Kapes (genus)
Kapes is an extinct genus of procolophonid parareptile from the Lower and Middle Triassic of the United Kingdom and Russia. It is a member of the subfamily Procolophoninae.[1] The type species K. amaenus was named in 1975 from the banks of the Vychegda River in the Komi Republic of Russia. In 1983, a new species was brought into the genus, K. majmesculae. K. majmesculae was first named in 1968 as a member of the genus Tichvinskia. A third Russian species, K. serotinus, was named in 1991. In 2002, Kapes bentoni was named from the Middle Triassic Otter Sandstone Formation of Devon, England, extending the geographic range of Kapes. In the same paper, K. serotinus was synonymized with K. majmesculae and another Russian species was assigned to Kapes called K. komiensis. K. komiensis was first named in 1975 (in the same paper K. amaenus was named in) as a member of the genus Macrophon.[2]
| Kapes Temporal range: Lower - Middle Triassic | |
|---|---|
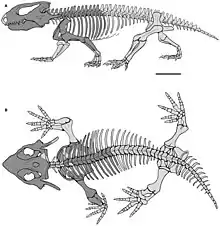 | |
| Skeleton of Kapes bentoni | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Clade: | †Parareptilia |
| Order: | †Procolophonomorpha |
| Family: | †Procolophonidae |
| Subfamily: | †Procolophoninae |
| Genus: | †Kapes Ivakhnenko, 1975 |
| Species | |
| |
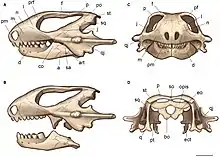
Phylogeny
Below is a cladogram from Ruta et al. (2011) showing the placement of Kapes within Procolophonidae:[3]
| Procolophonidae |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
- Cisneros, J. C. (2008). "Phylogenetic relationships of procolophonid parareptiles with remarks on their geological record". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 6 (3): 345–366. doi:10.1017/S1477201907002350. S2CID 84468714.
- Spencer, P. S.; Storrs, G. W. (2002). "A Re-evaluation of Small Tetrapods from the Middle Triassic Otter Sandstone Formation of Devon, England". Palaeontology. 45 (3): 447. doi:10.1111/1475-4983.00245.
- Ruta, M.; Cisneros, J. C.; Liebrecht, T.; Tsuji, L. A.; Müller, J. (2011). "Amniotes through major biological crises: Faunal turnover among Parareptiles and the end-Permian mass extinction". Palaeontology. 54 (5): 1117. doi:10.1111/j.1475-4983.2011.01051.x.