake Michigan shore from present-day Harbor Springs to Cross Village. By Act 119 of the Michigan Legislature approved 1 April 1840, a number of northern counties were delineated. Tonedagana County, a name derived from a Cross Village Odawa war chief, was delineated from Michilimackinac County but unorganized, so remained attached for judicial purposes.[9][10][11] The area was mostly reserved for native tribes by treaty provisions with the US federal government until 1875.
The Michigan Legislature renamed Tonedagana County as Emmet County, after Robert Emmet, on 8 March 1843.[9][10] In 1847, a group of Mormons settled on nearby Beaver Island and established a "kingdom" led by "King" James Jesse Strang. There were bitter disputes between Strang's followers and other white settlers. Strang, seeking to strengthen his position, gained election to the Michigan State House of Representatives. In January 1853, he pushed through legislation titled, "An act to organize the County of Emmet", which enlarged Emmet County by attaching the nearby Lake Michigan islands to the county, as well as a portion of Cheboygan County. It also annexed the old Charlevoix County, which was originally named Keskkauko County and was as yet unorganized, as a township of Emmet County. Due to Strang's influence, Mormons came to dominate county government, causing an exodus of many non-Mormon settlers to neighboring areas. In 1855, the non-Mormon resistance succeeded in getting the Michigan Legislature to reorganize Emmet County. The islands, including Beaver Island and North and South Manitou Islands, were transferred into the separate Manitou County, which effectively eliminated Mormons from Emmet County government.
Further Political Divisions
On April 27, 1857, an election selected Little Traverse (now named Harbor Springs) as the county seat. However, at about this time, investors were trying to promote development at Mackinaw City. Due to their influence, in February 1858, the State Legislature passed an act establishing Mackinaw City as the county seat. The Emmet County Board of Supervisors protested that the county seat had already been established at Little Traverse, and in 1861 the act was repealed as unconstitutional. In a contested election in 1867, residents voted to move the county seat to Charlevoix, which was upheld by a Circuit Court decision in 1868. However, in 1869, Charlevoix County was split from Emmet County, resulting in the county seat being in another county. No provisions for official relocation were authorized, although Harbor Springs served as the unofficial county seat until April 1902. The present county seat of Petoskey was selected at that time in a county-wide election.
Charlevoix Township was organized in 1853 and included all of the nine townships in the southern half of the county. In the 1855 reorganization, four new townships were created by the State Legislature:
- La Croix Township (name changed to Cross Village Township in 1875)
- Little Traverse Township (detached from Charlevoix Township)
- Bear Creek Township (detached from Charlevoix Township)
- Old Fort Mackinac (later absorbed into other townships)
In 1855, county supervisors also established the townships of Arbour Croche and Utopia. (The former was a mangled spelling derived from the French L'Arbre Croche, the historic village later renamed as Harbor Springs.) The state had inadvertently drawn boundaries for Little Traverse and Bear Creek townships such that one area was included in both. The county supervisors' Arbour Croche was defined as having the same boundaries as the state-defined Little Traverse Township, excluding the area overlapping with Bear Creek. Eventually the name Arbour Croche disappeared in favor of Little Traverse. The township of Utopia was later absorbed into other townships.
In 1877, six additional townships were organized:
- Bliss Township
- Friendship Township
- Littlefield Township
- Maple River Township
- Pleasantview Township
- Readmond Township
Center Township was added in 1878 and Carp Lake Township in 1879. Resort Township and Springvale Township were formed in 1880, but were at that time part of Charlevoix County. Those townships, along with Bear Creek, experienced numerous boundary changes. The now defunct townships of Bear Lake and Spring Lake were created out of portions of these townships. In 1897, the portions of these townships remaining in Emmet County were absorbed into Bear Creek and Springvale townships.
Also organized in 1897 were West Traverse Township (from portions of Friendship and Little Traverse Townships) and Egleston Township (name changed to McKinley Township in 1903). In 1923, Wawatam Township was the last township organized in the county, when it was detached from Carp Lake Township.
