Hachimantai, Iwate
Hachimantai (八幡平市, Hachimantai-shi) is a city located in Iwate Prefecture, Japan. As of 1 April 2020, the city had an estimated population of 25,076, and a population density of 29 persons per km2 in 10,531 households.[1] The total area of the city is 862.30 square kilometres (332.94 sq mi).
Hachimantai
八幡平市 | |
|---|---|
City | |
 Hachimantai City Hall | |
 Flag  Seal | |
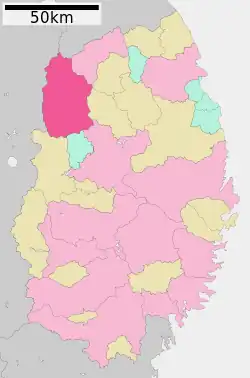 Location of Hachimantai in Iwate Prefecture | |
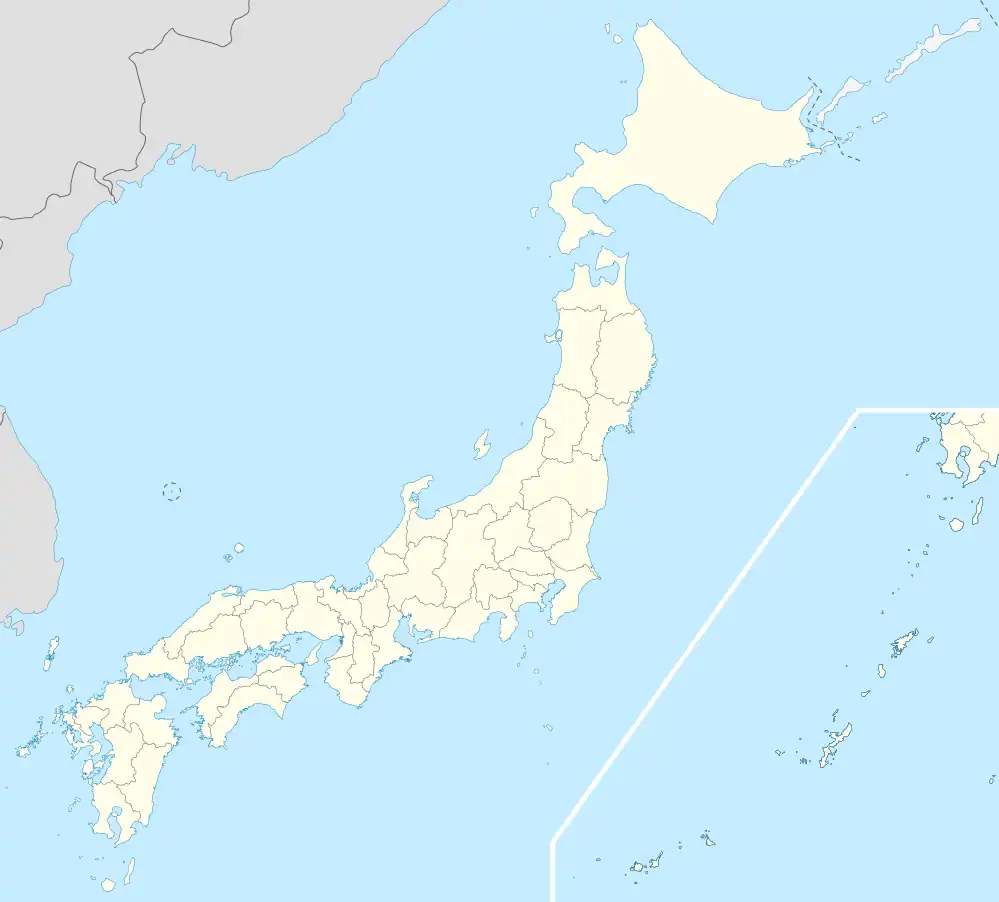 Hachimantai | |
| Coordinates: 39°57′22″N 141°4′16″E | |
| Country | Japan |
| Region | Tōhoku |
| Prefecture | Iwate |
| Area | |
| • Total | 862.30 km2 (332.94 sq mi) |
| Population (April 1, 2020) | |
| • Total | 25,076 |
| • Density | 29/km2 (75/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+9 (Japan Standard Time) |
| Phone number | 0195-76-2111 |
| Address | 62 Ōfuke dai-35 jiwari, Hachimantai-shi, Iwate-ken 028-7192 |
| Climate | Dfa |
| Website | Official website |
| Symbols | |
| Bird | Copper pheasant |
| Flower | Rindo |
| Tree | Japanese red pine |

Geography
Hachimantai is located in the Ōu Mountains of far northwest Iwate Prefecture, bordered by Aomori Prefecture to the north and Akita Prefecture to the west. The headwaters of the Yoneshiro River are in Hachimanai. Part of Mount Hachimantai and Mount Iwate are within its borders. Parts of the city are within the borders of the Towada-Hachimantai National Park. Mount Iwate, the highest mountain in Iwate Prefecture, is on the border of Hachimantai with Shizukuishi and Takizawa.
