Kapas Island
Kapas Island (Malay: Pulau Kapas, Terengganuan: Pula Kapah) is an island in Marang District, Terengganu, Malaysia, with a smaller island, Pulau Gemia, located north of it.[1] It measures roughly 1.5 by 2.5 km (0.93 by 1.55 mi).[2] Its name, Pulau Kapas (Malay for cotton island), refers to the island's white beaches. The island has tropical jungle, clear seawater, white sand beaches and coral reefs in the surrounding waters. It is promoted as a "diving and snorkeling paradise".[1] The island is reached by ferry from Marang. Kapas is the location where most of the research on the enigmatic Amphidromus snails is carried out (unlike all other snails, Amphidromus are amphidromine: they usually exist of clockwise and anticlockwise individuals).[3]
Native name: Pulau Kapas ڤولاو كاڤس Pula Kapah | |
|---|---|
.jpg.webp) Landscape of Kapas Island | |
 Kapas  Kapas 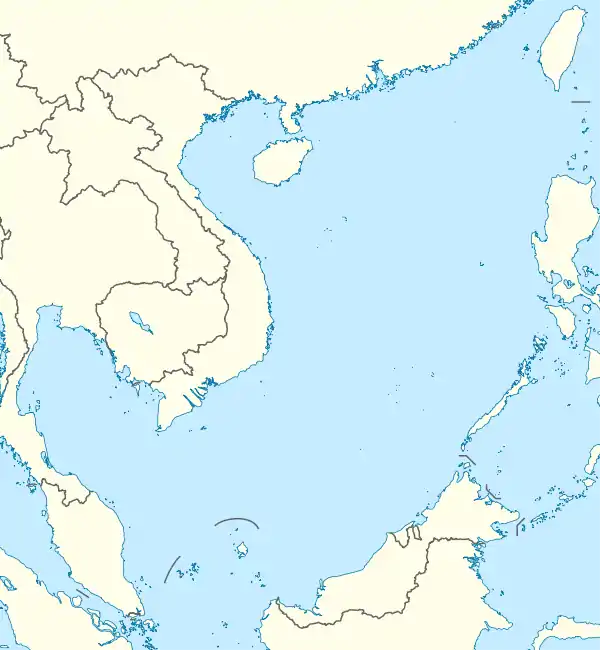 Kapas | |
| Geography | |
| Location | South China Sea |
| Coordinates | 5°13′08″N 103°15′55″E |
| Total islands | 2 |
| Administration | |
Malaysia | |
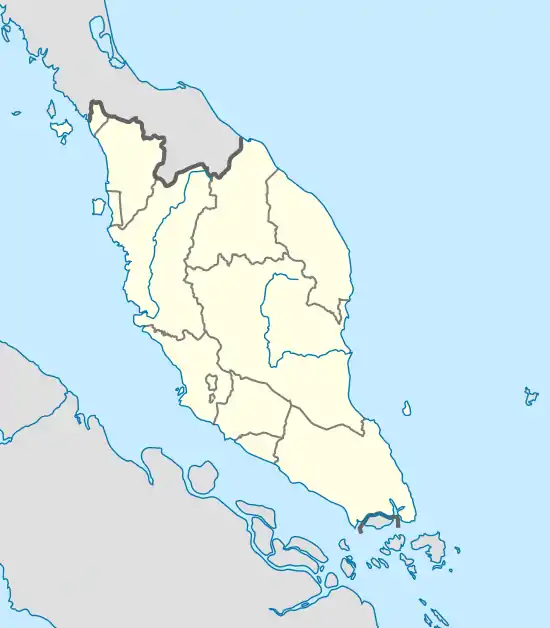
| State | Terengganu |
| District | Marang District |
References
- Emmons, Ron (2013) [Originally published 2008]. DK Eyewitness Travel Guide: Malaysia & Singapore. DK. p. 140. ISBN 978-1-4093-8650-6.
- Damian Harper (December 2006). Malaysia, Singapore & Brunei. Ediz. Inglese. Lonely Planet. pp. 309–. ISBN 978-1-74059-708-1.
- Schilthuizen, M., P. G. Craze, A. S. Cabanban, A. Davison, E. Gittenberger, J. Stone & B. J. Scott, 2007. Sexual selection maintains whole-body chiral dimorphism. Journal of Evolutionary Biology, 20: 1941-1949.
External links
- Tourism Malaysia - Pulau Kapas
 Kapas travel guide from Wikivoyage
Kapas travel guide from Wikivoyage