Hatzerim Airbase
Hatzerim Israeli Air Force Base (Hebrew: בָּסִיס חֵיל-הַאֲוִויר חֲצֵרִים, Basis Heil HaAvir Hatzerim) (ICAO: LLHB) is an air base of the Israeli Air Force in the Negev Desert on the west outskirts of Beersheba, near Kibbutz Hatzerim. Apart from fighter jets, it houses the IAF Flight Academy, the IAF Aerobatic Team and the IAF Museum.
| Hatzerim Israeli Air Force Base Air Force Base 6  | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
בָּסִיס חֵיל-הַאֲוִויר חֲצֵרִים | |||||||||||
| Beersheba, Southern District in Israel | |||||||||||
 | |||||||||||
 Hatzerim AB Shown within Israel | |||||||||||
| Coordinates | 31°14′00.09″N 34°39′45.21″E | ||||||||||
| Type | Airbase | ||||||||||
| Site information | |||||||||||
| Owner | Israel Defense Forces | ||||||||||
| Operator | Israeli Air Force | ||||||||||
| Site history | |||||||||||
| Built | 1960s | ||||||||||
| In use | 1966 - present | ||||||||||
| Airfield information | |||||||||||
| Identifiers | ICAO: LLHB | ||||||||||
| Elevation | 220 metres (722 ft) AMSL | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
History
Hatzerim Airbase was constructed during the early 1960s and declared operational on October 3, 1966. It was the first base built from the ground up, as a new base for the IAF, and not on existed base areas of the Royal Air Force.[1] Initially, the IAF Flight Academy was moved here from Tel Nof Airbase and has since been using the northwestern part of the airbase and its runway together with the IAF Aerobatic Team. The southern area with the three other runways is reserved for operational fighter jets (see map in gallery).
The Flight Academy had already flown the French two-seater Fouga CM.170 Magister Tzukit at Tel Nof Airbase since 1960, which it kept for a total of 50 years until it was decommissioned in 2010 and was also flown by the Aerobatic Team during this time. These Hatzerim aircraft were also used during the Six-Day War to carry out attacks on enemy radar stations and anti-aircraft artillery and also did close air support (CAS).[2]
From 1996, the "Hammers" Squadron[3] based on Hatzerim received the F-15I Ra'am, which was adapted to Israeli needs and is derived from the F-15E Strike Eagle. From 2006, the "Knights Of The Orange Tail" Squadron[4] finally received the adapted F-16I Sufa, derived from the two-seat F-16D Block 50/52 Plus. Both squadrons had previously flown the F-4E Phantom II Kurnas since the 1970s.
On September 6, 2007, four F-15Is from the "Hammers" Squadron on Hatzerim and four F-16Is from Ramon Airbase flew an attack on an almost completed nuclear reactor in Syria under the code name Operation Outside the Box and destroyed it. It was only more than 10 years later that Israel officially acknowledged the attack.[5] They wanted to prevent Syria from building atomic bombs from the nuclear material obtained.
 Machines and cadets of the IAF Flight Academy on Hatzerim in 1969
Machines and cadets of the IAF Flight Academy on Hatzerim in 1969 Four pilots of the IAF Aerobatic Team on Hatzerim in 1976
Four pilots of the IAF Aerobatic Team on Hatzerim in 1976 A retired Fouga CM.170 Magister Tzukit of the IAF Aerobatic Team
A retired Fouga CM.170 Magister Tzukit of the IAF Aerobatic Team.jpg.webp)
 The Syrian nuclear reactor destroyed by Operation Outside the Box in 2007
The Syrian nuclear reactor destroyed by Operation Outside the Box in 2007
Current
In addition to two squadrons with operational fighter jets, the base also houses the IAF Flight Academy[2], the IAF Aerobatic Team[6] and – outside the security area – the IAF Museum[7][8]. The Flight Academy trains prospective pilots on the German Grob G 120A Snunit, the US Bell 206 Sayfan helicopter, the Italian M-346 Lavi jet trainer and other aircraft.[9] All pilots in the aerobatic team also work as instructors at the flight academy and fly the same machines in both facilities, currently T-6 Texan II Efroni two-seater.