Neighboring municipalities
Aomori Prefecture
Akita Prefecture
Iwate Prefecture
Climate
Hachimantai has a humid continental climate (Köppen climate classification Dfa), the same as much of Hokkaido to the north, characterized by warm to hot summers and cold winters with heavy snowfall. The average annual temperature in Hachimantai is 9.3 °C. The average annual rainfall is 1387 mm with September as the wettest month and February as the driest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 22.9 °C, and lowest in January, at around -3.4 °C.[2]
| Climate data for Hachimantai[lower-alpha 1] (1991−2020 normals, extremes 1976−present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 12.4 (54.3) |
12.2 (54.0) |
19.9 (67.8) |
28.8 (83.8) |
32.6 (90.7) |
33.5 (92.3) |
35.2 (95.4) |
35.7 (96.3) |
34.0 (93.2) |
27.8 (82.0) |
20.7 (69.3) |
16.9 (62.4) |
35.7 (96.3) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 0.8 (33.4) |
1.9 (35.4) |
6.2 (43.2) |
13.5 (56.3) |
19.8 (67.6) |
23.6 (74.5) |
26.6 (79.9) |
27.7 (81.9) |
23.4 (74.1) |
17.1 (62.8) |
10.0 (50.0) |
3.4 (38.1) |
14.5 (58.1) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −3.1 (26.4) |
−2.5 (27.5) |
1.4 (34.5) |
7.6 (45.7) |
13.8 (56.8) |
18.0 (64.4) |
21.6 (70.9) |
22.5 (72.5) |
18.1 (64.6) |
11.4 (52.5) |
5.0 (41.0) |
−0.4 (31.3) |
9.4 (48.9) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −7.9 (17.8) |
−7.6 (18.3) |
−3.7 (25.3) |
1.4 (34.5) |
7.8 (46.0) |
13.0 (55.4) |
17.5 (63.5) |
18.3 (64.9) |
13.3 (55.9) |
5.8 (42.4) |
0.1 (32.2) |
−4.5 (23.9) |
4.5 (40.1) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −21.8 (−7.2) |
−22.2 (−8.0) |
−15.4 (4.3) |
−11.0 (12.2) |
−2.7 (27.1) |
1.7 (35.1) |
7.7 (45.9) |
7.7 (45.9) |
1.3 (34.3) |
−4.3 (24.3) |
−11.0 (12.2) |
−18.0 (−0.4) |
−22.2 (−8.0) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 42.5 (1.67) |
41.7 (1.64) |
66.7 (2.63) |
65.0 (2.56) |
75.8 (2.98) |
87.4 (3.44) |
154.5 (6.08) |
158.3 (6.23) |
149.1 (5.87) |
100.5 (3.96) |
75.4 (2.97) |
67.1 (2.64) |
1,076.8 (42.39) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 122 (48) |
108 (43) |
60 (24) |
5 (2.0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
10 (3.9) |
90 (35) |
392 (154) |
| Average rainy days | 10.9 | 9.9 | 11.2 | 9.9 | 9.8 | 8.7 | 11.6 | 10.7 | 11.2 | 10.9 | 12.5 | 12.8 | 130.1 |
| Average snowy days | 16.0 | 13.8 | 7.2 | 0.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.4 | 10.8 | 49.9 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 82.7 | 88.1 | 139.0 | 173.7 | 187.9 | 152.5 | 118.3 | 135.8 | 128.1 | 131.4 | 102.6 | 75.1 | 1,515.9 |
| Source 1: JMA[3] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: JMA[4] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Arayashimmachi, Hachimantai (1991−2020 normals, extremes 1976−present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 12.3 (54.1) |
13.5 (56.3) |
18.5 (65.3) |
28.1 (82.6) |
32.3 (90.1) |
33.4 (92.1) |
34.1 (93.4) |
35.0 (95.0) |
32.9 (91.2) |
28.6 (83.5) |
21.2 (70.2) |
16.2 (61.2) |
