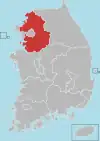
Gyeonggi Province
Gyeonggi Province (Korean: 경기도, Korean pronunciation: [kjʌ̹ŋ.ɡi.do̞]) is the most populous province in South Korea.
Gyeonggi Province
경기도 | |
|---|---|
| Korean transcription(s) | |
| • Hangul | 경기도 |
| • Hanja | 京畿道 |
| • Revised Romanization | Gyeonggi-do |
| • McCune‑Reischauer | Kyŏnggido |
 Flag Logo | |
 | |
| Coordinates: 37°30′N 127°15′E | |
| Country | |
| Region | Seoul Capital |
| Capital | Suwon |
| Subdivisions | 28 cities; 3 counties |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Kim Dong-yeon (Democratic) |
| • Legislature | Gyeonggi Assembly |
| Area | |
| • Total | 10,184 km2 (3,932 sq mi) |
| • Rank | 5th |
| Population (Census 2020) | |
| • Total | 13,511,676 |
| • Rank | 1st |
| • Density | 1,327/km2 (3,440/sq mi) |
| Provincial symbols | |
| • Flower | Forsythia |
| • Tree | Ginkgo |
| • Bird | Dove |
| Gross Regional Product (2020) | |
| • Total | KR₩491.3 trillion US$393.0 billion |
| ISO 3166 code | KR-41 |
| Dialect | Gyeonggi |
| Blog | Official blog |
| Website | Official website (English) |
Seoul, the nation's largest city and capital, is in the heart of the area but has been separately administered as a provincial-level special city since 1946. Incheon, the nation's third-largest city, is on the coast of the province and has been similarly administered as a provincial-level metropolitan city since 1981. The three jurisdictions are collectively referred to as Sudogwon and cover 11,730 km2 (4,530 sq mi), with a combined population of over 26 million - amounting to over half (50.25%) of the entire population of South Korea at the 2020 Census.
Etymology
Its name, Gyeonggi, means "京 (the capital) and 畿 (the surrounding area)". Thus, Gyeonggi-do can be translated as "Seoul and the surrounding areas of Seoul".
History
Gyeonggi-do has been a politically important area since 18 BCE, when Korea was divided into three nations during the Three Kingdoms period. Ever since King Onjo, the founder of Baekje (one of the three kingdoms), founded the government in Wiryeseong of Hanam, the Han River Valley was absorbed into Goguryeo in the mid-fifth century, and became Silla's territory in the year 553 (the 14th year of King Jinheung).[nb 1] Afterward, the current location of Gyeonggi-do, one of the nine states of Later Silla, was called Hansanju.
The Gyeonggi region started to rise as the central region of Goryeo as King Taejo of Goryeo (the kingdom following Silla) set up the capital in Gaesong. Since 1018 (the 9th year of Goryeo's King Hyeonjong), this area has been officially called "Gyeonggi".

During the Joseon, which was founded after the Goryeo, King Taejo of Joseon set the capital in Hanyang, while restructuring Gyeonggi's area to include Gwangju, Suwon, Yeoju, and Anseong, along with the southeast region. Since the period of King Taejong and Sejong the Great, the Gyeonggi region has been very similar to the current administrative area of Gyeonggi-do.
In 1895 the 23-Bu system, which reorganized administrative areas, was effected. The Gyeonggi region was divided into Hanseong (modern Seoul), Incheon, Chungju, Gongju, and Kaesong.
During the Japanese colonial period, Hanseong-bu was incorporated into Gyeonggi-do. On October 1, 1910, it was renamed Keijo and a provincial government was placed in Keijo according to the reorganization of administrative districts.
After liberation and the foundation of two separate Korean states, Gyeonggi-do and its capital, Seoul, were separated with partial regions of Gyeonggi-do being incorporated into Seoul thereafter in 1946. Additionally, Kaesong became North Korean territory, the only city to change control after the countries were divided at the 38th parallel, which is now part of North Korea's North Hwanghae Province.
In 1967 the seat of the Gyeonggi provincial government was transferred from Seoul to Suwon. After Incheon separated from Gyeonggi-do in 1981, Gyeonggi regions such as Ongjin County and Ganghwa County were incorporated into Incheon in 1995.
