Far East Squadron
The French Far East Squadron (French: escadre de l'Extrême-Orient) was an exceptional naval grouping created for the duration of the Sino-French War (August 1884 – April 1885).



Background
In 1882 French interests in the Far East were protected by two naval divisions, the Cochinchina naval division (based at Saigon) and the Far East naval division (based at Yokohama). The Cochinchina naval division (division navale de Cochinchine) was responsible for monitoring coastal navigation between Singapore and the Hainan Strait and along the rivers of Cochinchina and Cambodia, while the Far East naval division (division navale de l'Extrême-Orient) policed the China Coast and the seas around China and Japan.[1]
Henri Rivière's intervention in Tonkin in April 1882 was made with vessels of the Cochinchina naval division. As France increased its commitment in Tonkin after Rivière's defeat and death at the Battle of Paper Bridge, a naval division was created at the end of May 1883 to patrol the Gulf of Tonkin. Command of this new Tonkin Coasts naval division (division navale des côtes du Tonkin) was given to Admiral Amédée Courbet.[2] A Tonkin Flotilla (flotille de Tonkin), consisting of a number of despatch vessels and gunboats, was also created for inland operations in the summer of 1883, and placed under the command of général de brigade Alexandre-Eugène Bouët (1833–87), the French commandant supérieur in Tonkin.
Composition
The Far East squadron was formally constituted on 27 June 1884, in response to the news of the Bắc Lệ ambush, by the amalgamation of the Tonkin Coasts naval division and the Far East naval division. The Tonkin Coasts naval division, under the command of Admiral Amédée Courbet since July 1883, consisted of the ironclads Bayard (the flagship) and Atalante, the cruiser Châteaurenault, the light frigates Hamelin and Parseval, the gunboats Lynx, Vipère and Aspic, the troopships Drac and Saône and Torpedo Boats Nos. 45 and 46. The Far East naval division, under the command of Admiral Sébastien Lespès since March 1884, consisted of the ironclads La Galissonnière (the flagship) and Triomphante, the cruisers d'Estaing, Duguay-Trouin, Villars, and Volta, and the gunboat Lutin.[3] The new squadron was placed under Courbet's command, with Lespès second in command.
In October 1884 the squadron was joined by the cruisers Rigault de Genouilly from the Levant station, Nielly from the Indian Ocean station and Champlain.[4] At the end of November 1884 a fourth cruiser, Éclaireur, arrived from the Pacific station.[5] In January 1885 the squadron was joined by the cruisers Duchaffault from New Caledonia and Lapérouse from France.[6] Around the end of March 1885 the cruiser Kerguelen, transferred from the Pacific station, joined the squadron. French naval forces in Tonkin were strongly reinforced in the spring of 1885 by the cruisers Fabert and La Clocheterie, and the seagoing gunboat Jaguar, previously based at Along Bay as part of the Tonkin flotilla, was also transferred to the Far East squadron at this period.
In April 1885 the squadron was reinforced by a third naval division, sent out from France in January 1885 under the command of Admiral Adrien-Barthélémy-Louis Rieunier. Rieunier's division consisted of the ironclad Turenne (his flagship), the cruisers Magon, Primauguet and Roland, and the gunboats Comète and Sagittaire. The division was accompanied by two more torpedo boats, Nos. 44 and 45, and by the 'auxiliary cruiser' Château-Yquem, a civilian vessel leased and armed by the French government for the duration of hostilities with China.[7] Rieunier's division reached Far Eastern waters too late to take part in active naval operations, but some of its ships took part in the continuing French blockade of the Yangzi River between April and June 1885.
In April 1885, at the end of the Sino-French War, the squadron consisted of the following vessels:
- Ironclads: Bayard, La Galissonnière, Turenne, Triomphante, Atalante
- Cruisers (1st Class): Duguay-Trouin, Villars, d'Estaing, Lapérouse, Nielly, Magon, Primauguet, Roland
- Cruisers (2nd Class): Champlain, Châteaurenault, Éclaireur, Rigault de Genouilly
- Cruisers (3rd Class): Kerguelen, Volta, Duchaffault
- Avisos-transports: Saône
- Gunboats: Lutin, Vipère, Lynx, Comète, Sagittaire, Aspic, Jaguar
- Transports (1st Class): Annamite, Tonkin
- Auxiliary Cruisers: Château-Yquem
- Torpedo Boats (2nd Class): Nos. 44, 45, 46 and 50.[8]
Admiral Courbet died aboard his flagship Bayard in Magong harbour in the Pescadores on 11 June 1885, and was briefly succeeded in command of the squadron by Admiral Sébastien Lespès. On 25 July 1885 the French government reconstituted the traditional Far East naval division at close to its 1883 strength. The division, under the command of Admiral Lespès, with Rieunier second in command, consisted of the ironclads La Galissonnière (the flagship), Turenne and Triomphante, the cruisers Lapérouse, Primauguet, Champlain and Roland, and the gunboats Vipère and Sagittaire.[9] The other ships returned to France, or were transferred to Tonkin, or were sent to the various stations of the French fleet around the globe:
Around the end of June each day saw the departure of one of our ships. D’Estaing and Kerguelen were the first to leave, towing Torpedo Boats Nos. 50 and 44 as far as Saigon, then continuing on to France. Villars and Éclaireur followed them, while Château-Yquem conveyed troops, artillery and mules to Along Bay. Then Annamite left, to repatriate the sick. Duguay-Trouin and Châteaurenault went next, to return to France. Magon and Fabert went back to the Pacific station, and Rigault de Genouilly to the Levant station. A little later Atalante left to decommission in Saigon, Nielly joined the Indian Ocean station and La Clocheterie, Lutin and Comète left for Tonkin to join General de Courcy's command.[10]
Operations