35.0 (95.0) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 0.2 (32.4) |
1.2 (34.2) |
5.3 (41.5) |
12.7 (54.9) |
19.0 (66.2) |
22.6 (72.7) |
25.5 (77.9) |
26.7 (80.1) |
22.7 (72.9) |
16.5 (61.7) |
9.5 (49.1) |
2.8 (37.0) |
13.7 (56.7) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −3.2 (26.2) |
−2.6 (27.3) |
0.8 (33.4) |
6.9 (44.4) |
13.2 (55.8) |
17.3 (63.1) |
20.9 (69.6) |
21.9 (71.4) |
17.6 (63.7) |
11.0 (51.8) |
4.9 (40.8) |
−0.7 (30.7) |
9.0 (48.2) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −7.6 (18.3) |
−7.2 (19.0) |
−4.1 (24.6) |
1.2 (34.2) |
7.3 (45.1) |
12.5 (54.5) |
17.1 (62.8) |
18.0 (64.4) |
13.2 (55.8) |
5.9 (42.6) |
0.4 (32.7) |
−4.4 (24.1) |
4.4 (39.8) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −20.1 (−4.2) |
−20.8 (−5.4) |
−18.4 (−1.1) |
−12.4 (9.7) |
−3.1 (26.4) |
2.0 (35.6) |
6.7 (44.1) |
7.1 (44.8) |
0.2 (32.4) |
−3.4 (25.9) |
−11.4 (11.5) |
−17.7 (0.1) |
−20.8 (−5.4) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 60.9 (2.40) |
53.1 (2.09) |
72.0 (2.83) |
66.9 (2.63) |
76.6 (3.02) |
95.9 (3.78) |
171.4 (6.75) |
175.3 (6.90) |
157.8 (6.21) |
119.3 (4.70) |
93.3 (3.67) |
90.8 (3.57) |
1,235.4 (48.64) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 15.8 | 14.3 | 13.9 | 11.8 | 10.8 | 9.8 | 12.0 | 12.2 | 12.2 | 12.9 | 14.7 | 16.4 | 156.8 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 62.1 | 78.4 | 122.8 | 167.6 | 184.6 | 158.1 | 124.8 | 149.6 | 137.7 | 137.2 | 100.2 | 63.3 | 1,486.3 |
| Source: JMA[5][6] | |||||||||||||
- Notes
- former Matsuo Village, now Matsuo-Hachimantai Station
Demographics
Per Japanese census data,[7] the population of Hachimantai peaked at around the year 1960 and has declined steadily over the past 60 years.
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1920 | 21,815 | — |
| 1930 | 27,328 | +25.3% |
| 1940 | 36,316 | +32.9% |
| 1950 | 47,852 | +31.8% |
| 1960 | 53,806 | +12.4% |
| 1970 | 36,764 | −31.7% |
| 1980 | 34,926 | −5.0% |
| 1990 | 33,287 | −4.7% |
| 2000 | 32,485 | −2.4% |
| 2010 | 28,690 | −11.7% |
| 2020 | 24,023 | −16.3% |
History
The area of present-day Hachimantai was part of ancient Mutsu Province. The area was dominated by the Nanbu clan from the early Muromachi period. During the Edo period Tokugawa shogunate, the area was under Morioka Domain, and was divided between Ninohe District in the north and Iwate District in the south.
In the early Meiji period, the village of Arasawa was created within Ninohe District on April 1, 1889, with the establishment of the modern municipalities system. Arasawa merged with neighboring Tayama Village on September 30, 1956, to form the town of Ashiro. Ashiro was transferred to Iwate District on April 1, 2002.
Likewise, on April 1, 1889, the villages of Tairadate, Obun, Dendo and Terada were established within Kita-Iwate District. Kita-Iwate was merged with Minami-Iwate in 1896. The four villages merged on September 30, 1956, for form the town of Nishine.
The city of Hachimantai was established on September 1, 2005, from the merger of the towns of Ashiro and Nishine, and the village of Matsuo.