Geography
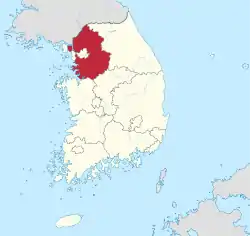
Gyeonggi Province is in the western central region of the Korean Peninsula, which is vertically situated in Northeast Asia and is between east longitude of 126 and 127, and north latitude of 36 and 38. Its dimension is 10% of Korea's territory, 10,171 square kilometres (3,927 sq mi).[2] It is in contact with 86 kilometres (53 mi) of cease-fire line to the north, 413 kilometres (257 mi) of coastline to the west, Gangwon-do to the east, Chungcheongbuk-do and Chungcheongnam-do to the south, and has Seoul, the capital of the Republic of Korea, in its center. Its provincial government is in Suwon, but some of its government buildings are in Uijeongbu for the administrative conveniences of the northern region.
Climate
The climate of Gyeonggi-do is the continental climate, which has a severe differentiation of temperature between summer and winter, and has distinctions of four seasons. Spring is warm, summer is hot and humid, autumn is cool, and winter is cold and snowy. The annual average temperature is between 11–13 °C (52–55 °F), where the temperature in the mountainous areas to the northeast is lower and the coastal areas to the southwest is higher. For January's average temperature, the Gyeonggi Bay is −4 °C (25 °F), the Namhangang (River) Basin is −4 to −6 °C (25 to 21 °F), and the Bukhangang (River) and Imjingang Basins are −6 to −8 °C (21 to 18 °F). It becomes colder and higher in temperature differentiation from coastal to inland areas. Summer has a lower local differentiation compared to winter. The inland areas are hotter than the Gyeonggi Bay area, the hottest area is Pyeongtaek, making the average temperature of August 26.5 °C (79.7 °F).
The annual average precipitation is around 1,100 millimetres (43 in), with a lot of rainfall. It is rainy in summer and dry during winter. The northeastern inland areas of Bukhangang and the upper stream of Imjingang has a precipitation of 1,300–1,400 millimetres (51–55 in), whereas the coastal area has only 900 millimetres (35 in) of precipitation.
Nature and national parks
The topography of Gyeonggi-do is divided into southern and northern areas by the Han River, which flows from east to west. The area north to the Han River is mainly mountainous, while the southern area is mainly plain.
The configuration of Gyeonggi-do is represented by Dong-go-seo-jeo (high in the east and low in the west), where the Gwangju Mountain Range and the Charyeong Mountain Range spreads from the east and drops in elevation in the west. The fields of Gimpo, Gyeonggi, and Pyeongtaek extend to the west.
Gyeonggi-do natural environment includes its rivers, lakes, mountains, and seas. Its representative rivers are the Hangang, Imjingang, and Anseongcheon Fg(Stream), which flow into the Yellow Sea, with Gyeonggi Plain, Yeonbaek Plain and Anseong Plain forming a fertile field area around the rivers. The Gwangju Mountain Range and the Charyeong Mountain Range stretch toward China in Gyeonggi Province. Most of the mountains that rise above 1,000 metres (3,300 ft), such as Myeongjisan (1,267 metres (4,157 ft)), Gukmangbong (1,168 metres (3,832 ft)) and Yongmunsan (1,157 metres (3,796 ft)) in the Gwangju Mountain Range. It iriidc Ktihas a developed granite area which, due to the granite's exfoliation effect, makes it full of strangely shaped cliffs and deep valleys. The Charyeong Mountain Range forms the boundary between Gyeonggi-do and Chungcheongbuk-do, but is a relatively low-altitude hilly area.
In Gyeonggi-do, there is Bukhansan National Park in Uijeongbu. For provincial parks, there are the Chukryeongsan Natural Recreation Area, Namhan-sanseong Provincial Park, Gapyeong Yeoninsan Provincial Park, and Mulhyanggi Arboretum. Besides the listed, the scenery of well-known mountains including Soyosan of Dongducheon City, Yongmunsan of Yangpyeong County, and Gwanaksan of Anyang and Gwacheon, along with Hangang and Imjingang are tourist sites of Gyeonggi-do.
- Moraksan, a 385-meter rock mountain.
Population
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1960 | 2,748,765 | — |
| 1980 | 3,703,761 | +1.50% |
| 1990 | 6,050,943 | +5.03% |
| 2000 | 8,984,134 | +4.03% |
| 2010 | 11,379,459 | +2.39% |
| 2015 | 12,479,061 | +1.86% |
| 2020 | 13,511,676 | +1.60% |
| Source: Citypopulation[3] | ||
Gyeonggi-do has shown a rapid increase in population due to the modernization and urbanization of the Republic of Korea. Its population has increased from 2,748,765 in 1960 to 3,703,761 in 1980; 6,050,943 in 1990; 8,984,134 in 2000; 11,379,459 in 2010; and 13,511,676 in 2020.
