1. FC Lokomotive Leipzig
1. Fußballclub Lokomotive Leipzig e.V. is a German football club based in the locality of Probstheida in the Südost borough of Leipzig, Saxony. The club was previously known as VfB Leipzig and was the first national champion of Germany. It has also been known as SC Leipzig. The club won four titles in the FDGB-Pokal and the 1965–66 Intertoto Cup during the East German era. It also finished runner-up in the 1986–87 European Cup Winners' Cup. 1. FC Lokomotive Leipzig was renamed VfB Leipzig after German re-unification and managed to qualify for the Bundesliga in 1993. However, like many clubs of the former DDR-Oberliga, VfB Leipzig faced hard times in reunified Germany and a steady decline soon followed. 1. FC Lokomotive Leipzig was refounded in 2003 and has climbed through divisions since then. The team competes in the fourth-tier Regionalliga Nordost as of 2021. The 1. in front of the club's name indicates that it was the first to be founded in the city.
 | |||
| Full name | 1. Fußballclub Lokomotive Leipzig e.V. | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Nickname(s) | Loksche | ||
| Founded | 11 November 1893 (as SC Sportbrüder Leipzig) | ||
| Ground | Bruno-Plache-Stadion | ||
| Capacity | 15,600 | ||
| Chairman | Thomas Löwe | ||
| Coach | Almedin Civa | ||
| League | Regionalliga Nordost (IV) | ||
| 2022–23 | 4th | ||
| Website | Club website | ||
|
| |||
History
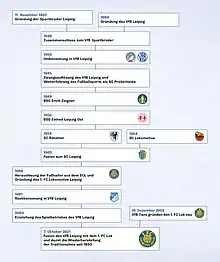
1. FC Lokomotive Leipzig claims to be the successor to the VfB Leipzig and SC Sportbrüder Leipzig, established in 1896 and 1893, respectively, and to be, therefore, one of the oldest clubs of the German Football Association. However, they are not nominal successors. In 2018, 1. FC Lokomotive announced a merger with the formally extant but bankrupt and dormant VfB Leipzig in order to be entitled to the forerunner's titles.[1] Due to the significant breaks and turmoils in the club's history, especially during the post-World War II era, many fans identify 1966 as the year of establishment rather than 1893.
VfB Leipzig (1893–1946)
The club was formed as VfB Leipzig on 13 May, 1896, out of the football department of the gymnastics club Allgemeine Turnverein 1845 Leipzig. However, the club laid claim to an earlier date of origin by reaching back to a club that was merged with VfB Leipzig in 1898, the SC Sportbrüder Leipzig, which was one of four football clubs formed in Leipzig in 1893.
Following the merger with SC Sportbrüder Leipzig, the club competed under the name VfB Sportbrüder 1893 Leipzig. VfB Sportbrüder 1893 Leipzig was one of the original 86 teams that came together in the city on 28 January 1900 to form the German Football Association (DFB). On 2 May, 1900, the Sportbrüder 1893 part of the name was dropped, and the team became again known as VfB Leipzig.


VfB Leipzig were immediately successful at their chosen sport and made their way to the first German national championship final held in 1903. Their opponents were DFC Prag, a German-Jewish side from Prague, which was then part of Austria-Hungary. The DFB had invited "German" clubs of this sort from other countries in order to boost numbers in their new national association.
DFC Prag had made their way to the final under circumstances that had allowed them to avoid playing a single playoff match, while VfB Leipzig had come through some hard-fought matches. Arriving in Hamburg for the match, the heavily favoured Pragers took themselves off on an ill-advised pub crawl the night before the contest and so arrived on the pitch in less than ideal match shape. The contest was delayed by half an hour as officials scrambled to find a football that was in good condition. The host, FC 93 Altona Hamburg, provided a new ball, and 11 minutes in, DFC Prag scored the first goal. At the end of the first half, the score stood at 1–1, but VfB Leipzig then pulled away to emerge as the first winners of the Viktoria Meisterschaftstrophäe ("Victoria Championship Trophy"), representative of German football supremacy, on the strength of a decisive 7–2 victory.
