Heterosaccus
Heterosaccus is a genus of barnacles in infraclass Rhizocephala. Like other taxa in this group, they parasitize crabs. Geoffroy Smith circumscribed the genus in 1906; he initially only included H. hians. Smith circumscribed a genus distinct from Sacculina due to a difference of the mesentery; in Heterosaccus, the mesentery does not stretch down to the mantle opening but rather only is present on the ring of attachment.[1]
| Heterosaccus | |
|---|---|
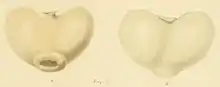 | |
| H. hians. | |
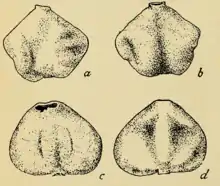 | |
| H. occidentalis. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Thecostraca |
| Subclass: | Cirripedia |
| Infraclass: | Rhizocephala |
| Family: | Sacculinidae |
| Genus: | Heterosaccus Smith, 1906 |
| Type species | |
| Sacculina hians Kossmann, 1872 | |
Species
As of 2017, WoRMS recognizes the following fifteen species.[2]
| Binominal name (Original combination) | Author citation | Type host | Type locality | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heterosaccus californicus | Boschma, 1933 | "Pugettia producta" | "Santa Cruz, California" | [3]: 236–237 |
| Heterosaccus distortus | Boschma, 1933 | "Schizophrys aspera" | "vicinity of Jolo," Philippines | [3]: 235–236 |
| Heterosaccus dollfusi | Boschma, 1960 | "Charybdis hoplites" | "Gulf of Suez" | [4] |
| Heterosaccus gongylus | Boschma, 1962 | Pleistacantha moseleyi | Andaman Sea | [5] apud WoRMS |
| Heterosaccus hians (Sacculina hians) | (Kossmann, 1872) | "Thalamita sp. aff. callianassae" | "Java" | [6] |
| Heterosaccus indicus | Boschma, 1957 | "Portunus pelagicus" | Mandapam Camp, Tamil Nadu | [7] apud WoRMS |
| Heterosaccus lunatus | Phillips, 1978 | "Charybdis callianassa" | "Moreton Bay," Queensland | [8] |
| Heterosaccus multilacinensis | Phillips, 1978 | "Charybdis truncata" | "East Moreton Bay," Queensland | [8] |
| Heterosaccus occidentalis (Drepanorchis occidentalis) | (Boschma, 1928) | "Mithrax forceps" (=Mithraculus forceps) | "Deadman's Bay, west coast of Florida" | [9] |
| Heterosaccus papillosus (Drepanorchis papillosa) | (Boschma, 1933) | "Charybdis bimaculatus" (=Charybdis bimaculata) | "vicinity of Marindugue Island, Philippine Islands" | [3]: 234 |
| Heterosaccus pellucidus | Shiino, 1943 | "Thalamita integra integra" | Japan | [10] apud WoRMS |
| Heterosaccus ruginosus | Boschma, 1931 | "Thalamita prymna" | "Singapore, coral reef" | [11] |
| Heterosaccus setoensis | Shiino, 1943 | "Thalamita wakensis" (= Thalamita seurati) | Seto Inland Sea | [10] apud WoRMS |
| Heterosaccus sibogae | Boschma, 1931 | "Thalamita admeta" (= Thalamita admete) | "Siau Reef", Indonesia | [12] |
| Heterosaccus tesselatus (Sacculina tessellata) | (Boschma, 1925) | "Mithrax ruber" (= Teleophrys ruber) | "Caracas Bay, Curaçao" | [13] |
References
- Smith, Geoffrey (1906). "Genus Heterosaccus". Rhizocephala. Fauna und Flora des Golfes von Neapal. Vol. 29. R. Friedländer & Sohn. pp. 113–114.
- Boyko, Christopher B.; Boxshall, G. (2015). "Heterosaccus Smith, 1906". WoRMS. World Register of Marine Species. Retrieved 26 September 2017.