In 2010 there were 4,527,282 households, with an average of 3 people per family. There were 6,112,339 males and 5,959,545 females. The population density was 1,119 people/km2, almost double the national average of 486 people/km2.
Excluding the two metropolitan cities (Seoul and Incheon), the most heavily populated area as of 2010 is Suwon (1,104,681) followed by Goyang (1,076,179), Seongnam (996,524), Yongin (891,708), Bucheon (890,875) and Ansan (753,862). The lowest populated area in 2010 was Yeoncheon County (45,973), followed by Gapyeong County (59,916) and Yangpyeong County (72,595).
Economy
As the backbone of Seoul in the means of manufacturing complex, Gyeonggi-do is evenly developed in heavy industry (electronics, machine, heavy and chemical industry, steel), light industry (textile), and farm, livestock and fisheries industry. Due to the influence of recent high wages, the weight of manufacturing industries has decreased in Korea's economy. Gyeonggi-do is making efforts in many ways to improve and modernize the conventional industry structure, resulting in quick growth of innovative small and medium-sized enterprises such as U-JIN Tech Corp. Gyeonggi-do is unsparingly investing in the promotion of service industries related to soft competitive power such as state-of-the-art IT industry, designing, conventions and tourism, along with its great leap as a commercial hub in Northeast Asia using the Pyeongtaek Harbor.[4]
Besides this, it is known for its special local products such as Icheon rice and Icheon/Gwangju ceramics. Leading companies representing Korea, including Samsung Electronics' headquarters, SK Hynix's headquarters, NAVER's headquarters, Samsung SDI's headquarters, and Paju LG Corporation's LCD complex, are gathered in southern Gyeonggi Province, including Suwon City.[5]
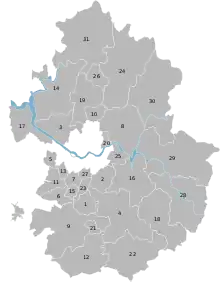
Administrative area

.JPG.webp)
Gyeonggi-do consists of 28 cities (special: 7, normal: 21) and three counties.[6] This is because many counties were elevated to city status owing to the influence of Seoul's new town development plan. Special cities are especially concentrated in the southern area of Gyeonggi-do.
Listed below is each entity's name in English, Hangul and Hanja.
| # | Name | Hangul | Hanja | Population (2015.5)[7] | Subdivisions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| — Special City — | |||||
| 1 | Suwon | 수원시 | 水原市 | 1,177,376 | 4 ilban-gu — 41 haengjeong-dong |
| 2 | Seongnam | 성남시 | 城南市 | 974,580 | 3 ilban-gu — 39 haengjeong-dong |
| 3 | Goyang | 고양시 | 高陽市 | 1,041,706 | 3 ilban-gu — 46 haengjeong-dong |
| 4 | Yongin | 용인시 | 龍仁市 | 968,346 | 3 ilban-gu — 1 eup, 6 myeon, 23 haengjeong-dong |
| 5 | Bucheon | 부천시 | 富川市 | 852,758 | 36 haengjeong-dong |
| 6 | Ansan | 안산시 | 安山市 | 704,765 | 2 ilban-gu — 24 haengjeong-dong |
| 7 | Anyang | 안양시 | 安養市 | 599,464 | 2 ilban-gu — 31 haengjeong-dong |
| 8 | Namyangju | 남양주시 | 南楊州市 | 640,579 | 5 eup, 4 myeon, 7 haengjeong-dong |
| 9 | Hwaseong | 화성시 | 華城市 | 565,269 | 4 eup, 10 myeon, 10 haengjeong-dong |
| — City — | |||||
| 10 | Uijeongbu | 의정부시 | 議政府市 | 431,149 | 15 haengjeong-dong |
| 11 | Siheung | 시흥시 | 始興市 | 393,356 | 17 haengjeong-dong |
| 12 | Pyeongtaek | 평택시 | 平澤市 | 453,437 | 3 eup, 6 myeon, 13 haengjeong-dong |
