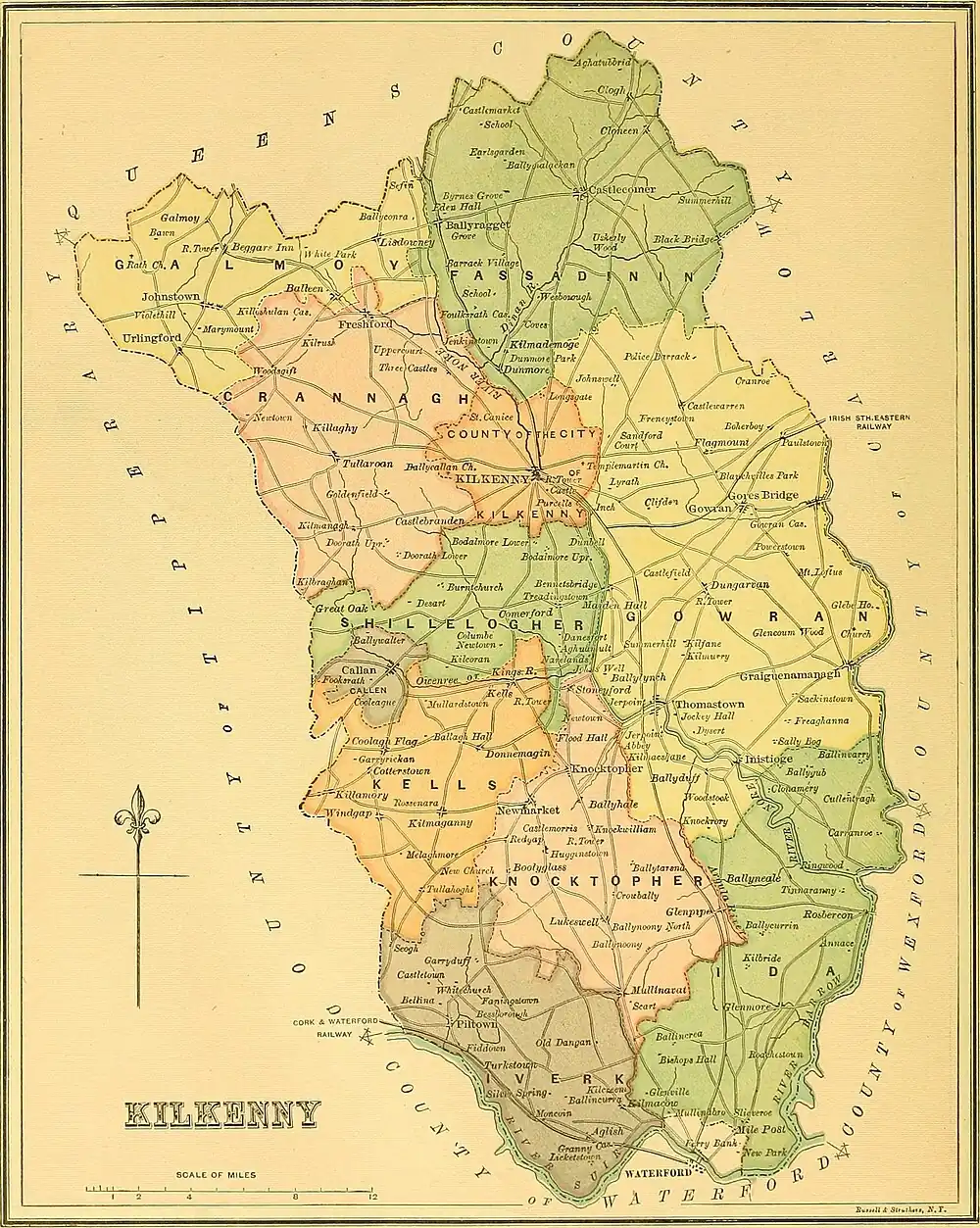
Kilculliheen
Kilculliheen (Irish: Cill Choilchín[l 1]) is a civil parish,[l 2] electoral division[l 3] and barony[l 1] in Ireland, on the north bank of the River Suir across from the centre of Waterford City. Historically, it has been transferred several times between the county of the city of Waterford and the counties of Kilkenny and Waterford. It now contains the only part of Waterford city on the left bank of the River Suir. The Parliamentary Gazetteer of 1846 states "as it lies on the left bank of the Suir, which, for the most part, divides co. Waterford from co. Kilkenny, most topographists mistakingly assign it to the barony of Ida, co. Kilkenny".[3] It is now partly in County Kilkenny and partly in Waterford City.[l 1][l 4][4] Of the barony's eleven townlands, five (Belmount, Ballinvoher, Newtown, Ballyrobin, and Rathculliheen[l 5]) are entirely in Kilkenny and six (Abbeylands, Christendom, Mountmisery, Mountsion, Newrath, and Rockshire[l 5][l 6]) are split between Kilkenny and Waterford. The city portion contains the formerly rural village of Ferrybank, which gives its name to a wider suburb which has spread across the county boundary.[5]
Barony of Kilculliheen
| |
|---|---|
| Etymology: church of Coilcín or Cailcín[2] | |
 Barony of Kilculliheen Location in Ireland | |
| Coordinates: 52°16′11″N 7°6′12″W | |
| Country | Ireland |
| Province | Leinster |
| County | County Kilkenny/Waterford |
| Civil parishes | List
|
History
Kilculliheen is an anglicisation of Cill Choilchín, church of Coilcín or Cailcín, a saint of Celtic Christianity whose feast day is 10 February.[6] Coilcín is also commemorated in the name of Rathculliheen, a townland within the parish. In 1151 Dermot MacMurrough founded St Mary's Abbey de Bello Portu, an Augustinian convent, at the presumed site of Coilcín's church in what is now the townland of Abbeylands.