Glasgow, Dumfries and Carlisle Railway
The Glasgow, Dumfries and Carlisle Railway was a railway company in Scotland, which constructed the line from near Cumnock to Gretna Junction, forming the route from Glasgow to Carlisle via Dumfries, in association with other lines. Its promoters hoped it would form the only railway between central Scotland and England, but it lost out to rival companies.
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Locale | Scotland |
| Dates of operation | 13 August 1846–28 October 1850 |
| Successor | Glasgow and South Western Railway |
| Technical | |
| Track gauge | 4 ft 8+1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) |
Glasgow, Dumfries and Carlisle Railway | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
It opened in stages between 1846 and 1850, and on completion of its line it merged with the Glasgow, Paisley, Kilmarnock and Ayr Railway. The combined company took the name Glasgow & South Western Railway (G&SWR). The G&SWR formed an alliance with the English Midland Railway and for many years express passenger trains ran between Glasgow and London over the routes. The line is open today, continuing to form part of the Glasgow - Kilmarnock - Dumfries - Carlisle line; but that has diminished in importance and is now a secondary route. Passenger services are operated by ScotRail.
History
A line into Ayrshire, and later to England?
In the 18th century, tracked systems called plateways were constructed in areas of Scotland where minerals were extracted; the need was to convey the heavy product to a river or a harbour, in many cases over a relatively short distance, so that water-borne transport could take it to market. By 1830 the technology had progressed and railway lines using edge rails (in which the vehicle wheels, rather than the plate "rails" had flanges for guidance) became commonplace. The Monkland and Kirkintilloch Railway of 1826 may be regarded as the pioneer in showing the way forward.[1]
The Liverpool & Manchester Railway opened in 1830 and demonstrated that inter-city lines could be profitable, and that passenger carriage could be a prime source of business and not just an adjunct to mineral haulage. As railways in England began to develop into a network, business people in Scotland started to think not merely of internal railways, but of eventual connection with England. When the Grand Junction Railway was authorised in 1833, to link Birmingham (and therefore London) with Manchester, it was possible to consider that railways might soon link central Scotland and the south of England.
In 1835 a railway from Glasgow into Ayrshire was being actively promoted, and a survey to be commissioned from John Miller, and he proposed a route from to Ayr and Kilmarnock. There was a clear view that this could be the start of a line to Carlisle, there linking up with whatever English railway might reach that city. The line into Ayrshire received the royal assent on 15 July 1837, and was called the Glasgow, Paisley, Kilmarnock and Ayr Railway (GPK&AR).[2]
The company's first shareholders' meeting (while the line was still under construction) was told that "the Glasgow & Ayrshire Railway (GPK&AR) will at no very distant period form part of the great trunk line to England".
The GPK&AR opened its line to Ayr in 1840, and to Kilmarnock on 4 April 1843. However the process of construction had been difficult, and getting money from subscribers[note 1] had proved difficult due to the tight financial conditions prevailing; moreover other priorities arose for the company, in particular the building of branches in Ayrshire for tactical reasons: to discourage rival companies from entering the area that the GPK&AR considered its own. Accordingly, the idea of the GPK&AR extending to Carlisle took a lower priority.
It was not only the GPK&AR who considered making a trunk line southwards: a strong body of opinion considered that a route directly over the hills of the Southern Uplands was superior, with a shorter mileage. This became known as the proposed Annandale route to Carlisle, but Kilmarnock was not an ideal starting point to go that way. The GPK&AR's supporters intended a line from Kilmarnock via Dumfries, and this was the proposed Nithsdale route. Although longer, this had much easier gradients—at the time engine power was considered to be inadequate for a hillier route—and would go through more populous districts, bringing in more intermediate business; in addition it would be cheaper to build. Meanwhile, many people supported an east coast route that would reach England from Edinburgh by way of Dunbar and Berwick.[2][4]
Controversy over routes
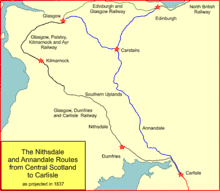
On 15 March 1841[note 2] a report[5] on the relative merits of the routes was submitted by two commissioners appointed by Parliament, Professor Peter Barlow (of the Royal Military Academy at Woolwich) and Sir Frederick Smith, the first Inspector-General of Railways for the Board of Trade. There were sixteen variations of proposed route; the Commissioners were frustrated that "the information supplied to us [by the respective promoters] has been very incomplete" and in fact they were unable to get detailed figures of costs and possible income for the Nithsdale route.