| 13 | Gwangmyeong | 광명시 | 光明市 | 346,888 | 18 haengjeong-dong |
| 14 | Paju | 파주시 | 坡州市 | 416,439 | 4 eup, 9 myeon, 7 haengjeong-dong |
| 15 | Gunpo | 군포시 | 軍浦市 | 288,494 | 11 haengjeong-dong |
| 16 | Gwangju | 광주시 | 廣州市 | 304,503 | 3 eup, 4 myeon, 3 haengjeong-dong |
| 17 | Gimpo | 김포시 | 金浦市 | 344,585 | 3 eup, 3 myeon, 6 haengjeong-dong |
| 18 | Icheon | 이천시 | 利川市 | 204,988 | 2 eup, 8 myeon, 4 haengjeong-dong |
| 19 | Yangju | 양주시 | 楊州市 | 203,519 | 1 eup, 4 myeon, 6 haengjeong-dong |
| 20 | Guri | 구리시 | 九里市 | 186,611 | 8 haengjeong-dong |
| 21 | Osan | 오산시 | 烏山市 | 207,596 | 6 haengjeong-dong |
| 22 | Anseong | 안성시 | 安城市 | 181,478 | 1 eup, 11 myeon, 3 haengjeong-dong |
| 23 | Uiwang | 의왕시 | 義王市 | 157,916 | 6 haengjeong-dong |
| 24 | Pocheon | 포천시 | 抱川市 | 155,629 | 1 eup, 11 myeon, 2 haengjeong-dong |
| 25 | Hanam | 하남시 | 河南市 | 155,752 | 12 haengjeong-dong |
| 26 | Dongducheon | 동두천시 | 東豆川市 | 97,407 | 8 haengjeong-dong |
| 27 | Gwacheon | 과천시 | 果川市 | 69,914 | 6 haengjeong-dong |
| 28 | Yeoju | 여주시 | 驪州市 | 110,560 | 1 eup, 8 myeon, 3 haengjeong-dong |
| — County — | |||||
| 29 | Yangpyeong | 양평군 | 楊平郡 | 106,445 | 1 eup, 11 myeon |
| 30 | Gapyeong | 가평군 | 加平郡 | 61,403 | 1 eup, 5 myeon |
| 31 | Yeoncheon | 연천군 | 漣川郡 | 45,314 | 2 eup, 8 myeon |
Claimed
Transportation
Gyeonggi-do's proximity to Seoul, South Korea's capital, and Incheon, its second-busiest port, has contributed to its extremely well-developed transportation infrastructure. It is close to both Incheon International Airport, South Korea's main international gateway and busiest airport, and Gimpo International Airport, its second-busiest airport. Use of water transportation from the harbor at Pyeongtaek is also high.
Road
The road pavement rate throughout the province averages 86.5 percent. The area has access to many of South Korea's expressways, including
- No. 1 Gyeongbu Expressway, Seoul–Busan
- No. 15 Seohaean Expressway, Seoul–Mokpo
- No. 35 Jungbu Expressway, Seoul–Tongyeong
- No. 37 Second Jungbu Expressway, Seoul–Yongin
- No. 45 Jungbu Naeryuk Expressway, Yeoju–Gimcheon
- No. 50 Yeongdong Expressway, Incheon–Gangneung
- No. 60 Seoul–Yangyang Expressway, Seoul–Chuncheon
- No. 100 Seoul Ring Expressway
- No. 110 Second Gyeongin Expressway, Incheon–Anyang
- No. 120 Gyeongin Expressway, Seoul–Incheon
- No. 130 Incheon International Airport Expressway, Incheon International Airport–Seoul
Rail
Gyeonggi-do is served by Korail commuter, standard and high-speed (KTX) services. It is home to Korea's first railroad, the Gyeongin Line, and includes portions of the Gyeongbu Line, Gyeongui Line, Jungang Line, and Honam Line. Gyeonggi has stations on the Suin, Bundang, Gyeongchun, and Shinbundang commuter rail services and the Gyeongbu and Honam High Speed Railways.
The area has numerous connections to the Seoul Metropolitan Subway system. Line 1 (formerly Korea National Railroad of Seoul) extends to Cheonan past Gyeonggi-do to the southwest, and to Dongducheon to the north. Line 3 connects to Goyang to the north, while Line 4 is connected to Gwacheon and Ansan to the southwest. Line 7 is connected to Uijeongbu to the north and Gwangmyeong to the south, while Line 8 is connected to Seongnam to the south.
Uijeongbu has its own light rail system, the U Line, which connects to Line 1.
