Lehigh Valley International Airport
Lehigh Valley International Airport (IATA: ABE, ICAO: KABE, FAA LID: ABE), formerly Allentown–Bethlehem–Easton International Airport, is a domestic airport located in Hanover Township in Lehigh County, Pennsylvania. Lehigh Valley International Airport is located in the center of the Lehigh Valley, roughly 7 miles (11 km) northeast of Allentown, 4 miles (6.4 km) northwest of Bethlehem, and 11 miles (18 km) southwest of Easton.
Lehigh Valley International Airport | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
.JPG.webp) Main terminal of Lehigh Valley International Airport, March 2014 | |||||||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||||||
| Airport type | Public | ||||||||||||||
| Owner/Operator | Lehigh–Northampton Airport Authority | ||||||||||||||
| Serves | Lehigh Valley | ||||||||||||||
| Location | Hanover Township, Pennsylvania, U.S. | ||||||||||||||
| Operating base for | Allegiant Air | ||||||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 393 ft / 120 m | ||||||||||||||
| Coordinates | 40°39′08.4″N 075°26′25.7″W | ||||||||||||||
| Website | flyabe.com | ||||||||||||||
| Maps | |||||||||||||||
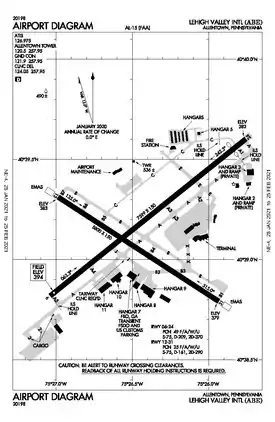 FAA diagram of the airport as of January 2021 | |||||||||||||||
 ABE Location of airport in Pennsylvania  ABE ABE (the United States) | |||||||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
| Statistics (2022) | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
Lehigh Valley International Airport is the fourth-busiest airport in Pennsylvania, after Philadelphia, Pittsburgh, and Harrisburg international airports and the only commercial passenger service airport located in the Lehigh Valley, Pennsylvania's third-most populous metropolitan region. As of 2020, the airport is utilized by 851,000 passengers annually.
The airport is also heavily utilized for the transport of air cargo due to growth of e-commerce and its close proximity to major population centers on the East Coast.[4] As of 2016, the airport ships more than 126 million pounds of cargo annually with growth of nearly 166% in cargo tonnage shipped between 2015 and 2016. Companies such as Amazon.com are using the airport, a major factor in its growth.[5]
History


Lehigh Valley International Airport opened in 1929. Scheduled airline flights began on September 16, 1935 with flights by United Airlines' Boeing 247s. The airport hangar initially served as the passenger terminal. The first terminal building at the airport was built in 1938 as part of a Works Progress Administration project.
During World War II, the U.S. Navy's V-5 flight training program was conducted at the airport in conjunction with ground training held at Muhlenberg College in nearby Allentown. In addition, the headquarters of Group 312 of the Civil Air Patrol was at Allentown–Bethlehem Airport. One of its activities was to provide a courier service for cargo defense plants. Allentown CAP pilots also patrolled the Atlantic coastline and were active in recruiting young men for the United States Army Air Forces's air cadet program.
By January 1944, work on a new runway was completed and a Class A United States Weather Bureau station had been installed. About 1,000 Naval Aviation Cadets were trained in 1943, and civil and military air traffic had increased. In late July, the War Production Board approved the construction of a second story addition to the administration building. The building housed the Lehigh Aircraft Company, the weather bureau station, the Civil Aeronautic communications station, and the office and waiting room of United Air Lines. In August, the V-5 flight training program ended when the Navy decided to move all flight training to naval air bases under Navy pilots.
In April 1946, the Lehigh Airport Authority was created to own and manage the airport. The October 1946 command and general staff diagram shows four runways forming an asterisk: runway 1 was 2680 feet long, runway 6 was 4000 feet, runway 9 was 3800 feet and runway 14 was 3100 feet.
Construction on a new passenger terminal began in 1948 and was finished in 1950. Allentown–Bethlehem–Easton (ABE) Airport, as it was then called, had flights on United, Trans World Airlines since 1947, and Colonial Airlines since 1949–50. Douglas DC-4s and DC-6s appeared after runway 6 was extended to 5,000 feet. TWA left in 1967, replaced by Allegheny Airlines; Colonial's successor Eastern Air Lines remained until 1991. Republic Airlines' McDonnell Douglas DC-9's offered nonstop flights to Detroit and were continued by Northwest Airlines after Northwest's acquisition of Republic. Northwest also offered one-stop flights to Detroit with a stop in Harrisburg. Regional partners replaced successor Northwest around 2003. Delta Air Lines started nonstop flights to Atlanta and Harrisburg in 1991 and later added flights to Cincinnati, initially operated by Delta until changing to Delta Connection carrier Comair.
