G Elias & Brother
G Elias & Brother was and American manufacturer of cabinets[1] and aircraft based in Buffalo, New York in the 1920s. A.G. Elias sat on the Manufacturers Aircraft Association's board of directors along with President Frank H. Russell, VP Glenn L. Martin, Charles L. Laurence, Chance M. Vought, S.S. Bradley,[2] George P. Tidmarsh,[3] and Donald Douglas.[4] E.J Elias promoted the construction of a Buffalo municipal airport to aid the local fledgling airplane industry of five aviation companies constructing airplanes and airplane parts.[5] From 1920 to 1925, Elias company's chief engineer, David Earle Dunlap (1896-1957), designed the Elias EM-2 Expeditionary planes. He designed the NBS-3 bomber fuselage and the Elias M-1 Mail plane. Dunlap's Elias TA-1 design was the first United States Army Air Corps Trainer to have a radial engine.[6] After tests a McCook Field, the Army Air Corps selected other manufacturers over the Elias bomber and trainer. The company designed the Elias EM-1 to meet requirements for a multirole amphibian marine expeditionary aircraft. Elias delivered six production Elias EM-2 aircraft with Liberty engines to the United States Navy in 1922.[7]
 | |
| Founded | circa 1920 |
|---|---|
| Defunct | 1929 |
| Headquarters | Buffalo, New York |
Key people | A.G. Elias & E.J Elias |
| Products | Commercial aircraft |
Aircraft
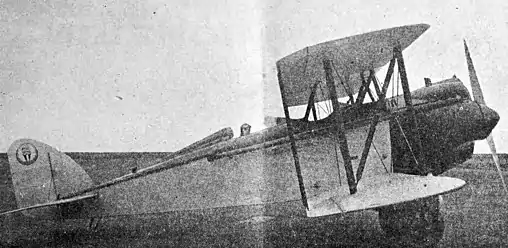
*Elias EC-1 Aircoupe
The EC-1 Aircoupe was a parasol wing monoplane powered by an 80 hp (60 kW) Anzani engine which first flew in 1928. [8][9] Designed by Joseph Cato, it had an open cockpit with a removable cabin enclosure. The airplane was known as the Airsport when flown without the cabin enclosure. The EC-1 was also available with a 100 hp (75 kW) Kinner K-5 engine.[9] One prototype is known, but more may have been produced.[9]
Data from www.aerofiles.com,[9] Jane's all the World's Aircraft 1928[10]
General characteristics- Crew: 2
- Length: 20 ft 11 in (6.38 m)
- Wingspan: 28 ft 2 in (8.59 m)
- Height: 7 ft 5 in (2.26 m)
- Wing area: 192 sq ft (17.8 m2)
- Empty weight: 870 lb (395 kg)
- Gross weight: 1,388 lb (630 kg)
- Powerplant: 1 × Anzani 6 cylinder two-row air-cooled radial piston engine, 80 hp (60 kW)
- Propellers: 2-bladed wooden fixed pitch propeller
Performance
- Maximum speed: 90 mph (140 km/h, 78 kn)
- Cruise speed: 80 mph (130 km/h, 70 kn)
- Stall speed: 30 mph (48 km/h, 26 kn)
- Range: 400 mi (640 km, 350 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 10,000 ft (3,000 m)
- Rate of climb: 590 ft/min (3.0 m/s)
- Wing loading: 7 lb/sq ft (34 kg/m2)
- Power/mass: 0.0576 hp/lb (0.0947 kW/kg)
- Fuel consumption: 5 gal/h (4.2 imp gal/h; 19 L/h)
- Oil consumption: 0.4 gal/h (0.33 imp gal/h; 1.5 L/h)
Elias EM
The Elias EM-1 was designed to meet a United States Marine Corps requirement for a multirole marine expeditionary aircraft. It was required to operate on either floats or wheels. The EM-1 was a tandem two-seat unequal-span biplane powered by a 300 hp (224 kW) Wright-Hispano H engine. The prototype was modified with equal-span wings and delivered to the Marine Corps in 1922. Six production aircraft were built (designated EM-2) having equal-span wings, being powered by 400 hp (298 kW) Liberty 12 inline engines.[7] One production aircraft was delivered to the United States Marine Corps and five to the United States Navy. One of the Navy aircraft was modified as an observation aircraft and redesignated EO-1. Variants include:
- EM-1: Prototype with a 300 hp (224 kW) Wright-Hispano H engine, one built.
- EM-2: Production aircraft with a 400 hp (298 kW) Liberty 12 inline engine, six built including one later converted to an EO-1.
- EO-1: One EM-2 aircraft converted as an observation aircraft.