The commissioners took the view that only one Anglo-Scottish line was viable: "We are led to believe ... that the amount of traffic which ... may be expected, is not such a would be likely to afford an adequate return for the construction of two distinct lines of railway, the one from Darlington to Edinburgh, and the other from Lancaster to Glasgow."[6]
They declared that the Anandale route was to be preferred, but "the promoters must prove their bona fide intention to complete the English portion of the line, otherwise preference would be given to the East Coast route". However their report was not binding: it was hedged with numerous qualifications, and by no means closed the matter. In particular they stated that if they had considered two routes in Scotland practicable, they would have recommended the east coast route and the decidedly superior mechanical properties of the Nithsdale route might well have offset the greater length. In any case the railways in England did not yet extend north of Lancaster. The Commissioners' report had the effect of suspending the enthusiasm for cross-border railways for a period, and killing off a few fanciful schemes, but after three years when interest in such lines was resumed, the report was completely irrelevant.[1]
Definite proposals at last
So interest did resume, and on 9 March 1844 the provisional committee of the Glasgow & Carlisle Railway Company (GD&CR) met. There was considerable overlap in membership with the GPK&AR, and the latter helped out with the committee's expenses at first. A critical need was to generate promises of subscriptions, and to distinguish this proposal from the Annandale route (now being identified as the Caledonian Railway), which was also being heavily promoted once again: the name was soon changed to the Glasgow Dumfries and Carlisle Railway, reflecting also the interests of Dumfries and other more southerly subscribers. The capital would be £1.3 million.
This proposal went to Parliament as a Bill in the 1845 session, but so did the Caledonian scheme. Locomotive power had improved in the recent few years, so that the gradients over Annandale were less significant; and the Annandale route could fork as it reached northwards and serve Edinburgh as well as Glasgow. Parliament was still unwilling to sanction two major lines, and on 31 July 1845 the Caledonian Railway won the battle: its Annandale route received the Royal Assent. However, in the same session the GPK&AR got approval to extend southwards from Kilmarnock to Horsecleugh, south of the mining town of Old Cumnock.[2]
The supporters of the Nithsdale scheme did not give up, and resolved to try again in the 1846 session. They dissolved the original GD&CR and established a new one under the same name; the route would now join the Caledonian line at Gretna, rather than running independently to Carlisle. With several new branches added to the scheme, the capital was once again to be £1.3 million. However it emerged that the British and Irish Union Railway was proposing a line to connect Carlisle and Portpatrick, from where the short sea route to the north of Ireland started. The B&IUR planned to run between Dumfries and Carlisle, along an alignment that the GD&CR intended to use; the Caledonian Railway was also considering using this route. In fact in the 1846 session a huge number of railway schemes were being proposed, many of them fanciful, but most of them requiring attention to consider what strategies might be necessary to avoid loss of the GD&CR's own scheme.[2]
And finally, authorisation
Most of these schemes fell away when the financial bubble burst, and on 13 August 1846 the Glasgow Dumfries and Carlisle Railway was authorised. Disastrously, the Act gave the Caledonian Railway rights to a "perpetual lease" of the line between Gretna and Annan. The first ordinary meeting of shareholders took place on 8 September 1846, and it was agreed that an objective was eventual amalgamation with the GPK&AR. Money was desperately short, and contracts were let for construction of the main line beyond what funds were available to pay; the numerous branches included in the Act were still considered definite intentions, as was a long line from Dumfries to Portpatrick; there was no match between available money and the ambition of these schemes. The GPK&AR was running its own railway and making a good profit, and it was persuaded to buy up unissued GD&CR shares; immediate amalgamation was considered, but the GD&CR was too demanding in its terms and the idea was postponed.
Relations with the Caledonian Railway were more often hostile than friendly, and it was a considerable relief when the GD&CR obtained an Act on 9 June 1847 repealing the authorisation for the CR to lease the Gretna to Annan section.
