Fluoroaspirin
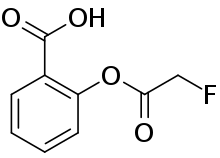
Fluoroaspirin is the fluoroacetate ester of salicylic acid. It is the fluoroacetate analog of aspirin. Like other fluoroacetate esters, fluoroaspirin is highly toxic.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-[(Fluoroacetyl)oxy]benzoic acid | |
| Other names
Fluoroacetylsalicylic acid, O-(Fluoroacetyl)salicylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H7FO4 | |
| Molar mass | 198.149 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
15 mg/kg (mice, subcutaneous) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Saunders, BC (1957). Some aspects of the chemistry and toxic action of organic compounds containing phosphorus and fluorine (PDF).
- Saunders, B. C.; Stacey, G. J. (1948). "358. Toxic fluorine compounds containing the C–F link. Part I. Methyl Fluoroacetate and Related Compounds". J. Chem. Soc. 70: 1773–1779. doi:10.1039/JR9480001773. PMID 18106001.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.