Jean de Bodt
Jean de Bodt (1670 – 3 January 1745) was a Baroque architect of the 18th century.
Jean de Bodt | |
|---|---|
 Jean de Bodt | |
| Born | 1670 |
| Died | 3 January 1745 |
| Other names | Johann von Bodt |
| Occupation | architect |
Biography
Bodt was born in Paris to French Huguenot parents, but his father came from Mecklenburg. He studied architecture, but was forced to flee from France after the Edict of Fontainebleau to the Dutch Republic. In 1688 he came in the entourage of William III of England to London. He was promoted to a Captain of the British Artillery and Engineer Corps.[1]
In 1699 he moved to Berlin to accomplish the construction of the Zeughaus (arsenal), which was now largely influenced by the French and British style of the late 17th century. Bodt also worked at the Palaces of Potsdam and Schlodien,[2] and completed the construction plans of the tower of the Berlin Parochialkirche in 1715. Then he was send to the Wesel citadel to improve the fortification of the city.[3] In 1719 he became governor of the city Wesel.[4]
In 1728 he switched into Saxonian service, where he became general intendant of civil and military buildings as successor of Count Wackerbarth and he received the title of General of the Infantry in 1741, but worked exclusively as an architect. Together with Pöppelmann and Longuelune he converted a small country house into the Japanese Palace at Dresden. He founded the Dresden Engineer Academy in 1742. Bodt died in Dresden.
Buildings by Jean de Bodt
 Berlin Zeughaus and Neue Wache
Berlin Zeughaus and Neue Wache Zeughaus, Berlin
Zeughaus, Berlin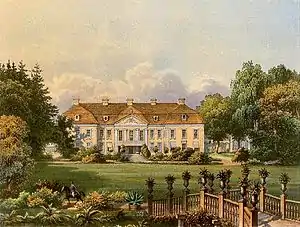 Schlodien Palace (East Prussia)
Schlodien Palace (East Prussia) Friedrichstein Palace (East Prussia) According to his drafts, it was built under the supervision of John von Collas for Count Dönhoff.
Friedrichstein Palace (East Prussia) According to his drafts, it was built under the supervision of John von Collas for Count Dönhoff. Berlin Gate at Wesel
Berlin Gate at Wesel Dresden, Japanisches Palais, Museum für Völkerkunde, Landesmuseum
Dresden, Japanisches Palais, Museum für Völkerkunde, Landesmuseum
See also
Literature
- Hans-Joachim Kuke: Jean de Bodt 1670–1745. Architekt und Ingenieur im Zeitalter des Barock. Verlag Werner, Worms 2002, ISBN 3-88462-179-3 (in German)
- Klaus-Ludwig Thiel: Staatsbauentwürfe Jean de Bodts für Friedrich I. in Theorie und Praxis. Kleikamp, Köln 1987 (in German)