VfB Leipzig played themselves into another final appearance in 1904, but the match was never contested. A protest by FV Karlsruhe over their disputed semi-final with Britannia Berlin was never resolved, and the DFB called off the final only hours before its scheduled start. There would be no champion that year. The following season, VfB Leipzig found themselves unable to cover the expense of travelling to participate in their scheduled first-round playoff match and so were eliminated from that year's competition. However, they did go on to raise the Viktoria again in 1906 and 1913 and also played in the 1911 and 1914 finals.
In the period leading up to World War II, VfB Leipzig was unable to repeat its early success. Gyula Kertész coached the side from 1932-33.[2]
After the reorganization of German football leagues under the Third Reich in 1933, the club found itself in Gauliga Sachsen, one of the 16 upper-tier divisions. While they earned strong results within their own division, they were unable to advance in the playoff rounds. In 1937, they captured the Tschammerpokal, known today as the DFB-Pokal, in a match against Schalke 04, the dominant side of the era.
Post-war turmoil

The club, like most other organizations in Germany, including sports and football clubs, was dissolved by the occupying Allied authorities in the aftermath of the war. Club members reconstituted the team in 1946 as SG Probstheida under the auspices of the occupying Soviets. After playing as BSG Erich Zeigner Probstheida and then BSG Einheit Ost, the club merged with sports club SC Rotation Leipzig in 1954 and played in the DDR-Oberliga, East Germany's top-flight league, but earned only mediocre results. In 1963, the city of Leipzig's two most important sports clubs, SC Rotation and SC Lokomotive Leipzig, were merged, resulting in the founding of two new sides: SC Leipzig and BSG Chemie Leipzig.
1. FC Lokomotive (1966–1990)
East German football went through a general reorganization in 1965, creating football clubs as centres of high-level football, during which the football department of SC Leipzig was separated from the sports club and reformed into football club 1. FC Lokomotive Leipzig, while rival Chemie Leipzig continued as a Betriebssportgemeinschaft (BSG), or corporate team. Like most East German clubs, it was assigned to a publicly owned enterprise as its "sponsor". In the case of Lokomotive, the providing enterprise was Deutsche Reichsbahn—the East German state railways—hence the name. The club's fortunes improved somewhat as they almost always finished well up the league table, but they were unable to capture the top honour in the DDR-Oberliga with losing final appearances in 1967, 1986, and 1988.
Lok earned a clutch of East German Cups (FDGB Pokal) with victories in 1976, 1981, 1986, and 1987, against failed appearances in the Cup final in 1970, 1973, and 1977. They also won the UEFA Intertoto Cup in 1966 and made an appearance in the 1987 final of the European Cup Winners' Cup, falling 0-1 to Johan Cruyff's Ajax after a Marco van Basten goal.
VfB Leipzig (1991–2004)
The re-unification in 1990 was followed by the merger of the football leagues of the two Germanies[3] a year later. A poor season led to a seventh-place finish in the transitional league, but an unexpectedly strong playoff propelled the club into the 2. Bundesliga.
1. FC Lokomotive grasped at their former glory by reclaiming the name VfB Leipzig. A third-place finish in 1993 advanced the team to the top-flight Bundesliga, where they finished last in the 1994 season. The new VfB began a steady slide down through the 2. Bundesliga into the Regionalliga Nordost (III) by 1998 and then further still to the NOFV-Oberliga Süd (IV) by 2001. They were bankrupted in 2004, their results were annulled, and the club was dissolved.
