Lacrimal gland
The lacrimal glands are paired exocrine glands, one for each eye, found in most terrestrial vertebrates and some marine mammals, that secrete the aqueous layer of the tear film.[1] In humans, they are situated in the upper lateral region of each orbit, in the lacrimal fossa of the orbit formed by the frontal bone.[2] Inflammation of the lacrimal glands is called dacryoadenitis. The lacrimal gland produces tears which are secreted by the lacrimal ducts, and flow over the ocular surface, and then into canals that connect to the lacrimal sac. From that sac, the tears drain through the lacrimal duct into the nose.
| Lacrimal gland | |
|---|---|
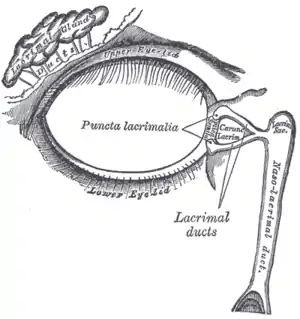 Lacrimal apparatus of the right eye. The lacrimal gland is to the upper left. The right side of the picture is towards the nose. | |
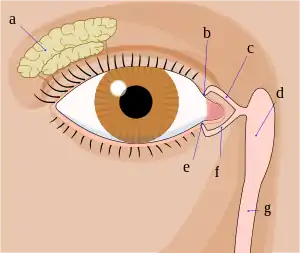 Tear system. a = lacrimal gland b = superior lacrimal punctum c = superior lacrimal canal d = lacrimal sac e = inferior lacrimal punctum f = inferior lacrimal canal g = nasolacrimal canal | |
| Details | |
| Artery | lacrimal artery |
| Vein | superior ophthalmic vein |
| Nerve | lacrimal nerve |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | glandula lacrimalis |
| TA98 | A15.2.07.057 |
| TA2 | 6846 |
| FMA | 59101 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Anatomists divide the gland into two sections, a palpebral lobe, or portion, and an orbital lobe or portion.[3] The smaller palpebral lobe lies close to the eye, along the inner surface of the eyelid; if the upper eyelid is everted, the palpebral portion can be seen.
The orbital lobe of the gland, contains fine interlobular ducts that connect the orbital lobe and the palpebral lobe.[4] They unite to form three to five main secretory ducts, joining five to seven ducts in the palpebral portion before the secreted fluid may enter on the surface of the eye. Tears secreted collect in the fornix conjunctiva of the upper lid, and pass over the eye surface to the lacrimal puncta, small holes found at the inner corner of the eyelids. These pass the tears through the lacrimal canaliculi on to the lacrimal sac, in turn to the nasolacrimal duct, which dumps them out into the nose.[5]
Lacrimal glands are also present in other mammals, such as horses.
Structure
Histology
The lacrimal gland is a compound tubuloacinar gland, it is made up of many lobules separated by connective tissue, each lobule contains many acini. The acini composed of large serous cells which, produce a watery serous secretion, serous cells are filled with lightly stained secretory granules and surrounded by well-developed myoepithelial cells and a sparse, vascular stroma. Each acinus consists of a grape-like mass of lacrimal gland cells with their apices pointed to a central lumen.
The central lumen of many of the units converge to form intralobular ducts, and then they unite to form interlobular ducts. The gland lacks striated ducts.
Blood supply
The lacrimal gland receives blood from the lacrimal artery, which is a branch of the ophthalmic artery. Blood from the gland drains to the superior ophthalmic vein.
Lymphatic drainage
No lymphatic vessels have been observed draining the lacrimal gland.
Nerve supply
The lacrimal gland is innervated by the lacrimal nerve, which is the smallest branch of the ophthalmic nerve, itself a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V). After the lacrimal nerve branches from the ophthalmic nerve it receives a communicating branch from the zygomatic nerve. This communicating branch carries postganglionic parasympathetic axons from the pterygopalatine ganglion. The lacrimal nerve passes anteriorly in the orbit and through the lacrimal gland providing parasympathetic and sympathetic innervation to it.