Geography

According to the US Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 882 square miles (2,280 km2), of which 467 square miles (1,210 km2) is land and 415 square miles (1,070 km2) (47%) is water.[12] The lower portion of the county forms Little Traverse Bay at the mouth of the bear River. Emmet County is considered to be part of Northern Michigan
Adjacent counties
By land
- Cheboygan County (east)
- Charlevoix County (south)
By water
- Charlevoix County (west)
- Mackinac County (north; accessed via Mackinac Bridge)

.jpg.webp)
Transportation
State-maintained highways
 I-75 is a north–south freeway that clips the extreme northeast corner of Emmet County in Mackinaw City. North of Emmet County, I-75 crosses the Straits of Mackinac via the Mackinac Bridge.
I-75 is a north–south freeway that clips the extreme northeast corner of Emmet County in Mackinaw City. North of Emmet County, I-75 crosses the Straits of Mackinac via the Mackinac Bridge. US 23 finds its northern terminus at I-75 in Mackinaw City. The highway continues east into Cheboygan County, and runs south along the coast of Lake Huron.
US 23 finds its northern terminus at I-75 in Mackinaw City. The highway continues east into Cheboygan County, and runs south along the coast of Lake Huron. US 31 serves as the primary north–south thoroughfare in Emmet County. It connects the communities of Petoskey, Conway, Oden, Ponshewaing, Alanson, Pellston, Levering, and Mackinaw City. To the south, US-31 parallels the Lake Michigan coast.
US 31 serves as the primary north–south thoroughfare in Emmet County. It connects the communities of Petoskey, Conway, Oden, Ponshewaing, Alanson, Pellston, Levering, and Mackinaw City. To the south, US-31 parallels the Lake Michigan coast. US 131 has its northern terminus at US-31 in Petoskey. South of Emmet County, US-131 also serves as another north–south thoroughfare, taking a more inland route than US-31.
US 131 has its northern terminus at US-31 in Petoskey. South of Emmet County, US-131 also serves as another north–south thoroughfare, taking a more inland route than US-31. M-68 is an east–west highway. M-68 begins at US-31 in Alanson, and continues east via the communities of Indian River, Tower, and Onaway before terminating at Rogers City on Lake Huron.
M-68 is an east–west highway. M-68 begins at US-31 in Alanson, and continues east via the communities of Indian River, Tower, and Onaway before terminating at Rogers City on Lake Huron. M-119 is a north–south highway entirely within Emmet County. Beginning at an intersection with US-31 between Bay View and Conway, and follows the shore of Little Traverse Bay and Lake Michigan via Harbor Springs to an intersection in Cross Village. The Tunnel of Trees lies along M-119.
M-119 is a north–south highway entirely within Emmet County. Beginning at an intersection with US-31 between Bay View and Conway, and follows the shore of Little Traverse Bay and Lake Michigan via Harbor Springs to an intersection in Cross Village. The Tunnel of Trees lies along M-119.
Previously, an additional highway, M-108, ran along the Emmet–Cheboygan county line in Mackinaw City. However, the highway was handed back to the Emmet County Road Commission in 2010.[13]
County-designated highways
 C-58 is an east–west road connecting Petoskey to I-75 at Wolverine in Cheboygan County.
C-58 is an east–west road connecting Petoskey to I-75 at Wolverine in Cheboygan County. C-64 is an east–west road connecting Pellston to M-27 in Cheboygan County.
C-64 is an east–west road connecting Pellston to M-27 in Cheboygan County. C-66 is an east–west road connecting M-119 in Cross Village to US-31 in Levering and US-23 in Cheboygan.
C-66 is an east–west road connecting M-119 in Cross Village to US-31 in Levering and US-23 in Cheboygan. C-71 is a north–south road connecting Horton Bay with US-31 near Bay Shore.