Opening, in stages
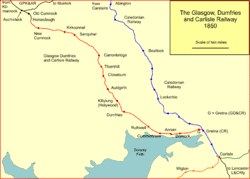
The GD&CR proceeded with construction contracts in a state of considerable financial difficulty, and on 21 August 1848 a special train for directors and their friends was run from Dumfries to Annan. The line opened to the public from Dumfries to Gretna on 23 August 1848; operation and provision of rolling stock was in the hands of the GPK&AR, who also underwrote any loss, or profit, on the operation. Running arrangements into Carlisle had not been finalised, so the passenger trains only ran as far as Gretna, from where passengers could change trains and continue in Caledonian Railway trains. At Dumfries the station was a temporary structure south of Annan Road.
On 15 October 1849, the line was opened from Dumfries to Closeburn, and on 20 May 1850, the final section was opened from Closeburn to Horsecleugh, where an end-on junction was made with the GPK&AR, which opened from Auchinleck to that point on the same day.[7] There was no station at Horsecleugh; it was probably an arbitrary boundary point. its location is thought to be at the Dumfries Road bridge.[8]
The authorising Acts of Parliament of 1846 and 1847 had confirmed that the GD&CR would merge with the GPK&AR on completion of the GD&CR line; in fact the GPK&AR as senior partner absorbed the GD&CR, and changed its name to the Glasgow & South Western Railway.[9]
On 28 October 1850 therefore, the Glasgow and South Western railway started its existence, and the GD&CR was dissolved.
The G&SWR
The new company had finally won its battle for a through line, though it had lost the race for primacy; the Caledonian Railway had a much shorter route to Glasgow and Edinburgh, and the North British Railway had been running through trains from Edinburgh to London on the east coast route via Berwick-upon-Tweed for two years.
On 26 June 1873 a line was opened from Barrhead to Kilmarnock, shortening the Glasgow to Kilmarnock run, and therefore the Glasgow to Carlisle run, considerably.
The new company needed an English partner to make a viable service to London, and eventually it found one, when the Midland Railway built its line to Carlisle, opening in 1875/6. From that time a firm alliance was formed, and express passenger trains to London ran over the Dumfries line and via Leeds on the Midland line, reaching London at St Pancras station.
The G&SWR expanded south-westward from Glasgow, where more traffic—mineral as much as passenger—was available than in the moorlands of Nithsdale.
The G&SWR continued in existence until the "grouping" of the main line railways in Great Britain, under the Railways Act 1921; the G&SWR, together with the Caledonian Railway, became constituents of the London, Midland & Scottish Railway (LMS).
In turn the LMS, together with other railways, was nationalised and the Scottish sections became British Railways, Scottish Region. The G&SWR lines retained a distinct informal identity through these changes, and the alliance with the old Midland Railway seemed to survive as well: a day train between Glasgow and St Pancras followed the G&SWR route and the Midland route; it was named the Thames-Clyde Express for most of its existence, ceasing to run in 1976. A night train with sleeping cars ran from Glasgow over the original route via Paisley and Dalry (to give Paisley a direct service) until the 1970s.
Now a secondary route, the line carries local passenger services operated by ScotRail; a moderate volume of freight also operates over the route.
Accident
On Sunday 14 August 1966, the previous evening's 22:10 Glasgow Central – London Euston consisting of five seating coaches, eight sleeping cars and two parcels vans hauled by EE Type 4 locomotive No. D311 crashed into a landslide between Sanquhar and Carrondale at 00:30. The loco and first ten coaches were derailed. None of the 270 passengers and four train crew were injured.[10]
Topography
The line opened from Dumfries (temporary station) to Gretna (Junction with the Caledonian Railway) on 23 August 1848. It was extended from Dumfries to Closeburn on 15 October 1849, and completed to Horsecleugh on 20 May 1850.
On 20 May 1850 the GD&CR ceased to exist, forming then part of the Glasgow and South Western Railway.
Stations on the line are shown below; events that took place after opening day are shown in italic.