- Boschma, H. (1933). "New species of Sacculinidae in the collection of the United States National Museum". Tijdschrift der Nederlandsche Dierkundige Vereeniging. 3: 234–237.
- Boschma, H. (1960). "A Rhizocephalan Parasite of the Crab Charybdis hoplites (Wood-Mason)". Crustaceana. 1 (1): 58–67. doi:10.1163/156854060X00078. JSTOR 20140988.
- Boschma, H. (1962). "A rhizocephalan parasite of a spider crab from the Andaman Sea". Proceedings of the Koninklijke Nederlandse Akademie van Wetenschappen. Series C. 65: 294–301 (fide WoRMS). Not seen.
{{cite journal}}: External link in|postscript= - Kossmann, R. (1872). "Beiträge zur Anatomie der schmarotzenden Rankenfüssler". Verhandlungen der physikalisch-medicinischen Gesellschaft in Würzburg. Neue Folge. 3: 329–330.
- Reprinted: Kossmann, R. (1874). "Beiträge zur Anatomie der schmarotzenden Rankenfüssler". Arbeiten aus dem Zoologisch-Zootomischen Institut in Würzburg. 1: 130–131; Pl. 5, Fig. 17a, b; Pl. 6, Fig. 2.
{{cite journal}}: External link in|postscript=
- Reprinted: Kossmann, R. (1874). "Beiträge zur Anatomie der schmarotzenden Rankenfüssler". Arbeiten aus dem Zoologisch-Zootomischen Institut in Würzburg. 1: 130–131; Pl. 5, Fig. 17a, b; Pl. 6, Fig. 2.
- Boschma, H. (1957). "Heterosaccus indicus, sp. nov., a rhizocephalan parasite of the crab Portunus pelagicus (L.)". The Annals of Biology. 2: 1–20 (fide WoRMS). Not seen.
{{cite journal}}: External link in|postscript= - Philips, W. J. (1978). "Some parasitic barnacles (Rhizocephala: Sacculinidae) from portunid crabs in Moreton Bay, Queensland". Memoirs of the Queensland Museum. 18 (2): 255–263.
- Boschma, H. (1928). "Two common species of parasitic crustacea (Sacculinidae) of the West Indies". Proceedings of the United States National Museum. 73 (2726): 4–6. doi:10.5479/si.00963801.73-2726.1.
- Shiino, S. M. (1943). "Rhizocephala of Japan". Journal of the Sigenkagaku Kenkyusyo. 1: 1–36 (fide WoRMS). Not seen.
{{cite journal}}: External link in|postscript= - Boschma, H. (1931). "Papers from Dr. Th. Mortensen's Pacific Expedition 1914–16. LV. Rhizocephala". Videnskabelige Meddedelser fra den Dansk Naturhistoriske Forening i København. 89: 361–365.
- Boschma, H. (1931). Die Rhizocephalen der Siboga Expedition. Supplement. Siboga-Expeditie. Vol. 31 bis. Leiden: E. J. Brill. pp. 54–55.
- Boschma, H. (1925). "Rhizocephala of Curaçao". Bijdragen tot de Dierkunde. 24 (1): 12–13. doi:10.1163/26660644-02401002. ISSN 0067-8546.
Further reading
- Brockerhoff, Annette M.; McLay, Colin L.; Rybakov, Alexi V. (2010). "Occurrence of Heterosaccus (Cirripedia: Rhizocephala) in the New Zealand Crab Metacarcinus novaezelandiae (Decapoda: Cancridae) and Distribution of Other Rhizocephala in the South Pacific". Journal of Crustacean Biology. 30 (3): 377–383. doi:10.1651/09-3270.1.
- Øksnebjerg, Bo (2000). "The Rhizocephala (Crustacea: Cirripedia) of the Mediterranean and Black Seas: Taxonomy, Biogeography, and Ecology". Israel Journal of Zoology. 46: 72–74. doi:10.1560/RCLC-NM2U-HV5L-6Q52.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.