C-71 is a north–south road connecting Horton Bay with US-31 near Bay Shore. C-77 is a north–south road serving central Emmet County, connecting Harbor Springs and Cross Village via a more inland route than the one taken by M-119.
C-77 is a north–south road serving central Emmet County, connecting Harbor Springs and Cross Village via a more inland route than the one taken by M-119. C-81 exists in two north–south segments. One segment, in the south of Emmet County, connects the Walloon Lake area with Petoskey, paralleling US-131. Another segment, in central Emmet County, connects Harbor Springs and Mackinaw City.
C-81 exists in two north–south segments. One segment, in the south of Emmet County, connects the Walloon Lake area with Petoskey, paralleling US-131. Another segment, in central Emmet County, connects Harbor Springs and Mackinaw City.
Bus
Indian Trails provides intercity bus service to Emmet County with stops in Petoskey and Pellston.
Air service
Emmet County is served by Pellston Regional Airport, with connections to Detroit and other locales in Northern Michigan.
Demographics
| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1860 | 1,149 | — | |
| 1870 | 1,211 | 5.4% | |
| 1880 | 6,639 | 448.2% | |
| 1890 | 8,756 | 31.9% | |
| 1900 | 15,931 | 81.9% | |
| 1910 | 18,561 | 16.5% | |
| 1920 | 15,639 | −15.7% | |
| 1930 | 15,109 | −3.4% | |
| 1940 | 15,791 | 4.5% | |
| 1950 | 16,534 | 4.7% | |
| 1960 | 15,904 | −3.8% | |
| 1970 | 18,331 | 15.3% | |
| 1980 | 22,992 | 25.4% | |
| 1990 | 25,040 | 8.9% | |
| 2000 | 31,437 | 25.5% | |
| 2010 | 32,694 | 4.0% | |
| 2020 | 34,112 | 4.3% | |
| US Decennial Census[14] 1790-1960[15] 1900-1990[16] 1990-2000[17] 2010-2018[2] | |||
As of the 2000 United States Census,[18] there were 31,437 people, 12,577 households, and 8,527 families in the county. The population density was 67 people per square mile (26 people/km2). There were 18,554 housing units at an average density of 40 per square mile (15/km2). The racial makeup of the county was 94.33% White, 0.47% Black or African American, 3.11% Native American, 0.43% Asian, 0.03% Pacific Islander, 0.16% from other races, and 1.47% from two or more races. 0.91% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race. 23.6% were of German, 11.4% English, 11.3% Irish, 9.0% Polish and 8.4% American ancestry. 96.9% spoke English and 1.1% Spanish as their first language.
There were 12,577 households, out of which 31.70% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 55.90% were married couples living together, 8.50% had a female householder with no husband present, and 32.20% were non-families. 26.90% of all households were made up of individuals, and 10.00% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.44 and the average family size was 2.97.
The county population contained 25.30% under the age of 18, 7.10% from 18 to 24, 28.10% from 25 to 44, 25.20% from 45 to 64, and 14.30% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 39 years. For every 100 females there were 96.80 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 93.70 males.
The median income for a household in the county was $40,222, and the median income for a family was $48,140. Males had a median income of $33,385 versus $24,173 for females. The per capita income for the county was $21,070. About 4.50% of families and 7.40% of the population were below the poverty line, including 7.30% of those under age 18 and 7.80% of those age 65 or over.
Government
Emmet County has largely voted Republican through the years. Since 1876 its voters have selected the Republican Party nominee in 78% (28 of 36) of the national elections, and in 19 of the last 20 national elections (through 2020) the Republican nominee carried the county.
