Languages of Togo
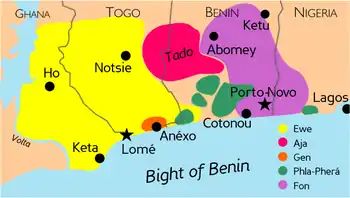
Togo is a multilingual country, which according to one count has 44 languages spoken.[1] The official language is French. In 1975, the government designated two indigenous languages - Ewé (Ewe: Èʋegbe) and Kabiyé - as national languages, meaning that they are promoted in formal education and the media. The two national languages tend to be used regionally with Ewé used in the south from Lomé to Blitta, and Kabiyé from Blitta to Dapaong in the north.
Togo joined the Commonwealth in June 2022.[2] Prior to its admission at the 2022 Commonwealth Heads of Government Meeting, Foreign Minister Robert Dussey said that he expected Commonwealth membership to provide opportunities for Togolese citizens to learn English and access new educational and cultural resources. He also remarked that the country sought "to forge closer ties with the anglophone world."[3]
References
- Le français au Togo: une aventure ambigüe, Isabelle Anzorge, Université Nice, 1998.
- Ethnologue, "Languages of Togo" (accessed Oct. 31, 2010)
- Turner, Camilla (2022-06-22). "Togo and Gabon to become newest members of Commonwealth this week". The Daily Telegraph. ISSN 0307-1235. Retrieved 2022-06-29.
- Lawson, Alice (2022-06-24). "Togo sees Commonwealth entry as pivot to English-speaking world". Reuters. Retrieved 2022-07-01.
External links
_Chez_Maman_la_Joie.jpg.webp)