 Two German Grob G 120A Snunit of the IAF Flight Academy 2007
Two German Grob G 120A Snunit of the IAF Flight Academy 2007.jpg.webp) Five aspiring female pilots from the IAF Flight Academy in 2011
Five aspiring female pilots from the IAF Flight Academy in 2011 ATC Tower in the southern area of Hatzerim Airbase
ATC Tower in the southern area of Hatzerim Airbase.JPG.webp) IAF Museum in 2008 on Independence Day with operational aircraft in the foreground
IAF Museum in 2008 on Independence Day with operational aircraft in the foreground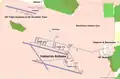 Map of the airbase with the Flight Academy, the Aerobatic Team and the IAF Museum
Map of the airbase with the Flight Academy, the Aerobatic Team and the IAF Museum An F-16I Sufa with full power afterburner takeoff at Hatzerim Airbase
An F-16I Sufa with full power afterburner takeoff at Hatzerim Airbase
The 25 F-15I Ra'am jets from the "Hammers" Squadron, which date back to the 1990s, are to be brought up to date in the coming years and receive the same avionics and systems as the USAF's new F-15EX Eagle II.[10] At the same time, the even older F-15C/D on Tel Nof will be gradually replaced by new F-15IA (Israel Advanced) – the Israeli variant of the F-15EX.[11]
Units
- 69th Squadron "Hammers" – operating the F-15I Ra'am[12]
- 102nd Squadron "Flying Tiger" – operating the M-346 Lavi for the Flight Academy[13]
- 107th Squadron "Knights Of The Orange Tail" – operating the F-16I Sufa[4]
- IAF Flight Academy – operating the Grob G 120A Snunit, Bell 206 Sayfan, Beechcraft King Air Tzofit and others[2]
- IAF Aerobatic Team – operating the T-6 Texan II Efroni[6]
 An F-15I Ra'am of 69th Squadron "Hammers", based on Hatzerim
An F-15I Ra'am of 69th Squadron "Hammers", based on Hatzerim An Italian M-346 Lavi jet trainer of the IAF Flight Academy
An Italian M-346 Lavi jet trainer of the IAF Flight Academy_107_Squadron_%22Knights_of_the_Orange_Tail%22_(29223012136).jpg.webp) An F-16I Sufa of 107th Squadron "Knights Of The Orange Tail"
An F-16I Sufa of 107th Squadron "Knights Of The Orange Tail"
 A Bell 206 Sayfan for helicopter training at the IAF Flight Academy
A Bell 206 Sayfan for helicopter training at the IAF Flight Academy Cadet graduation ceremony at Hatzerim Airbase
Cadet graduation ceremony at Hatzerim Airbase
Note: IAF aircraft can usually be assigned to their squadron by the symbols on the tail
See also
- List of airports in Israel
- Timeline of the Israeli–Palestinian conflict in 2023
- Outline of the 2023 Israel–Hamas war
References
- Dudi Houri (2004). "עניין של בניין" [Matter of building]. Israeli Air Force Journal (in Hebrew) (159).
- "Flight Academy". IAF website. Retrieved 2023-09-26.
- "The Hammers Squadron". IAF website. Retrieved 2023-09-26.
- "Knights Of The Orange Tail Squadron". IAF website. Retrieved 2023-09-26.
- "After a decade Israel admits: We bombed Syria nuclear reactor in 2007". The Jerusalem Post. 2018-03-22. Retrieved 2023-09-27.
- "A National Symbol". IAF website. 2021-04-13. Retrieved 2023-09-26.
- "Welcome to the IAF Museum". IAF website. Retrieved 2023-10-03.
- "Israeli Air Force Museum". touristisrael.com. Retrieved 2023-10-03.
- "Italy wins IAF with combat trainer jet bid". The Jerusalem Post. 2012-02-16. Retrieved 2023-09-26.
- "Israel formally requests 25 F-15 EX from the US". breakingdefense.com. 2023-01-19. Retrieved 2023-10-24.
- "Senior Boeing official in Israel to push sale of advanced F-15 jets for Iran strike". The Times Of Israel. 2023-02-20. Retrieved 2023-10-13.
- "Birthday of the "Hammers": 69th Squadron celebrates 75 years". IAF website (in Hebrew). 2023-09-11. Retrieved 2023-09-26.
- "The 102nd Squadron Goes Back in Time". IAF website. 2021-03-08. Retrieved 2023-09-26.