In 2012, Frontier Airlines started twice a week nonstop Airbus A319 flights to Orlando International Airport; they ended in 2013. Allegiant Air now flies nonstop from Lehigh Valley to Orlando via Orlando Sanford International Airport (SFB) in nearby Sanford, Florida.[6][7]
Construction began on the present terminal in 1973. The project, designed by Wallace & Watson, was completed in 1976.[8]
The most recent terminal renovations were completed in two phases:
- Phase I (April 2009). Cost: $7,253,235; PENNDOT grant amount: $3 million; general contractor: Lobar, Inc. (Dillsburg, PA); architect: Breslin, Ridyard, Fadero Architects (Allentown, PA); square footage of the Phase I project: 24,000 sq.ft., 7,000 sq.ft. of which is new space.
- Phase II (November 2010). Cost: about $7,225,000; PENNDOT grant amount: $3.5 million; general contractor: E.R. Stuebner Construction, Inc. (Reading, PA); architect: Breslin, Ridyard, Fadero Architects (Allentown, PA); square footage of renovated space: 33,600 sq.ft.[9]
On May 26, 2016, Solar Impulse 2 (SI2), piloted by Bertrand Piccard, completed the 13th leg (from Dayton, Ohio) of the first around the world (43,041 km) fuel-less flight by this solar-powered plane with a landing at ABE.[10] On June 11, 2016, André Borschberg began the 14th leg (ABE to JFK, which included a dramatic Statue of Liberty flyover).[11] While at ABE, an open house was held for public viewing of the SI2 aircraft.
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems for 2023–2027 categorizes Lehigh Valley International Airport as a small hub primary commercial service facility.[12] In 2019 to 2023, the FAA categorized the airport as a "non-hub primary" and previous years it was categorized as a "small hub."
After several years of falling passenger counts in the early 2000s, the airport has lately experienced a significant rebound in passenger totals due to it being an alternative to congested airports in Philadelphia and Newark, its facility improvements, a rapidly growing regional population, carrier expansions (especially Allegiant Air), and multiple new routes being added for popular destinations and major hubs across the country. The airport was utilized by 911,970 passengers in 2019, which represents an increase of 15.01% over its use the previous year, in 2018. Much of this growth has been driven by Allegiant Airlines' expansion at the airport.[13][14][15][16]
One of the shortest scheduled jet flights in the contiguous US operated between Lehigh Valley (ABE) and Philadelphia International (PHL) airports. Piedmont Airlines operating as American Eagle (airline brand) regularly flew an Embraer ERJ-145 regional jet on the 55-mile route on behalf of American Airlines via a code sharing agreement. The average time in the air was 20 minutes. It was the shortest flight in the contiguous United States until 2017, when it was surpassed by United Express's San Francisco to Santa Rosa route in 2017, which had an average time in the air of 16 minutes. The ABE-PHL flights ended in 2020.[17]
Facilities
The airport covers 2,278 acres (922 ha) at an elevation of 393 feet (120 m). It has two asphalt runways: 6/24, 7,599 by 150 feet (2,316 x 46 m) and 13/31, 5,800 by 150 feet (1,768 x 46 m).[3][18] The airport has nine gates to service the passengers. The airport has six holding spots for cargo aircraft. Mainly Boeing 757 cargo aircraft fly in and out of the airport for FedEx along with Amazon Prime Air Boeing 767s.
In the year ending December 31, 2018 the airport had 75,231 aircraft operations, an average of 206[19] per day: 73% general aviation, 14% commercial airline, 12% air taxi, and <1% military. In May 2020, 137 aircraft were based at the airport: 73 single-engine, 11 multi-engine, 52 jet, and 1 helicopter.[3]
In the year ending March 2020 the airport handled about 192,000,000 pounds (87,000,000 kg) of freight/mail.[2]
The Lehigh-Northampton Airport Authority also operates two nearby general aviation airports, Allentown Queen City Municipal Airport in Allentown and Braden Airpark in Easton.