Data from The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Aircraft
General characteristics- Crew: two
- Length: 28 ft 6 in (8.69 m)
- Wingspan: 39 ft 8 in (12.09 m)
- Height: 10 ft 9 in (3.28 m)
- Gross weight: 4,233 lb (1,920 kg)
- Powerplant: 1 × Liberty 12 inline piston engine , 400 hp (298 kW)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 120 mph (193 km/h, 100 kn)
Armament
- dorsal 0.3 inch machine gun
*Elias XNBS-3
The Elias XNBS-3 was a 1920s prototype biplane bomber built for the United States Army Air Corps. [11] The bomber had a steel tube fuselage and was powered by two 425 hp (317 kW) Liberty 12A piston engines.[11] It had a conventional landing gear with a tailskid and a crew of four. The prototype was designated XNBS-3 (XNBS=prototype night bomber short distance). On 13 August 1924 Lieutenant John A. Macready test piloted the Elias XNBS-3 twin engine bomber for the United States Army Air Corps at McCook Field in Dayton, Ohio. The XNBS-3 had New York to Chicago non-stop range and five machine guns for defense.[12] It was similar to the earlier Martin NBS-1 and was no real improvement, so it was not ordered into production.[13]
Data from [13] National Museum of the United States Air Force
General characteristics- Crew: four
- Length: 48 ft 5 in (14.76 m)
- Wingspan: 77 ft 6 in (23.63 m)
- Height: 16 ft 10 in (5.13 m)
- Gross weight: 14,427 lb (10,763 kg)
- Powerplant: 2 × Liberty 12A , 425 hp (317 kW) each
Performance
- Maximum speed: 101 mph (163 km/h, 88 kn)
- Range: 465 mi (748 km, 404 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 8,680 ft (2,650 m)
Armament
- 1692 lbs of bombs
- Five 0.30in machine-guns
*Elias TA-1
The Elias TA-1 was a 1920s American biplane training aircraft. Only three aircraft were built for evaluation by the United States Army Air Service. The TA-1 (a United States military designation Trainer, Aircooled No. 1) was designed to meet a United States Army requirement for a training aircraft for the air service. The TA-1 was a conventional two-seat biplane. Three were built, two with a Lawrance R-1 engine and another with an ABC Wasp, the last two under McCook field project numbers Elias P-178 and Elias P-179. The aircraft performance was inferior to the other aircraft under evaluation (the Dayton-Wright TA-3) and no orders were placed or further aircraft built.
Data from The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Aircraft (Part Work 1982-1985), 1985, Orbis Publishing, Page 1599
General characteristics- Crew: two
- Length: 24 ft 9 in (7.54 m)
- Wingspan: 32 ft 7 in (9.93 m)
- Powerplant: × Lawrance R-1 , 140 hp (104 kW)
Gallery
 Elias Airmobile
Elias Airmobile XNBS-3
XNBS-3 Elias Aircoupe left side Le Document aéronautique March,1929
Elias Aircoupe left side Le Document aéronautique March,1929 Elias Aircoupe 3-view drawing from Le Document aéronautique March,1929
Elias Aircoupe 3-view drawing from Le Document aéronautique March,1929 Elias EM-1
Elias EM-1
References
- "Experienced Cabinet Makers". The Buffalo Times--Page 17. July 22, 1925. Retrieved July 20, 2020.
- "M.A.A. Elects Officers and Directors". books.google.com. 1924. Retrieved July 25, 2020.
- "Coast-to-Coast Passenger Air Transport to be started". Evening Star--Front Page. Evening Star Wash,DC--Front Page. June 19, 1927. Retrieved July 25, 2020.
- "Elias, Director of Aircraft Board". The Buffalo Times--Page 2. September 27, 1924. Retrieved July 20, 2020.
- "Would Bring Air Races to Buffalo". The Buffalo Times--Page 2. September 30, 1925. Retrieved July 20, 2020.
- "Search results for: David Earle Dunlap". Niagaraaerospacemuseum.org. NAM. Retrieved July 20, 2020.
- "Elias EM". Aerofiles.com. Aerofiles. Retrieved July 20, 2020.
- Orbis 1985, p. 1599
- "American airplanes: Ea - Ew". www.aerofiles.com. May 2, 2009. Retrieved November 19, 2011.
- Grey, C.G., ed. (1928). Jane's all the World's Aircraft 1928. London: Sampson Low, Marston & company, ltd. p. 219c.
- Andrade 1979, p. 136
- "Elias Bomber". The Buffalo Times--Page 1. August 14, 1924. Retrieved July 20, 2020.
- "Elias XNBS-3". National Museum of the United States Air Force. Archived from the original on June 16, 2012. Retrieved June 11, 2010.
Bibliography
- The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Aircraft (Part Work 1982-1985). Orbis Publishing.
- John Andrade, U.S.Military Aircraft Designations and Serials since 1909, Midland Counties Publications, 1979, ISBN 0-904597-22-9 (Page 171)
- The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Aircraft (Part Work 1982–1985), 1985, Orbis Publishing