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third party | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | |
| 2020 | 12,135 | 54.64% | 9,662 | 43.50% | 412 | 1.86% |
| 2016 | 10,616 | 55.89% | 6,972 | 36.71% | 1,406 | 7.40% |
| 2012 | 10,253 | 57.71% | 7,225 | 40.67% | 287 | 1.62% |
| 2008 | 9,314 | 51.32% | 8,515 | 46.92% | 320 | 1.76% |
| 2004 | 10,332 | 59.48% | 6,846 | 39.41% | 194 | 1.12% |
| 2000 | 8,602 | 58.47% | 5,451 | 37.05% | 658 | 4.47% |
| 1996 | 6,002 | 47.71% | 4,892 | 38.89% | 1,686 | 13.40% |
| 1992 | 5,312 | 40.15% | 4,245 | 32.08% | 3,675 | 27.77% |
| 1988 | 7,105 | 62.40% | 4,170 | 36.62% | 111 | 0.97% |
| 1984 | 7,760 | 70.04% | 3,254 | 29.37% | 66 | 0.60% |
| 1980 | 5,930 | 53.88% | 3,724 | 33.84% | 1,352 | 12.28% |
| 1976 | 5,910 | 58.49% | 4,013 | 39.72% | 181 | 1.79% |
| 1972 | 5,288 | 61.91% | 3,081 | 36.07% | 172 | 2.01% |
| 1968 | 4,405 | 58.83% | 2,624 | 35.04% | 459 | 6.13% |
| 1964 | 2,731 | 39.37% | 4,197 | 60.50% | 9 | 0.13% |
| 1960 | 4,574 | 63.55% | 2,602 | 36.15% | 22 | 0.31% |
| 1956 | 4,764 | 71.16% | 1,903 | 28.42% | 28 | 0.42% |
| 1952 | 5,113 | 72.90% | 1,871 | 26.68% | 30 | 0.43% |
| 1948 | 3,565 | 63.42% | 1,922 | 34.19% | 134 | 2.38% |
| 1944 | 3,538 | 61.19% | 2,206 | 38.15% | 38 | 0.66% |
| 1940 | 4,216 | 59.62% | 2,831 | 40.04% | 24 | 0.34% |
| 1936 | 2,893 | 44.58% | 3,075 | 47.39% | 521 | 8.03% |
| 1932 | 2,890 | 46.06% | 3,110 | 49.56% | 275 | 4.38% |
| 1928 | 3,679 | 75.36% | 1,166 | 23.88% | 37 | 0.76% |
| 1924 | 3,020 | 69.23% | 773 | 17.72% | 569 | 13.04% |
| 1920 | 3,059 | 68.88% | 1,070 | 24.09% | 312 | 7.03% |
| 1916 | 1,724 | 50.28% | 1,363 | 39.75% | 342 | 9.97% |
| 1912 | 830 | 25.00% | 920 | 27.71% | 1,570 | 47.29% |
| 1908 | 2,313 | 62.08% | 1,012 | 27.16% | 401 | 10.76% |
| 1904 | 2,710 | 69.15% | 941 | 24.01% | 268 | 6.84% |
| 1900 | 2,362 | 62.52% | 1,281 | 33.91% | 135 | 3.57% |
| 1896 | 1,727 | 54.17% | 1,337 | 41.94% | 124 | 3.89% |
| 1892 | 1,015 | 46.28% | 1,059 | 48.29% | 119 | 5.43% |
| 1888 | 946 | 44.88% | 1,056 | 50.09% | 106 | 5.03% |
| 1884 | 779 | 43.79% | 895 | 50.31% | 105 | 5.90% |
| 1880 | 814 | 56.96% | 495 | 34.64% | 120 | 8.40% |
| 1876 | 312 | 41.82% | 426 | 57.10% | 8 | 1.07% |
Emmet County operates the County jail, maintains rural roads, operates the major local courts, records deeds, mortgages, and vital records, administers public health regulations, and participates with the state in the provision of social services. The county board of commissioners controls the budget and has limited authority to make laws or ordinances. In Michigan, most local government functions – police and fire, building and zoning, tax assessment, street maintenance etc. – are the responsibility of individual cities and townships.