Parasympathetic innervation
.svg.png.webp)
The parasympathetic innervation to the lacrimal gland is a complex pathway which traverses through numerous structures in the head. Ultimately this two-neuron pathway involving both a preganglionic and postganglionic parasympathetic neuron increases the secretion of lacrimal fluid from the lacrimal gland. The preganglionic parasympathetic neurons are located in the superior salivatory nucleus. They project axons which exit the brainstem as part of the facial nerve (CN VII). Within the facial canal at the geniculate ganglion the axons branch from the facial nerve forming the greater petrosal nerve. This nerve exits the facial canal through the hiatus for the greater petrosal nerve in the petrous part of the temporal bone. It emerges to the middle cranial fossa and travels anteromedially to enter the foramen lacerum. Within the foramen lacerum it joins to the deep petrosal nerve to form the nerve of the pterygoid canal and then passes through this canal. It emerges in the pterygopalatine fossa and enters the pterygopalatine ganglion where the preganglionic parasympathetic axons synapse with the postganglionic parasympathetic neurons. The postganglionic neurons then send axons which travel with the zygomatic nerve to enter the inferior orbital fissure. As the zygomatic nerve travels anteriorly in the orbit it sends a communicating branch to the lacrimal nerve which carries the postganglionic parasympathetic axons. The lacrimal nerve completes this long pathway by travelling through the lacrimal gland and sending branches to which it provides parasympathetic innervation to increase the secretion of lacrimal fluid.
Sympathetic innervation
Sympathetic innervation to the lacrimal gland is of less physiologic importance than the parasympathetic innervation, however there are noradrenergic axons found within the lacrimal gland. Their cell bodies are located in the superior cervical ganglion.
Clinical significance
In contrast to the normal moisture of the eyes or even crying, there can be persistent dryness, scratching, itchiness and burning in the eyes, which are signs of dry eye syndrome (DES) or keratoconjunctivitis sicca (KCS). With this syndrome, the lacrimal glands produce less lacrimal fluid, which mainly occurs with ageing or certain medications. The Schirmer test, conducted by placing a thin strip of filter paper at the edge of the eye, can be used to determine the level of dryness of the eye. Many medications or diseases that cause dry eye syndrome can also cause hyposalivation with xerostomia. Treatment varies according to aetiology and includes avoidance of exacerbating factors, tear stimulation and supplementation, increasing tear retention, eyelid cleansing, and treatment of eye inflammation.[6]
In addition, the following can be associated with lacrimal gland pathology:
Additional images
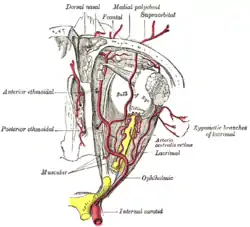 The ophthalmic artery and its branches.
The ophthalmic artery and its branches.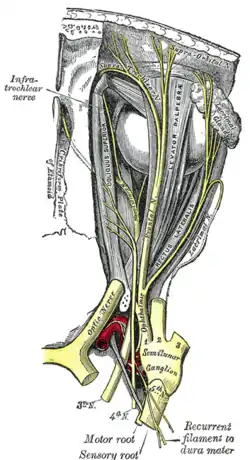 Nerves of the orbit. Seen from above.
Nerves of the orbit. Seen from above.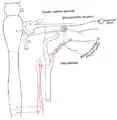 Sympathetic connections of the sphenopalatine and superior cervical ganglia.
Sympathetic connections of the sphenopalatine and superior cervical ganglia.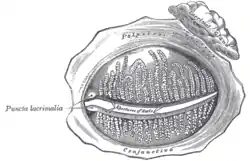 The tarsal glands, etc., seen from the inner surface of the eyelids.
The tarsal glands, etc., seen from the inner surface of the eyelids. Alveoli of lacrimal gland.
Alveoli of lacrimal gland.
See also
References
- Schwab, Ivan R. (2012). Evolution's Witness : How Eyes Evolved. New York. p. 245. ISBN 9780195369748.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Moore, Keith (2018). Clinically oriented anatomy. Wolters Kluwer. pp. 897–900. ISBN 9781496347213.
- Machiele, R (November 2018). "Anatomy Head and Neck". StatPearls [Internet]. PMID 30422509.
- Machiele, R (November 2018). "Anatomy, Head and Neck, Eye Lacrimal Gland". StatPearls(Internet). PMID 30422509.
- "eye, human."Encyclopædia Britannica. 2010. Encyclopædia Britannica 2010 Ultimate Reference Suite DVD 2010
- Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, page 153.
External links
- lesson3 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (orbit2)
- Diseases of the lacrimal gland at http://www.academy.org.uk/lectures/barnard11.htm