Laghouat
Laghouat (Arabic: الأغواط; English: Laghwat) is the capital of the Laghouat Province, Algeria, 400 km (250 mi) south of the Algerian capital Algiers. Located in the Amour Range of the Saharan Atlas, the town is an oasis on the north edge of the Sahara Desert. It is an important administrative and military center and marketplace, and is known for rug and tapestry weaving.
Laghouat
الأغواط | |
|---|---|
 | |
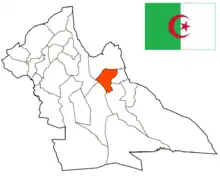 Location of Laghouat in Laghouat Province | |
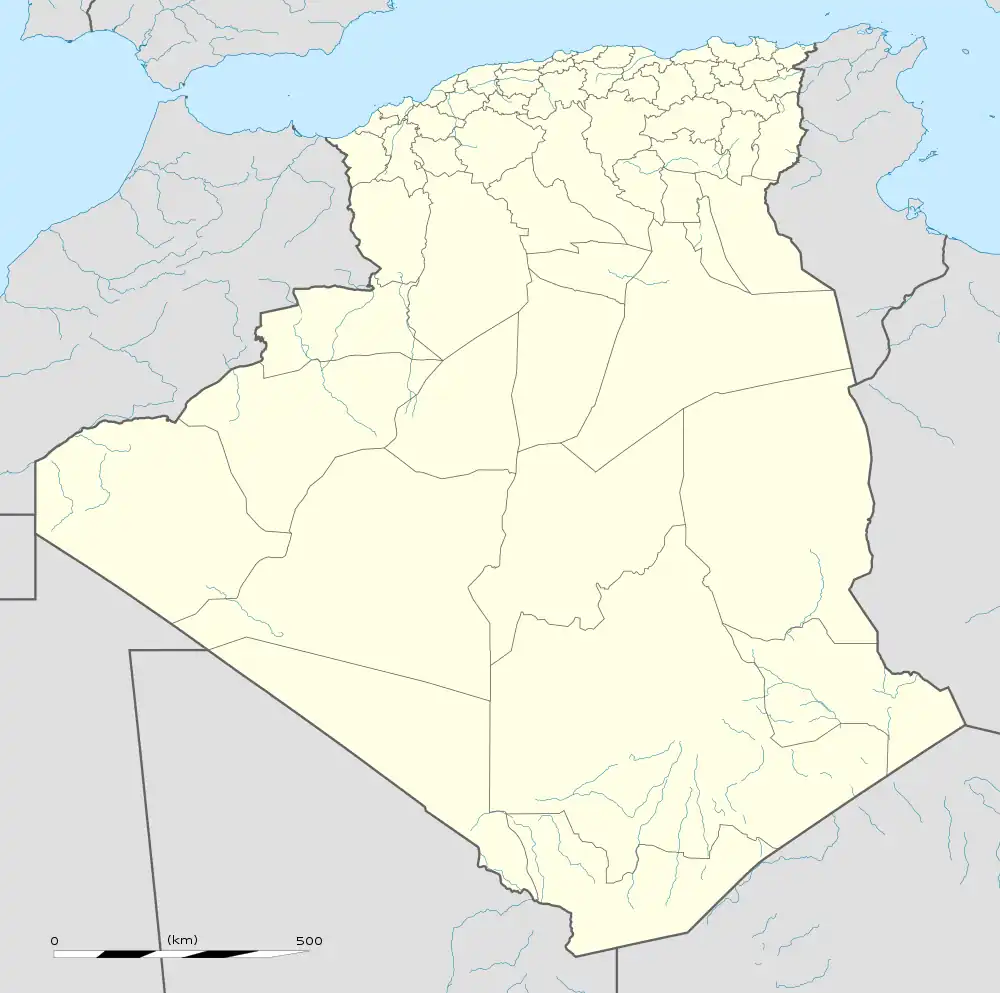 Laghouat Location of Laghouat in Algeria | |
| Coordinates: 33°48′10″N 2°52′30″E | |
| Country | |
| Province | Laghouat Province |
| District | Laghouat[1] |
| APC | 2012-2017 |
| Government | |
| • Type | Municipality |
| • Mayor | Benbehaz béchir |
| Area | |
| • Total | 400 km2 (200 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 769 m (2,523 ft) |
| Population (2008 census) | |
| • Total | 134,372 |
| • Density | 340/km2 (870/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| Postal code | 03000 |
| ISO 3166 code | CP |
| Website | www |
.jpg.webp)

Laghouat traces its history to at least the 11th century. It was ruled by the Ottoman Turks in 1786 and annexed to Beylik of Titteri (Médéa). The town experienced the brutal Siege of Laghouat in 1852, and came under French colonial rule until 1962.