A short section of the AREX line between Gimpo and Incheon airports passes through Gyeonggi, but there are no stops within the province.
Education
Gyeonggi-do is actively investing in education to foster a talented population suitable for the globalized economy. It is promoting the opening of local campuses of reputable universities as well as establishing special purpose high schools for high-quality education. It has also founded and operates at Paju the largest domestic "English village" for education in the English language, as well as villages in Ansan and Yangpyeong.
Universities of Gyeonggi Province
- National
- Anseong City
- Uiwang City
- Korea National University of Transportation (Uiwang Campus)
- Private
- Ansan City
- Anseong City
- Chung-Ang University (Anseong Campus)
- Anyang City
- Anyang University
- Sungkyul University
- Bucheon City
- Goyang City
- Gunpo City
- Gwangju City
- Seoul Jangsin University and Theological Seminary
- Hwaseong City
- Hyupsung University
- Shingyeong University
- Osan City
- Pochon City
- College of Medicine Pochon CHA University
- Daejin University
- Pyeongtaek City
- Pyongtaek University
- Seongnam City
- Siheung City
- Suwon City
- Ajou University
- Kyung Hee University
- Seoul National University (Gwanggyo Graduate School Campus)
- Sungkyungwan university (Natural Science Campus)
- Suwon Catholic University
- Suwon Science College
- Uijeongbu City
- Hanbuk University
- Yangpyeong County
- Yongin City
- Calvin University
- Dankook University
- Hankuk University of Foreign Studies (Global Campus)
- Kangnam University
- Kyung Hee University (International Campus)
- Luther University
- Myongji University (Science Departments Campus)
- Yongin University
Culture
Historical landmarks
Gyeonggi-do has long been a capital area, leaving many historic relics and ruins. For royal tombs (called reung), there are Donggureung of Guri, and Gwangreung, Hongreung and Yureung of Namyangju. For castles (called seong), there are Suwon Hwaseong, which is designated as the World Cultural Heritage, Namwonsanseong, Haengjusanseong, Ganghwasanseong, and Doksan Fortress. For Buddhist temples, there are many aged temples within Gyeonggi-do where one can experience 'temple stay'. You can view folk culture in the Korean Folk Village in Yongin, and the scene of Korea's division at Panmunjom in Paju.
Performing arts
Gyeonggi-do is investing a lot of money at a provincial level so that people do not have to go to Seoul to enjoy a high-class cultural life. There are performances at Gyeonggi Arts Center in Suwon as well as at Gyeonggi Korean Traditional Music Center in Yongin. Gyeonggi Provincial Museum in Yongin, Nam June Paik Art Center in Yongin, Gyeonggi Museum of Art in Ansan, and the Ceramics Museum in Gwangju are some of the facilities that are currently run by the province. There are also sightseeing opportunities at Jangheung Art Park, Publication Art Complex at Heyri, Paju, and the Icheon Ceramics Exposition.
Heyri Art Valley
Heyri Art Valley is Korea's largest art town. Various Korean artists constructed the cultural town of Heyri and it features several art galleries and museums; there are about 40 museums, exhibitions, concert halls and bookstores.
Religion
Religion in Gyeonggi-do (2005)[8]
According to the census of 2005, of the people of Gyeonggi-do 34.3% follow Christianity (21.9% Protestantism and 12.4% Catholicism) and 16.8% follow Buddhism.[8] 51.1% of the population is mostly not religious or follow indigenous religions.
Sports
The 2002 Korea-Japan World Cup matches were held in Suwon World Cup Stadium. As for the professional soccer teams with Gyeonggi-do as their home ground, there are the Suwon Samsung Bluewings and Seongnam FC.
Korea's foremost thoroughbred horse racing track Seoul Race Park is in Gwacheon.