- The line originated at Horsecleugh, an end-on junction with the Glasgow, Paisley, Kilmarnock and Ayr Railway; Horsecleugh was not a station;
- New Cumnock; closed on 6 December 1965; reopened 22 May 1991;
- Sanquhar; closed on 6 December 1965; reopened 27 June 1994;
- Carron Bridge; renamed Carronbridge 1 January 1871; closed on 7 December 1953;
- Thornhill; closed 6 December 1965 ;
- Closeburn; closed 11 September 1961;
- Auldgirth; closed 3 November 1952;
- Killylung; renamed Holywood on 28 October 1850; closed 26 September 1949;
- Racks; closed 6 December 1965;
- Dumfries; temporary station at first, relocated northwards in March 1859;
- Ruthwell; closed 6 December 1965;
- Cummertrees; closed 19 September 1955;
- Annan;
- Dornock; closed October 1854; reopened 2 January 1865; renamed Eastriggs 1 May 1923; closed 6 December 1965 ;
- Rigg; closed 1 November 1942;
- Gretna Green; closed 6 December 1965; reopened in a different location 20 September 1993;[11]
- The line terminated at Gretna Junction (not a station) with the Caledonian Railway.
Connections to other lines
- Glasgow, Paisley, Kilmarnock and Ayr Railway at Cumnock
- Ayr to Mauchline Branch at Cumnock
- Cairn Valley Railway at Cairn Valley Junction
- Castle Douglas and Dumfries Railway at Dumfries
- Dumfries, Lochmaben and Lockerbie Railway at Dumfries
- Solway Junction Railway at Annan
- Caledonian Railway Main Line at Gretna Junction
References
- C J A Robertson, The Origins of the Scottish Railway System, 1722 - 1844, John Donald Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh, 1983, ISBN 0-85976-088-X
- David Ross, The Glasgow and South Western Railway: A History, Stenlake Publishing Limited, Catrine, 2104, ISBN 978 1 84033 648 1
- Campbell Highet, The Glasgow and South Western Railway, The Oakwood Press, Lingfield, 1965
- Commission on Railway Communication between London, Dublin, Edinburgh and Glasgow, Third Report
- Barlow and Smith Report, quoted in Robertson, pages 278 - 282
- Stephenson Locomotive Society (SLS), The Glasgow and South Western Railway, 1850–1923, London, 1950
- Col M H Cobb, The Railways of Great Britain — A Historical Atlas, Ian Allan Publishing Limited, Shepperton, 2003, ISBN 07110 3003 0
- Glasgow and South Western Railway Incorporation Act, 1847, paraphrased in SLS
- Cooke, B.W.C., ed. (December 1966). "Rescue Work Rewarded: Four railwaymen share £300 gift from grateful passenger on derailed Anglo-Scottish express". Railway Magazine. Vol. 112, no. 788. pp. 686–688.
- R V J Butt, The Directory of Railway Stations, Patrick Stephens Limited, Sparkford, 1995, ISBN 1 85260 508 1
Notes
- Persons could subscribe to shares and only needed to pay a small percentage of the face value at once; in times when it seemed that easy profits were to be made from railway investments, many people made very ambitious subscriptions; in tighter money conditions later, they found themselves unwilling, or unable, to respond to calls for further sums due on the subscription.
- Highet says "in 1840" on page 15 but this refers to an interim report.
Sources
- Awdry, Christopher (1990). Encyclopaedia of British Railway Companies. Sparkford: Patrick Stephens Ltd. ISBN 1-8526-0049-7. OCLC 19514063. CN 8983.
- Butt, R. V. J. (October 1995). The Directory of Railway Stations: details every public and private passenger station, halt, platform and stopping place, past and present (1st ed.). Sparkford: Patrick Stephens Ltd. ISBN 978-1-85260-508-7. OCLC 60251199. OL 11956311M.
- Jowett, Alan (March 1989). Jowett's Railway Atlas of Great Britain and Ireland: From Pre-Grouping to the Present Day (1st ed.). Sparkford: Patrick Stephens Ltd. ISBN 978-1-85260-086-0. OCLC 22311137.
- Jowett, Alan (2000). Jowett's Nationalised Railway Atlas (1st ed.). Penryn, Cornwall: Atlantic Transport Publishers. ISBN 978-0-906899-99-1. OCLC 228266687.