It was formerly the administrative center of one of the four "Territories of the South" forming the region of Algeria administered under Martial Law until the reform instituted by the Statue of Algiers law of 20 September 1947.[2]
Since 1974, it has been the seat of a province of the same name.
The population of the town was 126,291 inhabitants in 2005. There are natural gas deposits in the region, and nearby Hassi R'Mel has the largest natural gas reserve in Africa. The city is served by Laghouat Airport. Ibn Khaldun described Laghouat as an important city in the Maghreb, located in an oasis, surrounded by mountains and fortified. He also wrote that the city was a center of trade and learning, with many madrasas (schools) and students coming from all over North Africa to study in Laghouat.
Ibn Khaldun also wrote about the history of Laghouat, which was founded by the Almoravids in the 11th century. He also wrote about the culture of Laghouat, which is Muslim and speaks Arabic and Berber. He also said that the people of Laghouat are known for their hospitality and their sense of hospitality.
Laghouat is an important city in the history of Algeria. It is a center of trade, learning, and culture, and a fortified city that played an important role in the defense of Algeria against Christians.
Here is a more detailed description of Laghouat, as written by Ibn Khaldun:
> "Laghouat is an important city in the Maghreb. It is located in an oasis, and it is surrounded by mountains. The city is fortified, and it is an important stronghold for Muslims against Christians. Laghouat is also a center of trade and learning. There are many madrasas (schools) in the city, and many students come from all over North Africa to study in Laghouat.
>
> The city of Laghouat was founded by the Almoravids in the 11th century. The Almoravids were a group of Muslims who conquered the Maghreb and Spain in the 11th century. They built many cities in the Maghreb, including Laghouat.
>
> The people of Laghouat are Muslims, and they speak Arabic and Berber. They are known for their hospitality and their sense of hospitality. Laghouat is a beautiful and important city, and it is a great place to visit if you are interested in learning more about the history and culture of the Maghreb."
Etymology
Laghouat literally means "houses surrounding gardens."[3]
The city and the region as a whole were named by several titles, including 'the capital of the steppe', 'the gateway to the Sahara', 'bride of the Saharan Atlas', and 'the city of the four seasons'.
Geography
The town of Laghouat is a regional center in the Algerian depression, an oasis south of Algiers. It is built on the banks of the Wadi Mzee, which flows eastwards from the Amour Range and is one of a large number of seasonal streams that empty into Chott Melrhir.
It is bordered to the north by the municipality of Sidi Makhlouf, to the west by Tadjemout and Kheneg, to the east the municipality of El Assafia, and to the south the municipality of Mekhareg.
Climate
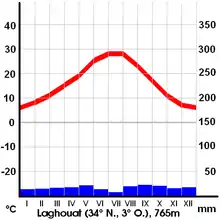
Laghouat has a cold desert climate (Köppen climate classification BWk). Rainfall is higher in winter than in summer. The average annual temperature in Laghouat is 17.4 °C (63.3 °F). About 176 mm (6.93 in) of precipitation falls annually. Rain falls irregularly, with severe droughts in some years. Sand dunes may encroach upon the town from the north in drought years, and have been countered with administrative buildings and a green belt of gardens around the city.