Association football
- K League 1 (3)
- K League 2 (2)
- K3 League (5)
- K4 League (5)
- WK-League (2)
Baseball
Basketball
- KBL (2)
- WKBL (4)
- Yongin Samsung Life Blueminx
- Ansan Shinhan Bank S-Birds
- Guri KDB Life Winnus
- Bucheon KEB-Hana
Volleyball
- V-League Men (2)
- V-League Women (3)
- Suwon Hyundai Engineering & Construction Hillstate
- Seongnam Korea Expressway Hi-pass Zenith
- Hwaseong IBK Altos
Ice hockey
Football
- Anyang LG Cheetahs (1996–2003, Anyang → Seoul)
- Bucheon SK (1996–2005, Bucheon → Jeju)
- Bucheon FMC Best (2010, Dissolved)
- Ansan H FC
- Goyang KB Kookmin Bank
- Namyangju United
Basketball
- Suwon Samsung Thunders (1997–2001, Suwon → Seoul)
- Bucheon Shinsegae Coolcat (2006–2012, Dissolved)
Tourism
Entertainment
- Everland theme park in Yongin-si
- Korean Folk Village in Yongin-si
- Munhwa Broadcasting Corporation (MBC) Dramia at Cheoin-gu in Yongin-si; is the filming location of historical dramas such as Moon Embracing the Sun, Jumong, Queen Seondeok and Dong Yi. Viewing tours are available, which includes traditional folk games, historical court dress and archery.[9]
- Hallyuworld theme park, which is based on the 'Korean Fever', is under construction in Goyang
- Seoul Grand Park in Gwacheon, which has the Korea's National Museum of Contemporary Art and a zoo * ski and golf resorts
- Icheon Hot Spring
- LetsRunPark in Gwacheon[10]
- The place is also known among KPOP fans as popular global KPOP Star Jin, member of BTS is from this province.
Gourmet
Gyeonggi-do has long been famous for its Icheon rice, Yangpyeong Korean beef, Suwon cow ribs and Korean court cuisine, and marine delicacies made of fresh marine products from the west coast.
Festival
| Area | Festival Name | Period | Main Contents | Sponsor/Supervision |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Suwon | Hwaseong Cultural Festival | October | Great King Jeong Jo parade, Hwaryeongjeon Heondarae, re-presentation of the 60th birthday banquet of Hyekyeongung Hong, re-presentation of Kwageo (state examination during the Joseon Dynasty)
National housewife scenery festival, traditional flag game, culture and art festival, international food festival, drawing of Mars |
Suwon City, Hwaseong Cultural Festival Committee |
| KBS Drama Festival | August ~ October | KBS Magic, Studio Tour, digital image machinery, public broadcasting, reconstructions of historical dramas, national amateur image contest | Suwon City, KBS | |
| Seongnam | Seongnam Global Folk Art Festival | May | Global folk dancing, music and clothing festival with 400 performers from 12 countries participating | Seongnam/Gyeongpyeong International Co., Ltd. |
| Seongnam Cultural Art Festival | May~June, September~October | International / dance / music / play / movie festivals, art / picture exhibitions, citizen composition contest, citizen singing contest | Seongnam City, Seongnam Art Assembly and Members | |
| Moran 5-Day Folk Festival | April | Traditional folk art performances, reminiscent folk song stage, art performance of modern taste | Moran 5-Day Folk Festival Committee | |
| Seongnam Art Village Lotus Festival | July | Lotus and nature workbook exhibition, lotus food and local food corner | Lotus Festival Committee | |
| Anyang | Anyang Cultural Art Festival | Mid-May | Culture and art events such as art, music, dancing and plays | Anyang Cultural Center and Art Assembly Anyang Branch |
| Anyang Citizen Festival | October | Local festival full of things to see / play / buy / eat | Anyang City/Anyang Citizen Festival Committee | |
| Goyang | Goyang Haengju Cultural Festival | April | Seungjeon Street Parade, folk contest, Haengju Daecheop memorial services and rites | Goyang City/Goyang Cultural Center |
| Bucheon | Boksagol Art Festival | May | Student and citizen composition contest, street festival, image and picture subscription, art festival, citizen singing contest, dance contest, family musicals for children, play contest, music contest, citizen movie contest, citizen photography contest | Korea Art Assembly Bucheon Branch |
| Ansan | Danwon Art Festival (Kim Hong-do Festival) | September | Art Contest: art subscription contest, art appreciation classroom, street art contest
Ansan Kim Hong-do Festival: Danwon PR Hall, antique necessity products exhibition, yard play, art experience, traditional eateries |
Ansan City/Danwon Art Festival Committee |
| Byeolmangseong Art Festival | September | Byeolmangseong Festival, Byeolchomu performance, fireworks, teenager play festival, national music festival, other art events | Ansan City/Ansan Art Assembly | |