1. FC Lokomotive (since 2003–04)
In late 2003, the club was re-established by a group of fans as 1. FC Lokomotive Leipzig. The renewed side had to start in the lowest league, eleventh-tier 3. Kreisklasse, Staffel 2, in 2004–05. Even so, they continued to receive solidly enthusiastic fan support: their match against Eintracht Großdeuben's second team in the Leipzig Zentralstadion on 9 October, 2004, broke the world record for lower-league attendance with 12,421 spectators. Thanks to a merger with SSV Torgau, the club could play in the seventh-tier Bezirksklasse Leipzig, Staffel 2, in 2005–06. Finishing this league as champions, the team qualified for the sixth-tier Bezirksliga. In 2006, 1. FC Lokomotive Leipzig also played a friendly match against FC United of Manchester (4–4) and qualified for the 2006–07 Landespokal by winning the Bezirkspokal. 1. FC Lokomotive Leipzig finished as champions of their group and were promoted to the fifth-tier Landesliga Sachsen Group for the 2007–08 season. The club finished second to Erzgebirge Aue and missed out on direct promotion to the NOFV-Oberliga Süd by two points in the 2007–08 season. It still had the chance to regain Oberliga status through a relegation play-off with Schönberg, winning the first leg 2–1 at Schönberg. In the return leg, in front of almost 10,000 spectators, the club lost 0–1 but still gained Oberliga promotion via the away goals rule.[4]
1. FC Lokomotive Leipzig finished the Oberliga in third place in 2008–09, 12th in 2009–10, and eighth in 2010–11. 1. FC Lokomotive Leipzig was promoted to Regionalliga Nordost after finishing Oberliga sixth due to the reserve teams of FC Rot-Weiß Erfurt, Dynamo Dresden, and FC Carl Zeiss Jena being ineligible for promotion. Lokomotive finished in tenth place in the 2012–13 season but were relegated to Oberliga Nordost after finishing 15th in 2013–14.[5][6]
The club stayed in contention for promotion back up to the Regionalliga during the 2014–15 season, having hired former German international Mario Basler as director of sports in early 2015. In the final match of the season, Lok supporters stormed the field after their club had fallen behind 2–0, forcing the match to be abandoned and the club to finish outside of the promotion ranks.[7] The club finished in first place in the southern group of the NOFV-Oberliga and returned to the Regionalliga Nordost for the 2016–17 season.
Rivalries
The club's fans share a fierce and often violent rivalry with the supporters of Chemie Leipzig. When both teams met in the quarter finals of the Sachsenpokal in 2016, German daily newspaper Die Welt called the match the "German hooligan summit".[8] An additional reason for the enmity between some fan groups (namely their ultras) is a political one. Whereas certain Chemie fan clubs express left-wing and anti-fascist political views, Lok has vocal supporters from the right and far-right of the political spectrum.[9][10] Lok also have lesser local rivalry with RB Leipzig.
Lokomotive Leipzig in European competitions
| Season | Competition | Round | Nation | Club | Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1963–64[lower-alpha 1] | Inter-Cities Fairs Cup | 1R | Újpesti Dózsa | 0–0, 2–3 | |
| 1964–65[lower-alpha 1] | Inter-Cities Fairs Cup | 1R | Wiener Sport-Club | 1–2, 0–1 | |
| 1965–66[lower-alpha 1] | Inter-Cities Fairs Cup | 2R | Leeds United | 1–2, 0–0 | |
| 1966–67 | Inter-Cities Fairs Cup | 1R | Djurgårdens IF | 3–1, 2–1 | |
| 2R | RFC Liège | 0–0, 2–1 | |||
