Hattingen
Hattingen is a town in the northern part of the Ennepe-Ruhr-Kreis district, in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany.
Hattingen | |
|---|---|
 Aerial view | |
 Flag  Coat of arms | |
Location of Hattingen within Ennepe-Ruhr-Kreis district 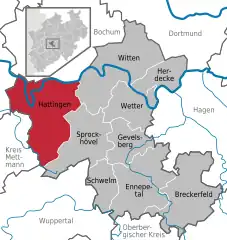 | |
 Hattingen  Hattingen | |
| Coordinates: 51°23′57″N 7°11′09″E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | North Rhine-Westphalia |
| Admin. region | Arnsberg |
| District | Ennepe-Ruhr-Kreis |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2020–25) | Dirk Glaser[1] (Ind.) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 71.40 km2 (27.57 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 306 m (1,004 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | 60 m (200 ft) |
| Population (2021-12-31)[2] | |
| • Total | 54,061 |
| • Density | 760/km2 (2,000/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| Postal codes | 45525–45527–45529 |
| Dialling codes | 02324 |
| Vehicle registration | EN |
| Website | www.hattingen.de |
History
Hattingen is located on the south bank of the River Ruhr in the south of the Ruhr region. The town was first mentioned in 1396, when the Duke of Mark granted permission to build a city wall. Today, Hattingen has a picturesque historic district with Fachwerk (timber-framed houses) built between the 14th and 16th centuries. The old city is still partly surrounded by the city walls today.
There are three castles remaining within the municipal area of Hattingen.[3] Isenburg Castle was built in the 12th century in the hillsides above the Ruhr. The castle was destroyed in 1225, but prominent ruins remain. Blankenstein Castle was built in the 13th century above the Ruhr river and Haus Kemnade is a moated castle from the 16th century. All three castles are famous tourist landmarks and open to the public.
Hattingen became part of the Hanseatic League in 1554 and became an important trading town. In 1720, there were 52 operating coal mines within the municipal area and Hattingen became one of the first industrial cities of the Ruhr region. Steel production started in 1853, when the Henrichshütte was founded. The Henrichshütte became one of the most important employers of the whole region and dominated the town until it closed in 1987.
Today, Hattingen still faces problems concerning structural change of the economy, but is becoming a centre of tourism, especially its historical downtown.
Neighbouring cities

The cities bordering Hattingen are Bochum, Essen, Sprockhövel, Velbert, Witten and Wuppertal.
Division of the town
Hattingen is divided into the districts of Blankenstein, Bredenscheid-Stüter, Hattingen-Mitte, Holthausen, Niederbonsfeld, Niederelfringhausen, Niederwenigern, Oberelfringhausen, Oberstüter, Welper and Winz-Baak.
Notable people
- Mathilde Franziska Anneke, feminist
- Erich Warsitz, world's first jet pilot
- John J. Gumperz, sociolinguist
- Harald Siepermann, Character Designer
- Marie-Luise Marjan, actress
- Jamiri (Jan-Michael Richter), comic artist
- Andreas Bieber, singer and actor
- Mirjam Müntefering, author
- Caliban (band)
- DJ Quicksilver, Disk Jockey
- Jost Gippert, German linguist
- Luke Hemmerich, German Football Player
Politics
In the local elections of 2004 the Social Democratic Party (SPD) was the largest party on the council with 24 seats. It was followed by the Christian Democratic Union (CDU) with 18 and the Alliance 90/The Greens with 7, the WBG (a conservative lis) and Free Democrats with four each, FLW (also a conservative list) with three, National Democratic Party two, and the PDS/WAL (socialists) and AUF Witten (a left wing list) with one each.
From 2004 to 2020, for the first time in its history, the council was led by a female mayor: Sonja Leidemann (SPD). In the election of 2020 she lost her mandate to Lars König (CDU).
Mayor
The current mayor of Hattingen is Dirk Glaser, who ran as an independent. The most recent mayoral election was held on 13 September 2020, with a runoff held on 27 September, and the results were as follows:
| Candidate | Party | First round | Second round | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Votes | % | Votes | % | |||
| Dirk Glaser | Independent | 8,756 | 39.4 | 9,356 | 58.3 | |
| Frank Mielke | Social Democratic Party | 6,723 | 30.2 | 6,695 | 41.7 | |
| Frank Staacken | Alliance 90/The Greens | 4,281 | 19.3 | |||
| Christian Siever | Independent | 1,285 | 5.8 | |||
| Thomas Bausch | Independent | 1,185 | 5.3 | |||
| Valid votes | 22,230 | 97.3 | 16,051 | 99.0 | ||
| Invalid votes | 614 | 2.7 | 154 | 1.0 | ||
| Total | 22,844 | 100.0 | 16,205 | 100.0 | ||
| Electorate/voter turnout | 45,151 | 50.6 | 45,151 | 35.9 | ||
| Source: City of Hattingen (1st round, 2nd round) | ||||||
City council
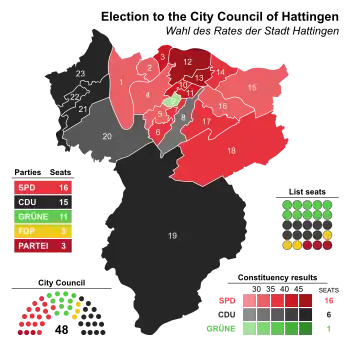
The Hattingen city council governs the city alongside the Mayor. The most recent city council election was held on 13 September 2020, and the results were as follows:
| Party | Votes | % | +/- | Seats | +/- | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Social Democratic Party (SPD) | 7,404 | 33.1 | 16 | |||
| Christian Democratic Union (CDU) | 6,893 | 30.9 | 15 | ±0 | ||
| Alliance 90/The Greens (Grüne) | 5,288 | 23.7 | 11 | |||
| Free Democratic Party (FDP) | 1,529 | 6.8 | 3 | |||
| Die PARTEI | 1,229 | 5.5 | New | 3 | New | |
| Valid votes | 22,343 | 97.8 | ||||
| Invalid votes | 496 | 2.2 | ||||
| Total | 22,839 | 100.0 | 48 | |||
| Electorate/voter turnout | 45,151 | 50.6 | ||||
| Source: City of Hattingen | ||||||
State Landtag
In the Landtag of North Rhine-Westphalia, Hattingen is part of the Ennepe-Ruhr-Kreis I constituency. Rainer Bovermann of the SPD has been representative since the constituency's creation in the 2005 election; he was most recently re-elected in 2017.
Federal parliament
In the Bundestag, Witten is part of the Ennepe-Ruhr-Kreis II constituency. Axel Echeverria of the SPD was elected as representative in the 2021 German federal election.
Gallery
 Historic town
Historic town Glockenturm in the background
Glockenturm in the background Historic Fachwerk house, the Bügeleisenhaus
Historic Fachwerk house, the Bügeleisenhaus Menschen aus Eisen
Menschen aus Eisen
References
- Wahlergebnisse in NRW Kommunalwahlen 2020, Land Nordrhein-Westfalen, accessed 19 June 2021.
- "Bevölkerung der Gemeinden Nordrhein-Westfalens am 31. Dezember 2021" (in German). Landesbetrieb Information und Technik NRW. Retrieved 20 June 2022.
- Historic Town Center – Hattingen Archived 2017-05-27 at the Wayback Machine Historische Stadt- & Ortskerne. Retrieved March 9, 2010