HMS Immortalité (1887)
HMS Immortalité was one of seven Orlando-class armoured cruisers built for the Royal Navy in the mid-1880s. She was sold for scrap on 11 January 1907.
.jpg.webp) HMS Immortalité | |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name | HMS Immortalité |
| Namesake | The French word for immortality |
| Builder | Chatham Dockyard |
| Laid down | 18 January 1886 |
| Launched | 7 June 1887 |
| Fate | Sold for breaking up, 11 January 1907 |
| General characteristics | |
| Class and type | Orlando-class armoured cruiser |
| Displacement | 5,535 long tons (5,624 t) |
| Length | 300 ft (91.4 m) (p/p) |
| Beam | 56 ft (17.1 m) |
| Draught | 24 ft (7.3 m) |
| Installed power | |
| Propulsion |
|
| Speed | 18 kn (33 km/h; 21 mph) |
| Range | 8,000 nmi (15,000 km; 9,200 mi) at 10 knots (19 km/h; 12 mph) |
| Complement | 484 |
| Armament |
|
| Armour |
|
Design and description
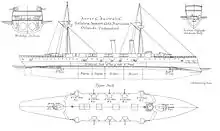
Immortalité had a length between perpendiculars of 300 feet (91.4 m), a beam of 56 feet (17.1 m) and a draught of 24 feet (7.3 m). Designed to displace 5,040 long tons (5,120 t), all of the Orlando-class ships proved to be overweight and displaced approximately 5,535 long tons (5,624 t). The ship was powered by a pair of three-cylinder triple-expansion steam engines, each driving one shaft, which were designed to produce a total of 8,500 indicated horsepower (6,300 kW) and a maximum speed of 18 knots (33 km/h; 21 mph) using steam provided by four boilers with forced draught. The ship carried a maximum of 900 long tons (910 t) of coal which was designed to give her a range of 8,000 nautical miles (15,000 km; 9,200 mi) at a speed of 10 knots (19 km/h; 12 mph). The ship's complement was 484 officers and ratings.[1]
Immortalité's main armament consisted of two breech-loading (BL) 9.2-inch (234 mm) Mk V guns, one gun fore and aft of the superstructure on pivot mounts. Her secondary armament was ten BL 6-inch (152 mm) guns, five on each broadside. Protection against torpedo boats was provided by six quick-firing (QF) 6-pounder Hotchkiss guns and ten QF 3-pounder Hotchkiss guns, most of which were mounted on the main deck in broadside positions. The ship was also armed with six 18-inch (457 mm) torpedo tubes: four on the broadside above water and one each in the bow and stern below water.[1]
The ship was protected by a waterline compound armour belt 10 inches (254 mm) thick. It covered the middle 200 feet (61.0 m) of the ship and was 5 feet 6 inches (1.7 m) high.[1] Because the ship was overweight, the top of the armour belt was 2 feet (0.61 m) below the waterline when she was fully loaded.[2] The ends of the armour belt were closed off by transverse bulkheads 16 inches (406 mm). The lower deck was 2–3 inches (51–76 mm) thick over the full length of the hull. The conning tower was protected by 12 inches (305 mm) of armour.[1]
Construction and service
_firing_salute.jpg.webp)
Immortalité, named for the French frigate Immortalité captured in 1798,[3] was laid down on 18 January 1886 by Chatham Royal Dockyard. The ship was launched on 7 June 1887, and completed in July 1889.[4]
In March 1900 she had successful machinery trials in the North Sea, and was transferred to the A division of the Medway Fleet Reserve.[5] She was commissioned at Chatham on 21 May 1901 by Captain Sackville Carden as seagoing tender to the Wildfire, flagship at Sheerness.[6] She took part in the fleet review held at Spithead on 16 August 1902 for the coronation of King Edward VII,[7] and two months later Captain Archibald Peile Stoddart succeeded Carden in command on 16 October 1902.[8]
Notes
- Chesneau & Kolesnik, p. 65
- Friedman, p. 146
- Silverstone, p. 242
- Lyon & Winfield, p. 269
- "Naval & Military intelligence". The Times. No. 36083. London. 7 March 1900. p. 10.
- "Naval & Military intelligence". The Times. No. 36461. London. 22 May 1901. p. 10.
- "The Coronation - Naval Review". The Times. No. 36845. London. 13 August 1902. p. 4.
- "Naval & Military intelligence". The Times. No. 36906. London. 23 October 1902. p. 5.
References
- Chesneau, Roger & Kolesnik, Eugene M., eds. (1979). Conway's All the World's Fighting Ships 1860–1905. Greenwich, UK: Conway Maritime Press. ISBN 0-8317-0302-4.
- Friedman, Norman (2012). British Cruisers of the Victorian Era. Barnsley, South Yorkshire, UK: Seaforth. ISBN 978-1-59114-068-9.
- Lyon, David; Winfield, Rif (2004). The Sail & Steam Navy List. London: Chatham Publishing. ISBN 1-86176-032-9.
- Silverstone, Paul H. (1984). Directory of the World's Capital Ships. New York: Hippocrene Books. ISBN 0-88254-979-0.