European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages
The European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages (ECRML) is a European treaty (CETS 148) adopted in 1992 under the auspices of the Council of Europe to protect and promote historical regional and minority languages in Europe. However, the charter does not provide any criterion or definition for an idiom to be a minority or a regional language, and the classification stays in the hands of the national state.[1]
| CET 148 | |
|---|---|
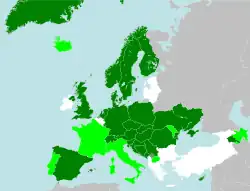 Member states that have signed and ratified in dark green, those that have signed but not ratified in light green, those that have neither signed nor ratified in white, non-member states of the Council of Europe in grey. Source: the list of signatories at the Council of Europe website. | |
| Signed | 5 November 1992 |
| Location | Strasbourg |
| Effective | 1 March 1998 |
| Condition | Ratification by 5 States |
| Signatories | 33 |
| Parties | 25 |
| Depositary | Secretary General of the Council of Europe |
| Languages | English and French |
| Full text | |
The preparation for the charter was undertaken by the predecessor to the current Congress of Local and Regional Authorities, the Standing Conference of Local and Regional Authorities of Europe because involvement of local and regional government was essential. The actual charter was written in the Parliamentary Assembly based on the Congress' Recommendations. It only applies to languages traditionally used by the nationals of the State Parties (thus excluding languages used by recent immigrants from other states, see immigrant languages), which significantly differ from the majority or official language (thus excluding what the state party wishes to consider as mere local dialects of the official or majority language) and that either have a territorial basis (and are therefore traditionally spoken by populations of regions or areas within the State) or are used by linguistic minorities within the State as a whole (thereby including such languages as Yiddish, Romani and Lemko, which are used over a wide geographic area).
Some states, such as Ukraine and Sweden, have tied the status of minority language to the recognized national minorities, which are defined by ethnic, cultural and/or religious criteria, thereby circumventing the Charter's notion of linguistic minority.[2]
Languages that are official within regions, provinces or federal units within a State (for example Catalan in Spain) are not classified as official languages of the State and may therefore benefit from the Charter. On the other hand, Ireland has not been able to sign the Charter on behalf of the Irish language (although a minority language) as it is defined as the first official language of the state. The United Kingdom has ratified the Charter in respect to (among other languages) Welsh in Wales, Scots and Gaelic in Scotland, and Irish in Northern Ireland. France, although a signatory, has been constitutionally blocked from ratifying the Charter in respect to the languages of France.
The charter provides many actions state parties can take to protect and promote historical regional and minority languages. There are two levels of protection—all signatories must apply the lower level of protection to qualifying languages. Signatories may further declare that a qualifying language or languages will benefit from the higher level of protection, which lists a range of actions from which states must agree to undertake at least 35.
Protections
Countries can ratify the charter in respect of its minority languages based on Part II or Part III of the charter, which contain varying principles. Countries can treat languages differently under the charter, for example, in the United Kingdom, the Welsh language is ratified under the general Part II principles as well as the more specific Part III commitments, while the Cornish language is ratified only under Part II.
Part II
Part II of the Charter details eight main principles and objectives upon which States must base their policies and legislation. They are seen as a framework for the preservation of the languages concerned.[3]
- Recognition of regional or minority languages as an expression of cultural wealth.
- Respect for the geographical area of each regional or minority language.
- The need for resolute action to promote such languages.
- The facilitation and/or encouragement of the use of such languages, in speech and writing, in public and private life.
- The provision of appropriate forms and means for the teaching and study of such languages at all appropriate stages.
- The promotion of relevant transnational exchanges.
- The prohibition of all forms of unjustified distinction, exclusion, restriction or preference relating to the use of a regional or minority language and intended to discourage or endanger its maintenance or development.
- The promotion by states of mutual understanding between all the country's linguistic groups.
Part III
Part III details comprehensive rules, across a number of sectors, by which states agree to abide. Each language to which Part III of the Charter is applied must be named specifically by the government. States must select at least thirty-five of the undertakings in respect to each language. Many provisions contain several options, of varying degrees of stringency, one of which has to be chosen "according to the situation of each language". The areas from which these specific undertakings must be chosen are as follows:[3]
- Education
- Judicial authorities
- Administrative authorities and public services
- Media
- Cultural activities and facilities
- Economic and social life
- Transfrontier exchanges
Languages protected under the Charter
| Countries that have ratified the Charter, and languages for which the ratification was made[4] |
|---|
ratification: 25 January 2002[5] |
ratification: 28 June 2001[5]
|
ratification: 21 September 2010[5] |
ratification: 5 November 1997[5] |
ratification: 26 August 2002[5] |
ratification: 15 November 2006[5]
|
ratification: 8 September 2000[5]
|
ratification: 9 November 1994[6] |
ratification: 16 September 1998[5]
|
ratification: 26 April 1995[5] |
ratification: 18 November 1997[5]
|
ratification: 22 June 2005[5]
|
ratification: 15 February 2006[5] |
ratification: 2 May 1996[5] |
ratification: 10 November 1993[5]
|
ratification: 12 February 2009[5] |
ratification 29 January 2008[5]
|
ratification: 15 February 2006[5] |
ratification: 5 September 2001[8] |
ratification: 4 October 2000[5] |
ratification: 9 April 2001[5]
|
ratification: 9 February 2000[5] |
ratification: 23 December 1997[5] |
ratification: 19 September 2005[5]
Ukraine does not specify languages by name, but rather ratifies on behalf of "the languages of the following ethnic minorities of Ukraine[10] |
ratification : 27 March 2001.[5]
|
See also
Notes and references
- Gabrielle Bernoville, Europe's forgotten words. The case of the European Regional and minority languages, La Regionisto,
- Hult, F.M. (2004). Planning for multilingualism and minority language rights in Sweden. Language Policy, 3(2), 181-201.
- "The European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages is the European convention for the protection and promotion of languages used by traditional minorities". European Charter for Regional
or Minority Languages. - "States Parties to the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languagesand their regional orminority languages(listed by language on p.6". Council of Europe. 28 April 2020. Retrieved 5 March 2021.
Updated version of the Charter
- "Chart of signatures and ratifications of Treaty 148". Council of Europe. 5 March 2021. Retrieved 5 March 2021.
- "Full list".
- "Report of the Committee of Experts on Luxembourg, December 2008" (PDF). Coe.int. Retrieved 2014-01-30.
- "Full list".
- "Aplicación de la Carta en España, Segundo ciclo de supervisión. Estrasburgo, 11 de diciembre de 2008. A.1.3.28 pag 7 ; A.2.2.5" (PDF). Coe.int. p. 107. Retrieved 2015-03-01.
- As of July 2007, Ukraine's entry on the Council of Europe site states the following Ukraine declares that the provisions of the Charter shall apply to the languages of the following ethnic minorities of Ukraine : Belarusian, Bulgarian, Gagauz, Greek, Jewish, Crimean Tatar, Moldavian, German, Polish, Russian, Romanian, Slovak and Hungarian.
- "Full list". Treaty Office.
- "Full list". Treaty Office.
External links
- European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages text
- More information on the treaty
- Charter website
- Eurolang (News agency about minority languages in Europe)
- Explanatory Report on the Charter
- lexpress.fr (in French)
- Application of the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages,Doc. 12881