Fire department
Aircraft rescue and firefighting (ARFF) is provided by the LNAA ARFF Department, which consists of seven full-time and three part-time personnel, operating from a 13,000 sq.ft. facility commissioned in October 2003.[20]
Airlines and destinations
.jpg.webp)


Passenger
| Airlines | Destinations | Refs |
|---|---|---|
| Allegiant Air | Denver, Fort Lauderdale, Myrtle Beach, Nashville, Orlando/Sanford, Punta Gorda (FL), Sarasota, Savannah, St. Petersburg/Clearwater Seasonal: Melbourne/Orlando (begins November 17, 2023)[21] | [22] |
| American Eagle | Charlotte | [23] |
| Delta Connection | Atlanta | |
| United Express | Chicago–O'Hare | [24] |
| Passenger destinations map |
|---|
 Allentown Destinations from Lehigh Valley International Airport Red = Year-round destination Green = Seasonal destination Blue = Future destination Pink = Destination being terminated |
Cargo
Amazon.com uses the Lehigh Valley International Airport (LVIA) as one of only 11 locations in the country for their Amazon Air shipping service. LVIA was one of the first airports selected for the pilot concept of the program due to its close proximity to large population centers, cost-effectiveness, robust infrastructure, and comparative ease of use. This location now ships more merchandise, has more flights and serves more people (over 75 million from Boston to Washington, D.C., as of late 2016) for Amazon than any other facility in the country. Both Amazon and LVIA continue to invest heavily in the local area to better support the ever-increasing demand for air cargo driven in large part by the explosive growth of e-commerce and the need for faster, more efficient delivery of merchandise.[25]
Due to the same aforementioned reasons for Amazon increasing its operations at the airport, FedEx Ground has selected an area near LVIA to construct its largest terminal in the country.[26]
ABE currently has six cargo parking spots for cargo operations.
| Cargo destinations map |
|---|
 Allentown Cargo destinations from Lehigh Valley International Airport = Year-round destination = Seasonal destination |
Former carriers
- Southeast Airlines (November 2002–August 2012)[27]
- AirTran Airways (April 2009–August 2012)[28]
- Air Canada, Air Toronto, Air Georgian (until 2012)[29]
- Trans World Airlines (November 1993-____)[30]
- Provincetown-Boston Airlines
- Freedom Airlines
- Eastern Airlines
- Frontier Airlines
- US Airways, USAir, Allegheny Airlines
- Republic Airlines
- Continental Airlines, Continental Express
- Piedmont Airlines, Piedmont Connection
- Presidential Airways
- Colgan Airways
- Suburban Airlines
- Altair Airlines
- Monmouth Airlines
- Canadian Partners, Ontario Express
- Holiday Airlines
- Hooters Air (May 2005-April 2006)[31]
Bus service
Trans-Bridge Lines runs several daily buses from ABE to Manhattan, stopping at both Newark (EWR) and New York (JFK) Airports. Travel time to EWR is about 75 minutes.[32]
United Airlines also has a bus service to Newark Liberty International Airport (EWR).[33] Continental Airlines, which later merged into United, previously operated flights from Allentown to Newark but switched to a bus service in 1995 due to constant delays from air traffic control.[34] The distance is 79 miles (127 km). As of 1997, the service was eight times daily. Today, the service is offered three times daily.[35] By February 2010, bus was the only form of service offered by Continental after it cancelled its Allentown to Cleveland Hopkins International Airport flights.[34]
American Airlines operates a bus service to Philadelphia International Airport.[36]
LANta provides local bus service to the airport with routes 215 (Bethlehem), 319 (Lehigh Valley Mall-Bethlehem Square), and 325 (Allentown).[37]
Statistics
Annual traffic
| Year | Passengers | Change | Year | Passengers | Change | Year | Passengers | Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 1,013,710 | — | 2010 | 838,141 | 2020 | 390,764 | ||
| 2001 | 912,904 | 2011 | 873,351 | 2021 | 752,111 | |||
| 2002 | 798,154 | 2012 | 723,556 | 2022 | 912,256 | |||
| 2003 | 982,777 | 2013 | 621,896 | |||||
| 2004 | 1,009,951 | 2014 | 612,650 | |||||
| 2005 | 831,570 | 2015 | 673,097 | |||||
| 2006 | 788,511 | 2016 | 688,505 | |||||
| 2007 | 847,527 | 2017 | 692,154 | |||||
| 2008 | 779,968 | 2018 | 792,974 | |||||
| 2009 | 748,482 | 2019 | 911,970 |
Carrier shares
| Carrier | Passengers (arriving and departing) |
|---|---|
| Allegiant | 485,000(56.29%) |
| PSA | 122,000(14.15%) |
| SkyWest | 111,000(12.88%) |
| Endeavor Air | 60,000(6.91%) |
| Air Wisconsin | 42,000(4.87%) |
| Other | 42,000(4.90%) |
Top destinations
| Rank | Airport | Passengers | Carriers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 96,000 | Allegiant | |
| 2 | 61,000 | American | |
| 3 | 60,000 | Delta | |
| 4 | 50,000 | American, United | |
| 5 | 45,000 | Allegiant | |
| 6 | 33,000 | Allegiant | |
| 7 | 21,000 | Allegiant | |
| 8 | 17,000 | Allegiant | |
| 9 | 15,000 | Allegiant | |
| 10 | 14,000 | Delta |
Incidents and accidents
20th century
- On May 5, 1972, Eastern Air Lines Flight 175, a Boeing 727 en route to Washington National Airport was hijacked by Frederick Hahneman, a Honduran-American. The plane eventually landed in Honduras after Hahneman parachuted in mid-flight with $300,000 in ransom money. There were no fatalities or injuries.
