Escharotomy
An escharotomy is a surgical procedure used to treat full-thickness (third-degree) circumferential burns. In full-thickness burns, both the epidermis and the dermis are destroyed along with sensory nerves in the dermis. The tough leathery tissue remaining after a full-thickness burn has been termed eschar. Following a full-thickness burn, as the underlying tissues are rehydrated, they become constricted due to the eschar's loss of elasticity, leading to impaired circulation distal to the wound. An escharotomy can be performed as a prophylactic measure as well as to release pressure, facilitate circulation and combat burn-induced compartment syndrome.
| Escharotomy | |
|---|---|
| ICD-9-CM | 86.09 |
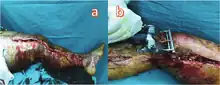
An escharotomy is performed by making an incision through the eschar to expose the fatty tissue below. Due to the residual pressure, the incision will often widen substantially.
Overview
Full-thickness circumferential and near-circumferential skin burns result in the formation of a tough, inelastic mass of burnt tissue (eschar). The eschar, by virtue of this inelasticity, results in the burn-induced compartment syndrome. This is caused by the accumulation of extracellular and extravascular fluid within confined anatomic spaces of the extremities or digits. The excessive fluid causes the intracompartmental pressures to increase, resulting in collapse of the contained vascular and lymphatic structures and, hence, loss of tissue viability. The capillary closure pressure of 30 mm Hg, also measured as the compartment pressure, is accepted as that which requires intervention to prevent tissue death. If ischemia (poor blood flow) persists for over six hours, then the irreversible process of muscle necrosis will begin.[1]
The circumferential eschar over the torso can lead to significant compromise of chest wall excursions and can hinder ventilation. Abdominal compartment syndrome with visceral hypoperfusion is associated with severe burns of the abdomen and torso. Due to the primarily diaphragmatic breathing done by children, anterior burns may be enough to warrant an escharotomy.[2] Similarly, airway patency and venous return may be compromised by circumferential burns involving the neck.
Escharotomy is the surgical division of the nonviable eschar, which allows the cutaneous envelope to become more compliant. Hence, the underlying tissues have an increased available volume to expand into, preventing further tissue injury or functional compromise.
Indications
Indications for emergency escharotomy are the presence of a circumferential eschar with one of the following:
- Impending or established vascular compromise of the extremities or digits.
- Impending or established respiratory compromise due to circumferential torso burns.[3]
- Severely burned extremities should be elevated and range of motion exercises performed every 15–30 minutes as tolerated by the patient. This can help to minimize tissue edema and elevated tissue pressures.
Neurovascular integrity should similarly be monitored frequently and in a scheduled manner. Capillary refilling time, Doppler signals, pulse oximetry, and sensation distal to the burned area should be checked every hour.[4] Limb deep compartment pressures should be checked initially to establish a baseline. Subsequently, any increase in capillary refill time, decrease in Doppler signal, or change in sensation should lead to rechecking the compartment pressures. Compartment pressures greater than 30 mm Hg should be treated by immediate decompression via escharotomy and fasciotomy, if needed.[3]
Procedure
During an escharotomy the patient is often sedated despite the insensible eschar. The burnt skin is incised down to the subcutaneous fat and into the healthy skin (up to 1 cm). The incisions should be deep enough to release all restrictive effects from the eschar. The operation can be performed on the trunk, limbs, or neck, all while avoiding critical nerves, veins, and vessels.[2] Following the operation the wounds are dressed primarily with an absorbent, antimicrobial material, then wrapped lightly in a bandage. Elevation (if possible) and observation are encouraged.[4]
References
- Saladin, Kenneth S. (January 2014). Anatomy & Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function (Seventh ed.). New York: McGraw Hill Education. p. 313. ISBN 978-0-07-340371-7.
- Nickson, Chris. "Releasing the Roman Breastplate". lifeinthefastlane.com. Retrieved 27 November 2014.
- Emergency Escharotomy at eMedicine
- "Burns Unit". The Royal Children's Hospital Melbourne. Retrieved 27 November 2014.