Government
Hachimantai has a mayor-council form of government with a directly elected mayor and a unicameral city legislature of 22 members. Hachimantai, together with the towns of Iwate and Kuzumaki contribute two seats to the Iwate Prefectural legislature. In terms of national politics, the city is part of Iwate 2nd district of the lower house of the Diet of Japan.
Economy
The local economy is based on agriculture, forestry and seasonal tourism.
Education
Hachimantai has ten public elementary schools and four public middle schools operated by the city government, and one public high school operated by the Iwate Prefectural Board of Education.
Transportation
Railway
![]() East Japan Railway Company (JR East) - Hanawa Line
East Japan Railway Company (JR East) - Hanawa Line
- Higashi-Ōbuke - Ōbuke - Tairadate - Kitamori - Matsuo-Hachimantai - Appi-Kōgen - Akasakata - Koyanohata - Arayashimmachi - Yokoma - Tayama - Anihata
Highway
 Tōhoku Expressway – Nishine IC, Iwatesan SA, Matsuo-Hachimantai IC, Maemoriyama PA, Ajiro JCT, Ajiro IC, Tayama PA
Tōhoku Expressway – Nishine IC, Iwatesan SA, Matsuo-Hachimantai IC, Maemoriyama PA, Ajiro JCT, Ajiro IC, Tayama PA Hachinohe Expressway – Ajiro JCT
Hachinohe Expressway – Ajiro JCT National Route 282 – Nishine roadside station
National Route 282 – Nishine roadside station
Sister cities
 Miyako, Iwate – from October 1, 1986
Miyako, Iwate – from October 1, 1986 Nago, Okinawa – from January 28, 1988
Nago, Okinawa – from January 28, 1988 Altenmarkt, Salzburg, Austria, friendship city from November 13, 1994, with former Matsuo Village
Altenmarkt, Salzburg, Austria, friendship city from November 13, 1994, with former Matsuo Village
Local attractions
- Towada-Hachimantai National Park
- Mount Hachimantai
- Yakehashiri Lava Flow[8]
- Appi Kogen Ski Resort[9]
- Fudō Falls, One of Japan's Top 100 Waterfalls[10]
- Matsuo mine, an abandoned mine
- Matsukawa Gorge [11]
- Matsukawa Geothermal Power Plant, the first commercial geothermal plant in Japan
- Nanbu Fuji Golf Course [12]
- Hachimantai hot spring resorts [13]
Notable people from Hachimantai
- Hideji Oda, manga artist
- Hanahikari Setsuo, sumo wrestler
- Ryoyu Kobayashi, ski jumper
- Junshirō Kobayashi, ski jumper
References
- Hachimantai city official statistics
- Hachimantai climate data
- 観測史上1~10位の値(年間を通じての値). JMA. Retrieved February 19, 2022.
- 気象庁 / 平年値(年・月ごとの値). JMA. Retrieved February 19, 2022.
- 観測史上1~10位の値(年間を通じての値). JMA. Retrieved February 25, 2022.
- 気象庁 / 平年値(年・月ごとの値). JMA. Retrieved February 25, 2022.
- Hachimantai population statistics
- "Yakehashiri Lava Flow ( Hachimantai City )". A Trip to Iwate. Iwate Prefecture Tourism Portal. Retrieved 28 March 2017.
- "Hachimantai Resort ( Panorama Ski Area/Shimokura Ski Area ) ( Hachimantai City )". A Trip to Iwate. Iwate Prefecture Tourism Portal. Retrieved 28 March 2017.
- "Fudo no Taki Falls ( Hachimantai City )". A Trip to Iwate. Iwate Prefecture Tourism Portal. Retrieved 28 March 2017.
- "Matsukawa Gorge ( Hachimantai City )". A Trip to Iwate. Iwate Prefecture Tourism Portal. Retrieved 28 March 2017.
- "Nambu Fuji Country Club ( Hachimantai City )". A Trip to Iwate. Iwate Prefecture Tourism Portal. Retrieved 28 March 2017.
- "Hachimantai Hot Springs and Appi Hot Springs ( Hachimantai City )". A Trip to Iwate. Iwate Prefecture Tourism Portal. Archived from the original on 16 March 2017. Retrieved 28 March 2017.
External links
![]() Media related to Hachimantai, Iwate at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Hachimantai, Iwate at Wikimedia Commons
- Official Website (in Japanese)