| Seongho Cultural Festival | May | Seongho admiration services, National Cultural Festival performances, Gyeonggi folk song choir performance, Seongho ideology academic contest, other events | Ansan City/Ansan Cultural Center | |
| Ansan Street Arts Festival[11] | May | Ansan Street Arts Festival is street arts gala as a part of performing arts, which started in 2005 at Ansan and held in every May. | Ansan City/Ansan Culture Square area | |
| Uijeongbu | Tongil Art Festival | June | Exhibition, traditional dance performance, Hanmaeum Citizen Singing Contest, composition contest, modern arts invitation | Art Assembly Uijeongbu Branch |
| Hoeryong Cultural Festival | October | Reproduction of royal parade, exhibition, dragon dance, yard drama | Uijeongbu Cultural Center | |
| Uijeongbu International Music Performance Festival | May | Overseas group invitation/performance, college student showcase event, exhibition | Uijeongbu Arts Center | |
| Namyangju | Dasan Cultural Festival | September~October | Awarding of Dasanmokmin Award, literature contest, traditional folk performance experience event | Namyangju City/Namyangju Cultural Center |
| Namyangju Outdoor Performance Festival | August | Invitation/performance of famous domestic/foreign performers, teenager get-together yard, experience event | Namyangju City | |
| Gwangmyeong | Gureum Mt. Art Festival | October | National Music Festival, art exhibition, painting exhibition, picture exhibition, composition contest, student music contest, play performance, National Music Contest | Art Assembly Gwangmyeong Branch/Respective Associations |
| Ori Cultural Festival | May | Lecture on the life and ideology of Lee Won-ik, yard games, picture drawing, musicals, shortened marathon, masque dance performance | Gwangmyeong Cultural Center | |
| Siheung | Mulwang Art Festival | May | National music yard festival, literature and art event, citizen singing contest | Art Assembly Siheung Branch/Siheung City Hall |
| Yeonseong Cultural Festival | October | Juvenile drama, composition contest, open concert, totem trimming and services | Siheung Cultural Center/Siheung City Hall | |
| Gunpo | Gunpo Citizen's Grand Festival | April | Masquerade parade, street exhibition, village concert, silver festival, photography contest | Gunpo Cultural Information Department |
| Cheoljjuk Dongsan Festival | April | Exhibitions and concerts | ||
| Guri | Guri Han River Rape Flower Festival | May | Fly away butterflies, concerts, citizen singer contests, art, writing contest, photography contest, teenager rock concert | Guri/Korea Art Assembly Guri Branch |
| Guri Cosmos Festival | September | Eve celebration, Chinese arts circus, open-air movie appreciation, smiling picture photography, experience events | Guri/Korea Art Assembly Guri Branch | |
| Hanam | Hanam Iseong Cultural Festival | September | Public broadcast attraction, provincial troupe performance, citizen performance, citizen participation yard | Hanam City Hall/Hanam Cultural Center |
| Uiwang | Uiwang Baekwun Art Festival | October | Walking on old street in Uiwang, I am an Artist Events: composition contest, sketch contest, fairy tale recital, puppet show, scenery games, making traditional toys, guitar performance | Uiwang Baekwun Art Festival Committee |
| Anseong | Anseong Namsadang Bawudeogi Festival | September | Art and science contest, taffy seller play, masque performance, tightrope walking performance, Baudeoki PR Hall, wayfaring male entertainer play of 6 yards, street play, general play, yard play, folk market and cattle market remake | Anseong |
| Anseong Juksan International Art Festival | June | Dance, music, creative performance, Avantgarde Exhibition with globally famous artists, make-your-own-product with artists, film contest | Smile Stone Co., Ltd. | |
| Juksan Children Festival | May | For-children performance twice a day, experience | Festival Troupe Mucheon | |
| Yangju | Yangju Traditional Culture and Art Festival | May | Intangible cultural assets and traditional folk art performance | Yangju Festival Committee |
| Yangju Cultural Festival | October | Traditional folk art performance and participation event, unit event | ||
| Osan | Doksanseong Culture and Art Festival | September | Art events such as culture event performance, citizen participation yard | Osan City/Osan Cultural Center |
| Yeoju | Sejong Cultural Grand Feast | October | Resident concert, Hangeul writing contest, empress travel, exhibitions, national picture subscription | Yeoju City, Yeoju Cultural Center