[6] It was a daughter house of the abbey of St Mary de Hoggis in Tallaght, and after the Norman invasion of Ireland was endowed by the future King John and David fitz Milo.[3] In 1532, abbess Alice (or Elicie) Butler was deposed amid charges of sexual and financial impropriety; modern historians view her as a pawn in a jurisdictional dispute between the Bishop of Waterford and the Bishop of Ossory.[7][8] At the dissolution of the monasteries under Henry VIII, the abbey's lands were assigned to the Corporation of Waterford city, and six of its nuns granted compensation for the loss of its revenue.[6][8] Waterford's city charter of James I transferred the entire parish of Kilculliheen from Kilkenny to the county of the city of Waterford.[9] The Civil Survey of the 1650s surveyed the parish both as part of the barony of Ida in Kilkenny and again as part of the city of Waterford.[10]
In the 1830s only a sliver of land from Waterford Bridge to Ferrybank Catholic church was within the municipal boundary; the rest of the parish constituted the northern "liberties" of the city.[11] The Municipal Corporations (Ireland) Act 1840 transferred the liberties of each city from the county of the city to the adjacent county-at-large. The application of this in regard to Kilculliheen was unclear, and the justices of the peace of County Kilkenny assumed it had been annexed to that county.[12] When their error was discovered, an 1845 Act of Parliament was required to allow their judgments to stand.[12] The 1846 Parliamentary Gazetteer and the censuses of 1841 to 1861 described Kilculliheen as part of the Waterford barony of Gaultier.[3] The 1871 census lists it as a barony, with footnote:[13] Kilculliheen did not appear as a barony in the Tables of previous censuses, it having formed a portion of Gaultiere barony. As, however, it has for some years past been described as a distinct barony in documents emanating from the office of the Privy Council and other Public Departments, it is so treated in these Tables.
