Intertransverse ligament
The intertransverse ligaments are weak, sheet-like[1] ligaments interconnecting adjacent transverse processes in the thoracic spine, and adjacent accessory processes in the lumbar spine. They act to limit lateral flexion and rotation of the spine.[2]
| Intertransverse ligament | |
|---|---|
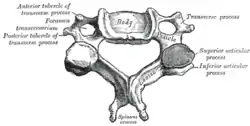 A cervical vertebra (transverse processes labeled at upper right) | |
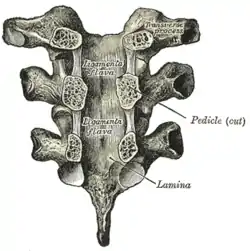 Vertebral arches of three thoracic vertebrae viewed from the front | |
| Details | |
| From | Transverse processes |
| To | Transverse processes |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Ligamenta intertransversaria |
| TA98 | A03.2.01.004 |
| TA2 | 1676 |
| FMA | 13426 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Structure
In the cervical region, they consist of a few irregular fibers that are largely replaced by the intertransversarii.[3] In the thoracic region, they are rounded cords intimately connected with the deep muscles of the back.[4] In the lumbar, region they are thin and membranous.[3]
The intertransverse ligaments often blend with the intertransverse muscles.[5]
References
- Sinnatamby C (2011). Last's Anatomy (12th ed.). Elsevier Australia. p. 424. ISBN 978-0-7295-3752-0.
- Sobotta Anatomy Textbook. Friedrich Paulsen, Tobias M. Böckers, J. Waschke, Stephan Winkler, Katja Dalkowski, Jörg Mair, Sonja Klebe, Elsevier ClinicalKey. Munich. 2018. p. 120. ISBN 978-0-7020-6760-0. OCLC 1132300315.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) CS1 maint: others (link) - Standring, Susan (2020). Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice (42 ed.). Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 836. ISBN 978-0-7020-7707-4. OCLC 1201341621.
- "Gray, Henry. 1918. Anatomy of the Human Body". Bartleby.com. Retrieved 30 March 2013.
- "Intertransverse ligaments". AnatomyExpert. Retrieved 30 March 2013.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.