Forstinning
Forstinning is a community in the district of Ebersberg in Upper Bavaria, Germany.
Forstinning | |
|---|---|
 Coat of arms | |
Location of Forstinning within Ebersberg district 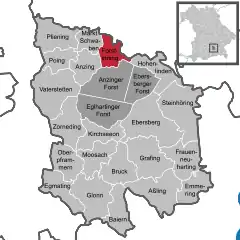 | |
 Forstinning  Forstinning | |
| Coordinates: 48°10′N 11°55′E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Bavaria |
| Admin. region | Oberbayern |
| District | Ebersberg |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2020–26) | Rupert Ostermair[1] (CSU) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 12.26 km2 (4.73 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 512 m (1,680 ft) |
| Population (2022-12-31)[2] | |
| • Total | 3,992 |
| • Density | 330/km2 (840/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| Postal codes | 85661 |
| Dialling codes | 08121 |
| Vehicle registration | EBE |
| Website | www.forstinning.de |
Geography
Forstinning lies in the Munich region in the north of the Ebersberg district and on the northern edge of the Munich Schotterebene (a sandur) and the Ebersberg Forest. Neighbouring municipalities and unincorporated areas bordering the community are, clockwise beginning with those also in the Ebersberg district, Hohenlinden, the Ebersberg Forest (unincorporated), Anzing and Markt Schwaben, and continuing with those in the Erding district, Ottenhofen, Pastetten and Forstern.
Forstinning has only one traditional rural land unit – Gemarkung in German – also called Forstinning. Forstinning's constituent communities include Aich, Aitersteinering, Berg, Köckmühle, Kressiermühle, Moos, Neupullach, Niederried, Salzburg, Schußmühle, Schwaberwegen, Sempt, Siegstätt, Steffelmühle, Wagmühle, Wind and Wolfmühle.
History
Forstinning's history begins in Sempt, where the area's transport hub lay, with the Grafenburg (“Count’s Castle”) as the trading post, with a market lent by the king (fiscale forum, 11th century), and the Reichshof (“Imperial Court”, curtis fiscalis, 934). The first greatness that this far-flung spot knew, however, does not date merely from Bavarii times, but from much longer ago, as witnessed by many archaeological finds nearby. The bronze ram figurine kept in the state's prehistoric collection may relate to the Celtic square dig site near Aitersteinering whose walls have been largely flattened by earthworks over time. The most recent findings suggest that such sites served as places of worship. There are many further traces of prehistory in the area. In the nearby state forest are found large groups of barrows from Hallstatt times. A Roman villa's remains were found a few decades ago at a remote mountain near Forstinning, and in Forstinning in 1958 a digger brought up a Bronze Age sword whose age was reckoned to be roughly 3,200 years. Only one old mill is nowadays left standing in Sempt. Now and then remnants of the old castle's and the old church's walls, the latter having been torn down in 1803, are brought to light when the Sempt brook overflows. This flooding sometimes also uncovers the castle graves whose loosely layered soil cannot withstand storm flooding quite as well as residual soil. Sempt Castle had the aforesaid brook as its moat.
Even though Ebersberg may have taken over Sempt's heritage in a way, Forstinning must have been closely tied to the market town of Sempt. The church there, dedicated to John the Baptist, could have been the original Forstinning Parish's baptismal church. The find of a Bavarii row grave yard strengthens what the form of the placename already suggests: Forstinning was founded in the time when the land was first occupied by its current inhabitants. The first settler was an "Undeo" from one of the common local clans. About 1050, this may have yielded the local lordly family, as witnessed by an "Engildeo". The community's earliest recorded name was, accordingly, "Undeoingas" in about 804 (the 1,200th anniversary was observed in 2004). After undergoing many changes over the years from Undeingin to Undingen and Inding, the name Forstinning – and sometimes also Pfarrinding – for this community only cropped up in the 17th century.
On 14 July 1894, Forstinning was beset by a tornado, which left great devastation in its wake.
Religion
Forstinning has a Roman Catholic parish church that belongs to the parish of Anzing-Forstinning and the Archdiocese of Munich-Freising.