The town relies on groundwater, which is abundant due to a large underground dam in Tadjmout, which is the largest of its kind in Africa and dates to the colonial period. It is also known for its mineral water, called milok water, which has attracted investment from a Spanish bottler.
| Climate data for Laghouat | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 12.9 (55.2) |
15.5 (59.9) |
18.1 (64.6) |
22.8 (73.0) |
26.8 (80.2) |
32.6 (90.7) |
36.3 (97.3) |
35.3 (95.5) |
30.0 (86.0) |
23.5 (74.3) |
18.1 (64.6) |
13.4 (56.1) |
23.8 (74.8) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 2.7 (36.9) |
3.4 (38.1) |
6.0 (42.8) |
8.9 (48.0) |
13.5 (56.3) |
18.4 (65.1) |
21.6 (70.9) |
20.6 (69.1) |
17.1 (62.8) |
11.4 (52.5) |
5.8 (42.4) |
3.4 (38.1) |
11.1 (51.9) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 12 (0.5) |
12 (0.5) |
13 (0.5) |
15 (0.6) |
16 (0.6) |
12 (0.5) |
3 (0.1) |
26 (1.0) |
19 (0.7) |
20 (0.8) |
15 (0.6) |
13 (0.5) |
176 (6.9) |
| Source: Climate-Data.org, Climate data | |||||||||||||
Demographics

Most residents of Laghouat Province trace their origins to Berbers and Arabs and neighboring Bedouin tribes that roamed the area. The population was very small due to the relatively isolated nature of the city. In1928 it had 7,000 people, and 11,999 in 1954. After independence in 1962 it was recorded that about 1000 Europeans and 600 Jews departed, but the overall population increased very fast to the economic influx spurred on by the oil and gas industry.[2]
The town had a population of 170,693 people, according to 2012 estimates.
| the year | 1977 | 1987 | 1998 | 2008 | 2012 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| population | 42.186 | 69.435 | 106.665 | 144.747 | 170.693 |
History
Early history
Rock paintings and other archeological evidence indicate that people were living in the area during the Stone Age, from about 9,000 BC. It is believed that climatic change displaced these prehistoric peoples, as it later displaced Roman and Byzantine settlements. The town's location was noted in Roman records on a plateau called Tizgrarin. The inhabitants refused to submit to the Byzantines and convert to Christianity, and resisted paying tribute or taxes to the empires which followed, who sometimes called it a "rebel city".
Medieval and pre-colonial history
In the 14th century, Ibn Khaldoun reported the existence of a walled town which housed a faction of the "laghouat" tribe (called laghouat-ksel ), a branch of the Berber tribe of the Maghraouas. Over time, the majority of these peoples migrated westward, leaving only two factions in the city: the Berber-descended Sargins and the Ahlaf ("alliance") clans of Arabs. Various nomadic peoples also populated the town at times. In the 1650s the Moroccans established nominal control over the city, and in 1708 they sent out an expedition to create a tributary in Laghouat.[4] The region was taken from the Moroccans, and became a tributary of the Deylik of Algiers in 1727.[5] Other than occasional conflicts they regularly paid tribute annually of biannually to either the Bey of Oran, or the Bey of Titteri until 1828.[6]
French occupation
The due tribute payment was cut short in 1830, as the Deylik of Algiers collapsed in 1830 following the French invasion of Algiers.[7]
%252C_huile_sur_toile_%252C_Titre-_Le_dernier_combat_(_Bataille_de_LAGHOUAT_1852_).jpg.webp)
Laghouat was a center of resistance against French colonial rule from 1831 under Sheikh Moussa Ibn Hassen El Misri. In 1852, France launched a punitive campaign to eradicate the resistance. The Siege of Laghouat began on 21 November and concluded with the storming of the town on 4 December.[8] Several days of brutal massacres followed, which included one of the first recorded uses of chemical weapons on civilians. About two-thirds of the population perished, which became known locally as the Khalya (Arabic: emptiness). It also started a local tradition of protecting young boys from evil with an earring (then done to disguise them as girls).
Other settlements quickly capitulated following the example set at Laghouat, and the French used the town as a gateway for a land route to Sub-Saharan Africa, furthering their colonial ambitions.
