Halogeton
Halogeton is a plant genus of the family Amaranthaceae. The genus name, Halogeton, derives from the Greek words for "salt" and for "neighbor."[1]
| Halogeton | |
|---|---|
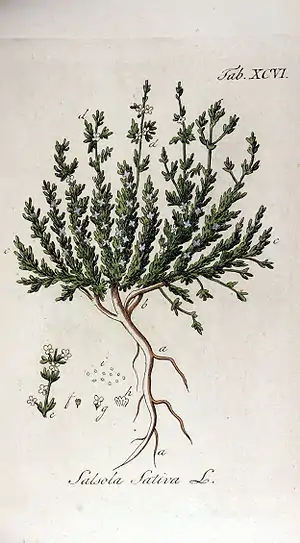 | |
| Halogeton sativus | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Order: | Caryophyllales |
| Family: | Amaranthaceae |
| Subfamily: | Salsoloideae |
| Tribe: | Salsoleae |
| Genus: | Halogeton C.A.Mey. |
| Species | |
|
About 5 species, see text | |
Description
The genus Halogeton includes both annual and perennial species. The leaves are fleshy cylindrical, terminating in a persistent or caducous bristle. There are three to several flowers in the axil of each floral leaf. The perianth segments are membranous. The stamens are fixed on a papillose staminodial disk. In fruit, the tepals develop five wings.
Distribution and habitat
The annual species grow in temperate salines and ruderal places, while the perennials are found in warm and hot deserts. They are tolerant of fairly saline soils.
Uses
Halogeton sativus was cultivated for the enormous 18th Century barilla industry in Spain that produced soda ash. The species was considered to be a "saltwort" plant.
Weeds
Halogeton glomeratus is considered a noxious weed in most regions of the United States;[2] a particular difficulty with H. glomeratus is that it is poisonous to sheep, and possibly to cattle, due to the high concentration of sodium oxalate in the dry plant.[3] The common names for H. glomeratus include halogeton (the same as the genus), barilla, and saltlover.[4]
Ecology
Halogeton species are used as food plants by the larvae of some Lepidoptera species including The Nutmeg and the Coleophora case-bearers C. klimeschiella and C. parthenica.
Systematics
The genus Halogeton was published in 1829 by Carl Anton von Meyer (in Ledeb., Icon. Pl. Fl. Ross. 1: 10), with the type species Halogeton glomeratus (M. Bieb.) C.A.Mey. Synonyms are Agathophora (Fenzl) Bunge and Micropeplis Bunge. The genus includes about 5 species:
- Halogeton alopecuroides (Delile) Moq.
- Halogeton arachnoideus Moq.
- Halogeton glomeratus (M. Bieb.) C. A. Mey.
- Halogeton sativus (L.) Moq., Synonym Salsola sativa L.
- Halogeton tibeticus Bunge (Bunge 1862; Botschantzev 1977).
References
- Holmgren, Ned A. (2004). "HalogetonC. A. Meyer," in Flora of North America: North of Mexico Volume 4: Magnoliophyta: Caryophyllidae, part 1, Editorial Committee of the Flora of North America (Oxford University Press, 2004). ISBN 978-0-19-517389-5. Online versions retrieved May 22, 2007.
- Natural Resources Conservation Service, United States Department of Agriculture (2007). "PLANTS Profile for Halogeton glomeratus (saltlover)," webpage retrieved May 20, 2007.
- Agricultural Research Service, United States Department of Agriculture (2007). "Halogeton (Halogeton Glomeratus)," webpage retrieved May 23, 2007.
- Integrated Taxonomic Information Service (2007). Halogeton, retrieved May 19, 2007.
Hossein Akhani, Gerald Edwards, Eric H. Roalson:Diversification Of The Old World Salsoleae S.L. (Chenopodiaceae): Molecular Phylogenetic Analysis Of Nuclear And Chloroplast Data Sets And A Revised Classification In: International Journal of Plant Sciences, 168(6), p. 942 and 945-946, 2007. (chapters Description, Habitat, Systematics)