21st century
- On September 19, 2008, Mesa Airlines Flight 7138, a Bombardier CRJ700, was forced to make a high-speed aborted takeoff and swerve in order to avoid a collision with a Cessna 172 that had yet to exit the airport's runway after landing. There were no fatalities or injuries.[42]
- On November 16, 2008, US Airways Flight 4551, a US Airways Express De Havilland Canada Dash 8 turboprop operated by Piedmont Airlines, took off from Lehigh Valley International Airport at 8:20 am headed to Philadelphia International Airport when the flight was forced to make an emergency landing. The flight crew indicated that the front nose gear had not come down, and the plane had to make a flyover of the runway for confirmation. There were no injuries among the 35 passengers and three crew members.[43]
- On June 27, 2009, Allegiant Air Flight 746, a McDonnell Douglas MD-80 aircraft, made an emergency landing at the airport after flames were observed coming from the aircraft's left engine. The flight was bound for Orlando Sanford International Airport. During takeoff, one of the aircraft's tires shredded and part of it was sucked into the engine, causing engine failure and a momentary fire. The plane landed safely minutes later with no injuries reported.[44]
- On February 27, 2023, Mark Muffley, a passenger from Lansford, Pennsylvania, attempted to board an Allegiant Air flight from Lehigh Valley International Airport to Orlando International Airport after having allegedly checked luggage that included an explosive device. After being paged, the passenger fled the airport and was later arrested by federal agents and charged with "possessing an explosive in an airport and attempting to place an explosive on an aircraft", according to New York Post.[45]
Notable visits
In 1960, then U.S. Vice President Richard Nixon and Senator John F. Kennedy made campaign stops at ABE. President George H. W. Bush visited ABE in 1992 onboard Air Force One, a Boeing VC-25 (747). Former President Donald Trump also made two campaign stops at ABE in May and October 2020.[46]
References
- Lehigh Valley International Airport, official website
- "RITA BTS Transtats – ABE". transtats.bts.gov.
- FAA Airport Form 5010 for ABE PDF, effective May 21, 2020
- Assad, Matt. "LVIA weighs future with Amazon as air cargo becomes big business". Lehigh Valley Business Cycle. Retrieved August 19, 2017.
- Kraus, Scott. "LVIA air traffic jumped in 2016, due mostly to cargo". Lehigh Valley Business Cycle. Retrieved August 19, 2017.
- Tom Zanki (February 28, 2012). "Frontier Airlines to Join Lehigh Valley International Airport". Express-Times.
- "Frontier Airlines Drops Nonstop Service between LVIA and Orlando". Lehighvalleylive.com. November 15, 2012.
- "The A-B-E Airport" (PDF). Modern Steel Construction. New York: American Institute of Steel Construction. 15 (3): 6–7. 1975. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 14, 2012. Retrieved June 16, 2012.
- "Lehigh Valley International Airport Files Phase I and II 6102666001". Retrieved December 25, 2012.
- "13th Leg from Dayton to Lehigh Valley". Solar Impulse.
- "14th Leg from Lehigh Valley to New York". Solar Impulse.
- "National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems (NPIAS) 2023–2027: Appendix A – List of NPIAS Airports" (PDF). FAA. p. 103. Retrieved February 22, 2023.
- "Cargo traffic soars, as more passengers choose LVIA, too". lehighvalleylive.com. Retrieved August 19, 2017.