| 1/8 | Benfica | 3–1, 1–2 | |||
| 1/4 | Kilmarnock | 1–0, 0–2 | |||
| 1967–68 | Inter-Cities Fairs Cup | 1R | Linfield | 5–1, 0–1 | |
| 2R | Vojvodina | 0–0, 0–2 | |||
| 1968–69 | Inter-Cities Fairs Cup | 1R | KB | Walkover | |
| 2R | Hibernian | 1–3, 0–1 | |||
| 1973–74 | UEFA Cup | 1R | Torino | 2–1, 2–1 | |
| 2R | Wolverhampton Wanderers | 3–0, 1–4 | |||
| 1/8 | Fortuna Düsseldorf | 1–2, 3–0 | |||
| 1/4 | Ipswich Town | 0–1, 1–0 (4–3 a.p.) | |||
| 1/2 | Tottenham Hotspur | 1–2, 0–2 | |||
| 1976–77 | UEFA Cup Winners' Cup | 1R | Hearts | 2–0, 1–5 | |
| 1977–78 | UEFA Cup Winners' Cup | 1R | Coleraine | 4–1, 2–2 | |
| 1/8 | Real Betis | 1–1, 1–2 | |||
| 1978–79 | UEFA Cup | 1R | Arsenal | 0–3, 1–4 | |
| 1981–82 | UEFA Cup Winners' Cup | Q | Politehnica Timișoara | 0–2, 5–0 | |
| 1R | Swansea City | 1–0, 2–1 | |||
| 1/8 | Velež Mostar | 1–1, 1–1 (a.e.t.) (4–1 p) | |||
| 1/4 | Barcelona | 0–3, 2–1 | |||
| 1982–83 | UEFA Cup | 1R | Viking | 0–1, 3–2 | |
| 1983–84 | UEFA Cup | 1R | Bordeaux | 3–2, 4–0 | |
| 2R | Werder Bremen | 1–0, 1–1 | |||
| 1/8 | Sturm Graz | 0–2, 1–0 | |||
| 1984–85 | UEFA Cup | 1R | Lillestrøm | 7–0, 0–3 | |
| 2R | Spartak Moscow | 1–1, 0–2 | |||
| 1985–86 | UEFA Cup | 1R | Coleraine | 1–1, 5–0 | |
| 2R | Milan | 0–2, 3–1 | |||
| 1986–87 | UEFA Cup Winners' Cup | 1R | Glentoran | 1–1, 2–0 | |
| 1/8 | Rapid Wien | 1–1, 2–1 | |||
| 1/4 | Sion | 2–0, 0–0 | |||
| 1/2 | Bordeaux | 1–0, 0–1 (a.p.) | |||
| Final | Ajax | 0–1 | |||
| 1987–88 | UEFA Cup Winners' Cup | 1R | Marseille | 0–0, 0–1 | |
| 1988–89 | UEFA Cup | 1R | Aarau | 3–0, 4–0 | |
| 2R | Napoli | 1–1, 0–2 | |||
- Participated as part of sports club SC Leipzig.
European record
| Competition | Record | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G | W | D | L | Win % | |||
| UEFA Cup | 32 | 15 | 4 | 13 | 46.88 | ||
| UEFA Cup Winners' Cup | 25 | 10 | 8 | 7 | 40.00 | ||
| Inter-Cities Fairs Cup[lower-alpha 1] | 22 | 8 | 4 | 10 | 36.36 | ||
| Total | 79 | 33 | 16 | 30 | 41.77 | ||
- Participated 1963-1966 as part of sports club SC Leipzig.
Honours
Leagues
- German Championship
- Winners: 1903,[lower-alpha 1] 1906,[lower-alpha 1] 1913[lower-alpha 1]
- Runners-up: 1904[lower-alpha 1](uncontested), 1911,[lower-alpha 1] 1914[lower-alpha 1]
- DDR-Oberliga
- Won by VfB Leipzig.
Cups
- DFB-Pokal
- Winners: 1936[lower-alpha 1]
- FDGB-Pokal
- Winners: 1975–76, 1980–81, 1985–86, 1986–87
- Runners-up: 1958,[lower-alpha 2] 1963–64,[lower-alpha 3] 1969–70, 1972–73, 1976–77
- Won by VfB Leipzig.
- SC Lokomotive Leipzig.
- SC Leipzig.
International
- UEFA Cup Winners' Cup
- UEFA Cup
- Semi-finalist: 1973–74
- International Football Cup (Intertoto Cup)
- Winners (1): 1965–66
- Runners-up: 1964–65[lower-alpha 1]
- SC Leipzig.
Regional
- Central German football championship (I)
- Winners (11): 1903,[lower-alpha 1] 1904,[lower-alpha 1] 1906,[lower-alpha 1] 1907,[lower-alpha 1] 1910,[lower-alpha 1] 1911,[lower-alpha 1] 1913,[lower-alpha 1] 1918,[lower-alpha 1] 1920,[lower-alpha 1] 1925,[lower-alpha 1] 1927[lower-alpha 1]
- Runners-up: 1914,[lower-alpha 1] 1923,[lower-alpha 1] 1930[lower-alpha 1]
- Gauliga Sachsen (I)
- Runners-up: 1933–34,[lower-alpha 1] 1938–39[lower-alpha 1]
- Regionalliga Nordost (IV)
- Winners: 2019–20
- NOFV-Oberliga Süd (V)
- Winners: 2015–16
- Runners-up: 1998–99,[lower-alpha 1] 1999–2000,[lower-alpha 2] 2000–01
- Sachsenliga (VI)
- Winners: 1998[lower-alpha 2]
- Saxony Cup
- Winners: 1995–96,[lower-alpha 2] 2020–21, 2022–23
- Runners-up: 2016–17
- Won by VfB Leipzig.
