Höchstädt an der Donau
Höchstädt an der Donau is a town in the district of Dillingen, Bavaria, Germany. It is situated near the banks of the Danube. It consists of the following suburbs: Höchstädt an der Donau, Deisenhofen, Oberglauheim, Schwennenbach and Sonderheim. The town is the seat of the municipal association Höchstädt an der Donau, which includes the towns Blindheim, Finningen, Lutzingen and Schwenningen.
Höchstädt an der Donau | |
|---|---|
 Höchstädt Castle | |
 Coat of arms | |
Location of Höchstädt an der Donau within Dillingen district 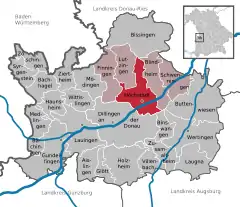 | |
 Höchstädt an der Donau  Höchstädt an der Donau | |
| Coordinates: 48°36′N 10°33′E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Bavaria |
| Admin. region | Schwaben |
| District | Dillingen |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2018–24) | Gerrit Maneth[1] (FW) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 37.45 km2 (14.46 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 416 m (1,365 ft) |
| Population (2022-12-31)[2] | |
| • Total | 7,014 |
| • Density | 190/km2 (490/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| Postal codes | 89420 |
| Dialling codes | 09074 |
| Vehicle registration | DLG |
| Website | www.hoechstaedt.de |
In the fifteenth and sixteenth century, the wealthy mercantile family Höchstetter, which came from the town, was part of the mercantile patriciate of Augsburg.
In the early 18th century, the town was the site of two battles. The First Battle of Höchstädt (German: Erste Schlacht von Höchstädt) on 20 September 1703 cost over 5,000 lives. A year later in 1704, the Battle of Blenheim or Second Battle of Höchstädt (German: Zweite Schlacht von Höchstädt) occurred between the British and Austrian forces (led by John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough and Prince Eugene of Savoy) on one side, and Bavarian and French troops (commanded by Maximilian II Emanuel, Elector of Bavaria, and the Comte de Tallard) on the other side.
The carnage of the Battle of Blenheim was so horrific (over 20,000 men died at the end of the day) that farmers are said to still dig up skulls from the fields today, as described in the poem "After Blenheim", written by Robert Southey, which tells about children finding the skull of one of the "... many thousand men, said he, Were slain in that great victory."[3]
In June 1800, the armies of the French First Republic, under command of Jean Victor Moreau, fought Austrian regulars and Württemberg contingents, under the general command of Pál Kray. Kray had taken refuge in the fortress at Ulm; Moreau diverted his army to approach Ulm from the east and, after a small group of men captured a foothold on the northern bank of the Danube, his forces were able to move against the fortress on both sides of the river. At this battle, the culmination of the Danube Campaign of 1800, Moreau forced Kray to abandon Ulm and withdraw into eastern Bavaria.[4]
References
- Liste der ersten Bürgermeister/Oberbürgermeister in kreisangehörigen Gemeinden, Bayerisches Landesamt für Statistik, accessed 19 July 2021.
- Genesis Online-Datenbank des Bayerischen Landesamtes für Statistik Tabelle 12411-003r Fortschreibung des Bevölkerungsstandes: Gemeinden, Stichtag (Einwohnerzahlen auf Grundlage des Zensus 2011)
- Robert Southey, Minor Poems: Battle of Blenheim. Longmans, Hurst, Rees, Orme, and Brown, 1823, pp. 167-172, p. 168 cited.
- "Höchstädt", History of the Wars of the French Revolution: Including Sketches of the Civil History of Great Britain and France, from the Revolutionary Movements, 1788, to the Restoration of a General Peace, 1815, Kuhl, France, 1820, p. 183.