Elected officials
- Prosecuting Attorney: James R. Linderman
- Sheriff: Peter A. Wallin
- County Clerk: Suzanne R. Kanine
- County Treasurer: Mary Mitchell
- Register of Deeds: Karen Cosens[20]
(information as of December 2020)
Parks and recreation
- Wilderness State Park is a 10,512-acre (4,254 ha) state park in Carp Lake township on the shores of Lake Michigan. A prominent physical feature of the park is Waugoshance Point, which juts westward into the lake. Beyond the tip of the point, Temperance Island and Waugoshance Island are also parts of the state park. Waugoshance Point and the adjacent islands are nesting grounds for the endangered piping plover.
- The Headlands is a 550-acre park located west of Mackinaw City, Michigan on the shores of Lake Michigan. The park contains woodlands, over two miles of undeveloped shoreline, and many species of rare and endangered plant life. Marked trails are provided for hiking, bicycling and cross-country skiing. In May 2011, Headlands Park was awarded International Dark Sky Park designation by the International Dark-Sky Association.
Environment and endangered species
Emmet County is home to Michigan's most endangered species and one of the most endangered species in the world, the Hungerford's Crawling Water Beetle. The species lives in only five locations in the world, two of which are in Emmet County. One of these, a two-and-a-half mile stretch downstream from the Douglas Road crossing of the East Branch of the Maple River, supports the only stable population of the Hungerford's Crawling Water Beetle, with roughly 1000 specimens. This area is largely within and along the boundary of the University of Michigan Biological Station. The other location in Emmet County, near the Oliver Road crossing of the Carp Lake River, revealed four adult specimens in 1997. Erosion along the road seems to have harmed the habitat and no specimens were found in the last survey conducted in 2003.
Communities
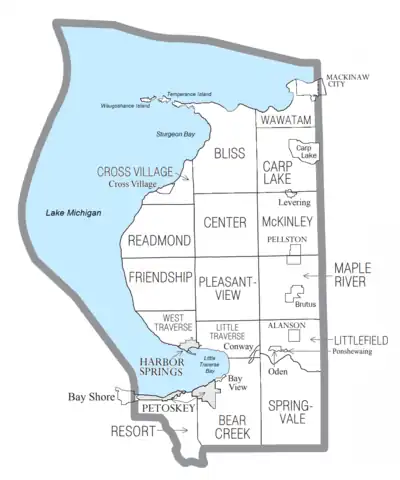
.png.webp)
Cities
- Harbor Springs
- Petoskey (county seat)
Villages
- Alanson
- Mackinaw City (partial)
- Pellston
Civil townships
- Bear Creek Township
- Bliss Township
- Carp Lake Township
- Center Township
- Cross Village Township
- Friendship Township
- Little Traverse Township
- Littlefield Township
- Maple River Township
- McKinley Township
- Pleasantview Township
- Readmond Township
- Resort Township
- Springvale Township
- Wawatam Township
- West Traverse Township
Census-designated places
Other unincorporated places
Indian reservations
- Burt Lake Band of Ottawa and Chippewa Indians
- Little Traverse Bay Bands of Odawa Indians occupies at least 13 scattered reservation areas within Emmet County, including portions within the city of Petoskey and the townships of Bear Creek, Bliss, Center, Little Traverse, McKinley, Readmond, Resort, Wawatam, and West Traverse.[21]
- Mackinac Bands of Chippewa and Ottawa Indians
Economy
The economy of Emmet County, along with that of the rest of Northern Michigan, is heavily boosted by local companies and manufacturing. Corporations in Emmet County, such as those in the fields of aerospace technology, gambling and candy making, among others, drive the county's economy.[22][23][24]
Manufacturing and industry
The Odawa Casino Resort in Resort Township is one of Emmet County's top attractions, as it is one of the many casinos in Northern Michigan.[25] Along with the Odawa, the LTBB Gaming Administration in Petoskey is one of the other casinos in the area, employing 250 people. The Kilwins chocolate-manufacturing company is based in Petoskey, although over 100 locations of the store exist in 21 states, mostly in popular tourist destinations. The company, founded in 1947 under a similar name by Don and Katey Kilwin, specializes in making ice cream, candy, chocolate, and fudge.[26][27][28] McLaren Northern Michigan Hospital in Petoskey is one of the top employers of Emmet County, with 950 employees. Overall, six companies in Emmet County employ 200 or more people.[29] Moeller Aerospace Technology in Harbor Springs manufactures various products.[30] The Petoskey News-Review is a daily newspaper, in circulation since 1878. Its current name dates from a 1953 merger with another newspaper company.[31]
See also
References
- "Bibliography on Emmet County". Clarke Historical Library, Central Michigan University. Retrieved January 19, 2013.