- The Morning Call, No U.S. Customs station at LVIA, but bluer skies may be ahead., Matt Assad, October 21, 2014, http://www.mcall.com/news/local/mc-allentown-airport-passenger-traffic-20141021-story.html
- "LVIA adds $5.2M transportation hub for buses, taxis and rental cars | LVB". Lehigh Valley Business. Retrieved August 19, 2017.
- "Passenger traffic increases nearly 20 percent at LVIA – LVB". November 27, 2017.
- "OST_R | Transtats". transtats.bts.gov.
- "ABE airport data at skyvector.com". skyvector.com. Retrieved September 16, 2022.
- http://aspm.faa.gov/opsnet/sys/opsnet-server-x.asp
- "Fire Department – Lehigh Valley International Airport (ABE)". flylvia.com. Archived from the original on September 18, 2017. Retrieved September 17, 2017.
- "Allegiant announces new flights to Florida from Lehigh Valley International Airport". The Morning Call. July 11, 2023.
- "Allegiant Air Route Map". allegiantair.com. Retrieved April 5, 2017.
- "Flight schedules and notifications". Retrieved April 5, 2017.
- "Flight schedules and notifications". Retrieved October 10, 2020.
- Assad, Matt. "Amazon has LVIA flying high". Lehigh Valley Business Cycle. Retrieved August 19, 2017.
- Salamone, Matt Assad, Anthony. "Lehigh Valley FedEx Ground terminal to be company's largest in U.S., VP says". Lehigh Valley Business Cycle. Retrieved August 19, 2017.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Cassi, Sarah (January 21, 2012). "AirTran pulls out of Lehigh Valley International Airport". lehighvalleylive.
- AirTran Airways Shifts Into High Gear with New Flights to Allentown, Pa. M2PressWIRE. June 25, 2009.
- Call, The Morning (January 20, 2012). "AirTran discontinuing service at LVIA". themorningcall.com.
- Call, The Morning (September 29, 1993). "TWA to begin service at A-B-E Airport". themorningcall.com.
- Kraft, Randy (September 27, 2012). "Now-defunct Hooters Air still owes LVIA $2 million". WFMZ.
- "Allentown / Clinton / New York".
- "United Archived October 27, 2016, at the Wayback Machine." Lehigh Valley International Airport. Retrieved October 27, 2016. "Non Stop to:[...]Newark"
- Karp, Gregory (May 4, 2010). "Airlines merger could halt bus flight". The Morning Call. Retrieved October 27, 2016.
- Wade, Betsy (December 14, 1997). "PRACTICAL TRAVELER; When the Plane Is Really a Bus". The New York Times. Retrieved October 27, 2016.
- Rains, Taylor (May 18, 2022). "American is expanding its bus service from small cities to hub airports as it cuts regional flying". Business Insider.
- "Routes and Schedules".
- "LNAA Fact Sheet – Lehigh Valley International Airport (ABE)". flylvia.com. Archived from the original on September 17, 2017. Retrieved September 17, 2017.
- "Dec 2015 Monthly Traffic Report" (PDF). flylvia.com. Retrieved September 17, 2017.
- "STRONG FINISH BRINGS INCREASE AT ABE". flylvia.com. January 23, 2018. Retrieved July 22, 2018.
- "LEHIGH VALLEY INTERNATIONAL AIRPORT MONTHLY TRAFFIC REPORT, DECEMBER 2021" (PDF). Retrieved June 19, 2022.
- "Press Release [November 19, 2008] - NTSB – National Transportation Safety Board". Archived from the original on May 29, 2014. Retrieved May 29, 2014.
- "Plane slides down Philly runway minus front wheels – Yahoo! News". Archived from the original on December 11, 2008. Retrieved January 14, 2017.
- "Plane makes emergency landing at Lehigh Valley International Airport". Archived from the original on July 1, 2009.
- "Bomb found in luggage at Lehigh Valley International Airport", New York Post, March 1, 2023
- Hall, Peter (October 26, 2020). "What you need to know about President Trump's Lehigh Valley visit". Morning Call. Retrieved June 19, 2022.
External links
- Official website
- Lehigh Valley International Airport on Twitter
- FAA Airport Diagram (PDF), effective October 5, 2023
- FAA Terminal Procedures for ABE, effective October 5, 2023
- Resources for this airport:
- AirNav airport information for KABE
- ASN accident history for ABE
- FlightAware airport information and live flight tracker
- NOAA/NWS weather observations: current, past three days
- SkyVector aeronautical chart for KABE
- FAA current ABE delay information