After the Local Government (Ireland) Act 1898, an order of the Local Government Board subdivided the poor law electoral division of Waterford into seven district electoral divisions (DEDs), one called Kilculliheen consisting of "that portion of the original electoral division not included within the municipal boundary of the borough of Waterford, and situate north of the River Suir".[14] A subsequent order transferred Kilculliheen DED from the judicial county of the city of Waterford to the administrative county Kilkenny.[15] In 1955, the county borough (now city) of Waterford was extended, thereby reclaiming some of the DED territory from Kilkenny.[16][17]
References
Notes
From "Irish placenames database". logainm.ie (in English and Ga). Department of Tourism, Culture, Arts, Gaeltacht, Sport and Media. Retrieved 13 August 2010.:
Footnotes
- Government 2003
- (Fiontar 2008, Kilculliheen/Cill Choilchín )
- "Kilculliheen". The Parliamentary Gazetteer of Ireland adapted to the new Poor-Law, Franchise, Municipal and Ecclesiastical arrangements ... as existing in 1844–45. Vol. II: D–M. Dublin: A. Fullarton & Co. 1846. p. 391.
- "I.R. Uimh. 520/2003 — An tOrdú Logainmneacha (Contae Chill Chainnigh) 2003". p. Schedule, Section A (Administrative units): Chapter 3 (Baronies): Number 9.
- "Over Ferrybank Way". Munster Express. 6 June 2007. Retrieved 14 August 2010.
- Walton, Julian C. (Spring 1994). "Monumental Inscriptions at the Abbey, Kilculliheen, Ferrybank, Waterford by Michael O'Sullivan: Editor's Introduction" (PDF). Decies. Old Waterford Society (49): 2. Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 September 2011.
- Bourke, Angela (2002). "An instrument concerning Elicie Butler of Kilculliheen (1532)". Irish women's writing and traditions. The Field Day Anthology of Irish Writing. Vol. 5. NYU Press. pp. 467–471. ISBN 9780814799062. Retrieved 3 August 2014.
- Mulholland, John (January 1984). "The trial of Alice Butler, Abbess of Kilculliheen, 1532" (PDF). Decies. Old Waterford Society (XXV): 45–46.
- Lewis, Samuel (1837). "Waterford". A Topographical Dictionary of Ireland.
- Simington, Robert (1942). County of Waterford, with appendices: Muskerry barony Co. Cork; Kilkenny City and Liberties (part); also valuations c. 1663–64 for Waterford and Cork cities. The Civil Survey A.D. 1654–56. Vol. VI. Stationery Office for the Irish Manuscripts Commission. pp. xxii–xxiii.
- "Six-inch map centred on Ferrybank Catholic church". Mapviewer. Ordnance Survey Ireland. 1830s. Archived from the original on 29 August 2012. Retrieved 2 August 2014.
- "8 & 9 Victoria c.121: Local Government (Drogheda and Meath) Act, 1845, Section 10". Irish Statute Book. Archived from the original on 11 August 2014. Retrieved 4 August 2014.
- "III. Area, houses, and population in 1841, 1851, 1861, and 1871, of each barony, also the general valuation in 1871 (county and city)". Census of Ireland, 1871; Vol.II, Province of Munster; Part VI, County and City of Waterford. Command papers. Vol. C.873-VI. Alexander Thom for HMSO. 1874. p. 865, note.
- Local Government Board (1899) pp.182–183
- Local Government Board (1899) p.276
- County Borough of Waterford (Extension of Boundary) Provisional Order, 1955, confirmed by section 3 of the Local Government Provisional Orders Confirmation Act, 1955.
- Central Statistics Office (1957). "Explanatory Notes". Census of population of Ireland (PDF). Vol. 1: population, area, and valuation of each district, electoral division, and of each larger unit of area (1956 ed.). Stationery Office. p. viii. Retrieved 26 December 2010.
Sources
- Fiontar (2008). "Placenames Database of Ireland". logainm.ie. Department of Tourism, Culture, Arts, Gaeltacht, Sport and Media of the Government of Ireland.
- Government (2003). Placenames (Co. Kilkenny) Order 2003 (PDF). Dublin: Government of Ireland. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 February 2017. Retrieved 14 November 2018.
- Local Government Board for Ireland (1899). Twenty-seventh report. Command papers. Vol. Cmd.9480. pp. 182–183.
External links
- "Barony of Kilculliheen, Co. Kilkenny". townlands.ie.