- "State & County QuickFacts". US Census Bureau. Retrieved September 15, 2021.
- "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Retrieved June 7, 2011.
- Newberry Library. "Michigan: Individual County Chronologies". Atlas of County Historical Boundaries. Archived from the original on November 6, 2016. Retrieved November 4, 2016.
- Blackbird, Andrew J.(1887): History of the Ottawa and Chippewa Indians of Michigan, The Ypsilantian Job Printing House .
- Karamanski, Theodore J. (2012). Blackbird's song : Andrew J. Blackbird and the Odawa people. East Lansing: Michigan State University Press. pp. 6, 8–9. ISBN 978-1-61186-050-4.
- Karamanski 2012, pp. 8–9.
- "Biography – Du Jaunay, Pierre – Volume IV (1771-1800)". Dictionary of Canadian Biography. Retrieved March 25, 2022.
- "Tonedagana County." Michigan Historical Collections, Volume 1, page 322. Pioneer Society of the State of Michigan, Michigan Historical Commission, 1877. Accessed 7 June 2020.
- "Blasts from the Past: How did Emmet County get named for an Irish Patriot?" Emmet County, Michigan, official website. Accessed 7 June 2020.
- George Dawson (1840). Acts of the Legislature of the State of Michigan Passed at the Annual Session of 1840. Detroit. pp. 196–200.
- "2010 Census Gazetteer Files". US Census Bureau. August 22, 2012. Archived from the original on November 13, 2013. Retrieved September 21, 2014.
- Michigan Department of Transportation (December 9, 2010). "Contract Numbers 2011-0033 and 2011-0033". Michigan Department of Transportation. Retrieved December 13, 2010.
- "US Decennial Census". US Census Bureau. Retrieved September 21, 2014.
- "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved September 21, 2014.
- "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". US Census Bureau. Retrieved September 21, 2014.
- "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). US Census Bureau. Archived (PDF) from the original on March 27, 2010. Retrieved September 21, 2014.
- "U.S. Census website". US Census Bureau. Retrieved January 31, 2008.
- US Election Atlas
- Emmet County - Officials & Depts
- "Michigan: 2010 Population and Housing Unit Counts 2010 Census of Population and Housing" (PDF). 2010 United States Census. United States Census Bureau. September 2012. p. E-19. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 19, 2012. Retrieved February 29, 2020.
- Bureau of Labor Statistics, Michigan
- MyNorth, Northern Michigan
- Smith, Jeff. "8 Companies Play Growing Role in Northern Michigan Economy". MyNorth. Retrieved July 11, 2018.
- "Odawa Casino". Retrieved July 11, 2018.
- "Our History and Timeline". Retrieved July 11, 2018.
- "Kilwins Store Locations". Retrieved July 11, 2018.
- Petoskey CofC, Kilwins
- Northern Lakes
- Moeller Aerospace
- Petroskey News
External links
- "Bibliography on Emmet County". Clarke Historical Library, Central Michigan University.
- Emmet County official site