Art Assembly Yeoju Branch |
| Yeoju Ceramics Exposition | May | Ceramics sales event, igniting of traditional oven, exhibition/performance event and experience event | Yeoju, Yeoju Ceramics Exposition | |
| Yeoju Artifact Exhibition | October | Farm products exhibition, outstanding product sales, international sweet potato cooking contest, farming experience event (sweet potato tour) | Yeoju Artifact Exhibition Committee
Yeoju Agricultural Technology Center | |
| Myeongseong
Empress Anniversary |
October | Yeongsan memorial services, hyewon exorcism | Yeoju City, Yeoju Cultural Center | |
| Paju | Yulgok Cultural Festival | September | Chuhyang ritual at Jawun Auditorium, art and science symposium, reconstruction of Confucian parade, Yulgok and Chinese poem writing contest, native writer invitation, calligraphy contest | Paju City/Paju Cultural Center |
| Paju Children Book Hanmadang | October | Publications exhibition and sales, book culture hanmadang, seminar games hanmadang, experience & study | Paju City, Paju Publication Complex | |
| Heyri Festival | October | Art and plastic product exhibition at Heyri Village, construction tourism, performance, percussion, dance, play, classic jazz, workshop classrooms | Paju City, Paju Construction Committee, Heyri Festival Committee | |
| Paju Art Festival | May | Music performance, national music performance, literature seminar, literary writing contest, art association member exhibition | Paju City/Paju Art Assembly | |
| Dongducheon | Dongducheon Rock Festival | August | Multi-day concert event featuring local, national, and international rock music performances. | Dongducheon, Soyosan Tourist Resort |
Partition proposal
Sisterhood relations
 Utah, United States
Utah, United States Aichi Prefecture, Japan[12]
Aichi Prefecture, Japan[12] Kanagawa Prefecture, Japan
Kanagawa Prefecture, Japan Liaoning, People's Republic of China
Liaoning, People's Republic of China North Holland, Netherlands
North Holland, Netherlands Gauteng, South Africa
Gauteng, South Africa State of Mexico, Mexico
State of Mexico, Mexico Virginia, United States
Virginia, United States Alto Paraná Department, Paraguay
Alto Paraná Department, Paraguay.svg.png.webp) Queensland, Australia
Queensland, Australia Catalonia, Spain
Catalonia, Spain Florida, United States
Florida, United States Guangdong, People's Republic of China
Guangdong, People's Republic of China.svg.png.webp) British Columbia, Canada
British Columbia, Canada Hebei, People's Republic of China
Hebei, People's Republic of China Shandong, People's Republic of China
Shandong, People's Republic of China Taiwan Province, Republic of China (Taiwan)
Taiwan Province, Republic of China (Taiwan) Pahang, Malaysia
Pahang, Malaysia
References
- "2021년 지역소득(잠정)".
- 위치와 자연환경 (in Korean). Gyeonggi Province. Archived from the original on 1 March 2014. Retrieved 18 March 2013.
- "South Korea: Provinces". Archived from the original on 2022-03-21. Retrieved 2022-03-12.
- "평택시, 정부에 평택항 경쟁력 강화 방안 건의". m.hankooki.com (in Korean). 2021-02-20. Retrieved 2021-02-20.
- "현대차 삼성SDI 시총 7위 경쟁 치열…네이버·카카오 가세". 이데일리 (in Korean). 2021-02-03. Archived from the original on 2021-02-12. Retrieved 2021-02-20.
- "Administrative Map". Gyeonggi Province. Archived from the original on 13 April 2013. Retrieved 22 March 2013.
- "Population". Gyeonggi Province. Archived from the original on 3 March 2011. Retrieved 22 March 2013.
- 2005 Census - Religion Results Archived 2015-09-04 at the Wayback Machine
- Lee, Cin Woo (16 March 2012). "Beyond Seoul: 19 reasons to explore Korea". CNN Go. Archived from the original on 21 April 2012. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- "KRA | RACING | Life and Love KRA". www.kra.co.kr. Archived from the original on 2019-01-03. Retrieved 2018-05-10.
- "ANSAN STREET ARTS FESTIVAL 2018". www.ansanfest.com. Archived from the original on 2018-05-10. Retrieved 2018-05-10.
- ベルギー3地域と「友好交流及び相互協力に関する覚書」を締結 (in Japanese). Government of Aichi Prefecture. Archived from the original on 28 August 2017. Retrieved 15 May 2017.
Notes
- In traditional Korean timekeeping, years are tracked by reign of monarchs. Today, this is practiced in addition to Common Era (CE).
External links
- Official website (in English)
- Official blog (in English)
- Invest in Gyeonggi Province – English
- Gyeonggi Tourism Guide – English
- DMZ – English
- KINTEX – English Archived 2012-10-11 at the Wayback Machine
- Goyang City Hall

.jpg.webp)