Population development
The community's land area was home to 2,069 inhabitants in 1970, 2,638 in 1987 and 3,225 in 2000.
Politics
The community's mayor (Bürgermeister) is Rupert Ostermair (CSU).
The community's tax revenue in 1999, converted to euros, was €1,671,000, of which €233,000 was from business taxes.
Coat of arms
Forstinning has canting arms in which one of the charges – the two stylized fir trees – suggests the key word element in the community's name, Forst – German for “forest”. This also symbolizes the community's location at the Ebersberg Forest. The Saint Sylvester Brotherhood (St. Silvesterbruderschaft), which looks back on a long history, could be said to be a local historical peculiarity. According to some documents pertaining to the local history, the Brotherhood also had at its disposal its own estate. Since the cross was associated with Saint Sylvester, it has been incorporated as a charge in the community's arms.
The arms might heraldically be described thus: In azure a three-knolled hill (Dreiberg in German heraldry) Or, on each flanking knoll a fir tree Or, between which a cross argent.
Town partnerships
Forstinning has a partnership with the Hungarian community of Dunasziget.
Culture and sightseeing
The parish church Mariä Heimsuchung (“Church of the Visitation”) took on its current shape through Munich building master Trischberger’s work in 1765 and 1766. The well maintained ceiling frescoes depict the Visitation and Pope Sylvester's worship of Mary. The high altar was built by a master craftsman from Markt Schwaben. The church's secondary patron was Saint Sylvester, upon whom a pilgrimage was bestowed by the Saint Sylvester Brotherhood, founded in the 15th century. He was said to be above all a patron of livestock.
Economy and infrastructure
Industry, agriculture, forestry
According to official statistics, 10 people on the social insurance contribution rolls were employed in agriculture and forestry in 1998 in Forstinning. In industry it was 227 and in trade and transport 183. In other fields, 129 people on the aforesaid rolls were employed, and 1,072 worked from their homes. There were no employees in processing industries. There were 12 businesses in contracting. Furthermore, in 2003, there were 36 agricultural businesses with a productive area of 972 ha.
Transport
Forstinning is connected to Germany’s Autobahn network by an interchange onto Bundesautobahn 94. Also, the Federal Highway (Bundesstraße) B 12, which joins the A94 in the community, runs through Forstinning, as does the regionally important state highway joining Rosenheim, Ebersberg, Markt Schwaben and Erding. Beyond the region, Forstinning is well known for the dispute over the extension of the A94. The disputed section lies between Forstinning and Ampfing.
The nearest railway station can be found in Markt Schwaben, connecting to the Munich S-Bahn line S2.
Public transport in Forstinning consists of buslines to Munich East Station (München-Ostbahnhof), Markt Schwaben, Gars, Hohenlinden and Ebersberg.
Munich Airport is about 30 km away.
Education
In 1999 the following institutions could be found in Forstinning:
- Kindergartens: 117 Kindergarten places with 130 children
- Elementary schools: 1 with 8 teachers and 160 pupils
Further schooling is available in Markt Schwaben (Gymnasium, Realschule, Hauptschule) as well as Erding (Berufsschule, Berufsoberschule, Fachoberschule).
Famous people
- Alois Hundhammer (25 February 1900 in Moos — 1 August 1974 in Munich), Bavarian education and cultural affairs minister, agriculture minister and acting Ministerpräsident
- Thomas Hitzlsperger (5 April 1982 in Munich), German national football player and professional player with Everton F.C., former Aston Villa, grew up in constituent community of Wagmühle, went to elementary school in Forstinning and played for the local team VfB Forstinning.
- In Moos near Forstinning the composer Carl Maria von Weber lived for a while.
- In 1871 and 1872, the later well known reform pedagogue Georg Kerschensteiner worked as an assistant teacher.
References
- Liste der ersten Bürgermeister/Oberbürgermeister in kreisangehörigen Gemeinden, Bayerisches Landesamt für Statistik, accessed 19 July 2021.
- Genesis Online-Datenbank des Bayerischen Landesamtes für Statistik Tabelle 12411-003r Fortschreibung des Bevölkerungsstandes: Gemeinden, Stichtag (Einwohnerzahlen auf Grundlage des Zensus 2011)