During World War II, the Laghouat prison camp held British and Commonwealth servicemen, under the authority of Vichy France. The camp also held a large number of Jews who were described by the French authorities as Communists. Following the war, captured German soldiers were held at the camp.
Post-colonial period
In January 2012, Laghouat was the site of anti-government protests over improper housing, infrastructure, and treatment of the elderly by police. The police used tear gas to disperse the protesters.[9][10]
Arts and culture

Laghouat has a long tradition as a meeting place and cultural center, and has developed handicrafts based around the local raw materials.
In modern times, sand blasting art has emerged in Laghouat. Al-Taher Jadid is a local master of the form.[11]
Traditional dress
The traditional dress does not differ greatly from what is prevalent in the ancient cities, especially in the steppe and desert region.
As for the man, there are the brannos, the djellaba, the kandoora, the Arab trousers, the innovated “bra” chest, the shirt and the turban, which vary in size and have shrunk over time.
As for what can be mentioned regarding women’s clothing, there is what is called “Qanbouz,” which is a serene veil that only protrudes one eye, and it was made of blue and then white cloth, and it had ancient analogues, like other cities, such as the “Fattah veil” and there is the dress, the holly, the protection and the khmer. ..
However, these traditional clothes are almost extinct now for the sake of modern and imported clothes, which necessitates the establishment of a local museum of crafts, traditional clothes and jewelry that will serve history and the balance of developments and social changes and the formation of a civilizational balance that can be taken as a reference to be used in studies and inspired by new creations.
Tourism

The province has sought to develop tourism with new 4-star hotels, though the existing hotels in Laghouat do not exceed the 3-star rating.
The region is known for its variety of landscapes – mountain valleys, plateaus, plains, sand dunes and steppes – within a small area. Some call it the city of the four seasons, due to the diversity of the terrain.
Landmarks of the town include the old mosque, the fortress of Sidi El Hajj Issa, its shrine, the old quarter, palm groves, and the French colonial cathedral.

The French colonial military fort Tizgraren Tower (also called Buskaran Tower) was opened as a tourist attraction in 2011. It is located at the highest point in the town and dates to 1857. It has four wings, catacombs, and a large square containing the tomb of General Buskaran, who was assassinated within the fort. In the last years of colonization, the tower was converted from a barracks to a military hospital specialized in treating respiratory conditions and allergies. Following Algerian independence, it was used by various security departments.
.
See also
References
- "Décret executif n° 91-306 du 24 août 1991 fixant la liste des communes animées par chaque chef de daïra. 03 - Wilaya de Laghouat" [List of municipalities animated by each District chief: 03 - Laghouat Province] (PDF) (in French). Journal officiel de la République Algérienne. 4 September 1991. p. 1294. Retrieved 2019-11-03.
- Gibb, H. A. R.; Kramers, J. H. (2008). Shorter Encyclopaedia of Islam. Pentagon Press. pp. 595–597. ISBN 978-81-8274-341-0. OCLC 756316986.
- "Synagogue at Laghouat, Algeria | Archive | Diarna.org". archive.diarna.org. Retrieved 2022-11-15.
- Petit, Odette (1976). Laghouat: essai d'histoire sociale (in French). O. Petit.
- Revue tunisienne (in French). Au Secrétariat général de l'Institut de Carthage. 1900.
- Bulletin du comité des travaux historiques et scientifiques: section de géographie (in French). Imprimerie nationale. 1894.
- Abou-Khamseen, Mansour Ahmad (1983). The First French-Algerian War (1830-1848): A Reappraisal of the French Colonial Venture and the Algerian Resistance. University of California, Berkeley.
- "La conquête coloniale de l'Algérie débute le 14 juin 1830". rebellyon.info (in French). Retrieved 2021-05-16.
- "10 injured, several arrested in Algeria protests". Agent France Press. Retrieved 13 January 2012.
- "Anger at squalid housing unleashes Algeria protest". Reuters. Retrieved 13 January 2011.
- Algerian Artist Creates Using "Sanding Technology", BBC Arabic.
.svg.png.webp)