- Won by reserve team.
Youth
- East German Junior Championship (de)[lower-alpha 1]
- Winners: 1961,[lower-alpha 2] 1971, 1974, 1976, 1977
- Runners-up: 1964,[lower-alpha 3] 1972, 1982
- East German Youth Championship (de)[lower-alpha 4]
- Winners: 1969, 1971, 1979, 1981, 1984 (record)
- Runners-up: 1966, 1970, 1978, 1980
- East German Junior Cup (Junge Welt-Pokal) (de)[lower-alpha 1]
- Winners: 1971, 1974, 1975, 1988
- East German Youth Cup (Youth FDGB-Pokal) [lower-alpha 4]
- Winners: 1959,[lower-alpha 2] 1968
- Corresponds to U19 level.
- Won by SC Rotation Leipzig.
- Won by SC Leipzig.
- Corresponds to U17 level.
Managers
BSG Leipzig-Ost
- Rudolf Walseck (1951–1952)
- Otto Winter (1952–1954)
- Arthur Fischer (1953–1954)
SC Rotation Leipzig
- Heinz Krügel (1954–1956)
- Werner Welzel (1956–1959)
- Martin Brunnert (1959–1960)
- Martin Schwendler (1961–1963)
SC Leipzig
- Rudolf Krause (1963–1965)
- Günter Konzack (1965–1966)
1. FC Lok Leipzig
- Hans Studener (1966–1969)
- Kurt Holke (1969–1971)
- Horst Scherbaum (1971–1976)
- Manfred Pfeifer (1976–1978)
- Heinz Joerk (1978–1979)
- Harro Miller (1979–1985)
- Hans-Ulrich "Uli" Thomale (1985 – February 1990)
- Gunter Böhme (February 1990 – 27 May 1991)
VfB Leipzig
- Jürgen Sundermann (28 May 1991 – 30 June 1993)
- Bernd Stange (1 July 1993 – 21 February 1994)
- Jürgen Sundermann (22 February 1994 – 8 April 1994)
- Damian Halata (9 April 1994 – 30 June 1994)
- Tony Woodcock (1 July 1994 – 30 October 1994)
- August "Gustl" Starek (31 October 1994 – 30 May 1996)
- Damian Halata (1 June 1996 – 30 June 1996)
- Sigfried "Siggi" Held (1 July 1996 – 7 October 1997)
- Damian Halata (8 October 1997 – 30 June 1998)
- Hans-Ulrich "Uli" Thomale (1 July 1998 – 28 March 1999)
- Dragoslav Stepanović (29 March 1999 – 29 August 1999)
- Joachim Steffens (30 August 1999 – 22 July 2001)
- Hans-Jürgen "Dixie" Dörner (23 July 2001 – 26 March 2003)
- Detlef Schößler (27 March 2003 – 3 June 2003)
- Hermann Andreev (24 June 2003 – 19 March 2004)
- Michael Breitkopf and Jörg Engelmann (20 March 2004 – 22 April 2004)
- Mike Sadlo (23 April 2004 – 30 June 2004) – Player/manager
1. FC Lok Leipzig
- Rainer Lisiewicz (1 July 2004 – 12 May 2009)
- Jörg Seydler (12 May 2009 – 29 November 2009)
- Uwe Trommer (29 November 2009 – 30 June 2010) – Caretaker
- Joachim Steffens (1 July 2010 – 7 June 2011)
- Mike Sadlo (7 June 2011 – 7 December 2011)
- Willi Kronhardt (3 January 2012 – 30 June 2012)
- Marco Rose (1 July 2012 – 30 June 2013)
- Carsten Hänsel (1 July 2013 – 23 September 2013)
- Heiko Scholz (8 October 2013 – 23 September 2018)
- Björn Joppe (27 September 2018 – 17 December 2018)
- Rainer Lisiewicz (18 December 2018 – 19 October 2019)
- Wolfgang Wolf (20 October 2019 – 30 June 2020)
- Almedin Civa (since 1 July 2020)
Current squad
- As of 21 August 2023[11]
Note: Flags indicate national team as defined under FIFA eligibility rules. Players may hold more than one non-FIFA nationality.