The Far East squadron was engaged on several occasions during the Sino-French War. The ironclad La Galissonnière, the cruiser Villars and the gunboat Lutin took part in the bombardment of Keelung on 5 August 1884, directed by Rear Admiral Lespès. The landing force put ashore by Lespès on the afternoon of 5 August to occupy Keelung consisted of the landing companies of Bayard and Villars, under the respective commands of capitaine de frégate Martin and lieutenant de vaisseau Jacquemier. Both companies were attacked by superior Chinese forces on the morning of 6 August, and had to make a fighting withdrawal to the coast, where they were re-embarked. French casualties in this operation were 2 dead and 11 wounded.[11]
Other ships were involved in the Battle of Fuzhou (23 August 1884), various operations in the Keelung Campaign, including landings at Keelung and Tamsui (1 to 8 October 1884), the blockade of Formosa (October 1884 to April 1885), the Battle of Shipu (14 February 1885), the so-called Battle of Zhenhai (1 March 1885), the Pescadores Campaign (March 1885) and the 'rice blockade' of the Yangtze River (March to June 1885).
There were also a number of exploits by individual vessels. The light frigate Parseval, sent to Shanghai in the summer of 1884 to observe the movements of China's Southern Seas fleet, made a daring night escape under the guns of the Wusong forts in September 1884.
Losses

None of the squadron's vessels were lost in battle, but there were several losses from other causes. The light frigate Hamelin (capitaine de frégate Roustan) stranded in the Min River in July 1884 and had to return to France for repairs.[12] Thirteen sailors were scalded to death aboard the cruiser Rigault de Genouilly on 15 November 1884 when a boiler exploded.[13]
Torpedo Boat No. 45, which had fought in the Battle of Fuzhou, was lost at sea on 21 March 1885 while sailing to Ningbo to join the French vessels blockading the mouth of the Yangzi River.[14] Torpedo Boat No. 46, which had attacked and sunk the Chinese corvette Yangwu during the Battle of Fuzhou, was lost at sea off Makung on 30 April 1885, shortly after the end of the Sino-French War.[15] Both torpedo boats were lost while under tow (by Châteaurenault and d'Estaing respectively), and on both occasions foundered after the towing rope snapped. There were no casualties in either incident.
The battle losses of the ships' crews and the squadron's landing companies were moderate. The squadron suffered minor losses in the Battle of Fuzhou and the subsequent descent of the Min River, and rather heavier casualties on 8 October 1884 in the failed landing at Tamsui during the Keelung Campaign. French casualties in the Battle of Shipu were minimal. Several sailors died of cholera during the four-month occupation of the Pescadores Islands following the Pescadores Campaign.
Ships of the Far East squadron
 Bayard (5,915 tons), Admiral Courbet's flagship
Bayard (5,915 tons), Admiral Courbet's flagship Atalante
Atalante La Galissonnière (4,585 tons)
La Galissonnière (4,585 tons)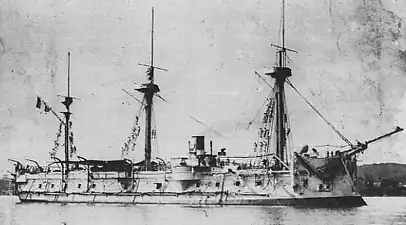 Triomphante (4,585 tons)
Triomphante (4,585 tons) Duguay-Trouin (3,479 tons)
Duguay-Trouin (3,479 tons).jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp) Volta
Volta.jpg.webp) Nielly
Nielly Parseval (870 tons)
Parseval (870 tons).jpg.webp) Lutin
Lutin_bf_1923.jpg.webp) Comète
Comète_img_2590.jpg.webp) Éclaireur
Éclaireur
Naval uniforms of the Far East squadron
 French sailor
French sailor 'Going into battle'
'Going into battle'
Notes
- The Far East naval division was also known as the China and Japan Seas naval division (division navale des mers de Chine et du Japon).
- Loir, 6–10
- Loir, 5–6
- Loir, 215
- Loir, 224
- Loir, 273 and 274
- Loir, 294–5
- Loir, 358–68
- Loir, 354–5
- Loir, 351–2
- Garnot, 23–31; Loir, 91–101
- Loir, 71–5
- Loir, 222
- Duboc, 294
- Loir, 331–2
References
- Destelan, P., Annam et Tonkin: Notes de voyage d'un marin (Paris, 1892)
- Duboc, Émile, Trente cinq mois de campagne en Chine, au Tonkin (Paris, 1899)
- Ferrero, Stéphane, Formose, vue par un marin français du XIXe siècle (Paris, 2005)
- Garnot, L'expédition française de Formose, 1884–1885 (Paris, 1894)
- Loir, Maurice, L'escadre de l'amiral Courbet (Paris, 1886)
- Lung Chang [龍章], Yueh-nan yu Chung-fa chan-cheng [越南與中法戰爭, Vietnam and the Sino-French War] (Taipei, 1993)
- Bernard, Hervé, L'Amiral Adrien, Barthélemy, Louis, Henri Rieunier (1833–1918) Ministre de la Marine – La Vie Extraordinaire d'un Grand Marin (Biarritz, 2005)
- Rawlinson, John, China's Struggle for Naval Development, 1839–1895 (Harvard, 1967)
- Rollet de l'Isle, Maurice, Au Tonkin et dans les mers de Chine (Paris, 1886)
- Wright, Richard, The Chinese Steam Navy, 1862–1945 (London, 2001)