|
|
Organizational history
1. FC Lokomotive Leipzig has undergone several reorganizations during its history and has taken several different forms and names. The club was a football department of sports clubs SC Rotation Leipzig and later SC Leipzig, before being reorganized as football club 1. FC Lokomotive Leipzig in 1966.
| Date | Name | Note |
|---|---|---|
| 13 May 1896 | VfB Leipzig | |
| 15 June 1898 | VfB 1893 Sportbrüder Leipzig | Merger with SC Sportbrüder Leipzig, founded on 11 November 1893. |
| 2 November 1900 | VfB Leipzig | The name 1893 Sportbrüder was dropped. |
| 1946 | SG Probstheida | VfB Lepzig was dissolved in 1946. The remains were reorganized as SG Probstheida. |
| 31 July 1950 | BSG Erich Zeigner Probstheida | The club was renamed. |
| 1953 | BSG Einheit Ost | The club was again renamed. |
| November 1954 | SC Rotation Leipzig | |
| July 1963 | SC Leipzig | |
| 20 January 1966 | 1. FC Lokomotive Leipzig | Football department of SC Leipzig was reorganized as a football club. |
| 1 July 1991 | VfB Leipzig | Renamed. |
| 10 December 2003 | 1. FC Lokomotive Leipzig | Refounded as 1. FC Lokomotive Leipzig. VfB Leipzig became defunct on 1 July 2004. |
References
- "Lok Leipzig: Fusion mit VfB ist näher gerückt" [Lok Leipzig: Merger with VfB is closer]. fussball.de (in German). Deutscher Fußball-Bund. 28 November 2018. Archived from the original on 30 November 2018. Retrieved 11 November 2011.
- "Gyula Kertész". worldfootball.net. Archived from the original on 3 October 2020. Retrieved 16 September 2020.
- JOACHIM REMAK. Two Germanies—and Then? Archived 3 June 2020 at the Wayback Machine. Journal of International Affairs.
- "Rückspiel Aufstiegs-Relegation zur Oberliga Saison 2007/2008". Lok Leipzig. Archived from the original on 15 May 2008. Retrieved 23 June 2008.
- "Das deutsche Fußball-Archiv". Das deutsche Fußball-Archiv (in German). Archived from the original on 24 February 2016. Retrieved 3 August 2015.
- "1. FC Lokomotive Leipzig". fussball.de (in German). Deutscher Fußball-Bund. Archived from the original on 10 July 2015. Retrieved 3 August 2015.
- "Lok Leipzig: Spielabbruch nach Platzsturm" [Lok Leipzig: Match cancelled after pitch invasion]. kicker (in German). Nuremberg: Olympia-Verlag. 14 June 2015. Archived from the original on 9 November 2017. Retrieved 3 August 2015.
- Wöckener, Lutz (12 November 2016). "Lok vs. Chemie Leipzig: Angst vor dem deutschen Hooligan-Gipfel am Sonntag" [Fear of the German hooligan summit on Sunday]. Die Welt (in German). Berlin: Axel Springer SE. ISSN 0173-8437. Archived from the original on 15 February 2020. Retrieved 2 June 2017.
- "St Pauli, politics and fighting (good and bad)". FourFourTwo. Bath: Future. 26 December 2009. ISSN 1355-0276. Archived from the original on 20 January 2018. Retrieved 2 June 2017.
At Leipzig right-wing supporters of Lok Leipzig prey on left-wing supporters of Chemie Leipzig.
- Krauss, Bastian (14 November 2016). "Wie Antifa und Neonazis ihren politischen Kampf im Leipziger Derby austragen" [How Antifa and Neo-Nazis carry out their political fight in the Leipzig derby]. Vice News (in German). Archived from the original on 11 November 2019. Retrieved 2 June 2017.
- "Spieler". lok-leipzig.com. Retrieved 21 August 2023.