Robert Jenkinson, 2nd Earl of Liverpool
Robert Banks Jenkinson, 2nd Earl of Liverpool, KG, PC, FRS (7 June 1770 – 4 December 1828) was a British Tory statesman who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1812 to 1827. He also held many other important cabinet offices such as Foreign Secretary, Home Secretary and Secretary of State for War and the Colonies. He was also a member of the House of Lords and served as leader.
The Earl of Liverpool | |
|---|---|
 Portrait by Thomas Lawrence, c. 1827 | |
| Prime Minister of the United Kingdom | |
| In office 8 June 1812 – 9 April 1827 | |
| Monarchs | |
| Regent | George, Prince Regent (1812–1820) |
| Preceded by | Spencer Perceval |
| Succeeded by | George Canning |
| Secretary of State for War and the Colonies | |
| In office 1 November 1809 – 11 June 1812 | |
| Prime Minister | Spencer Perceval |
| Preceded by | The Viscount Castlereagh |
| Succeeded by | The Earl Bathurst |
| Leader of the House of Lords | |
| In office 25 March 1807 – 9 April 1827 | |
| Prime Minister |
|
| Preceded by | The Lord Grenville |
| Succeeded by | The Viscount Goderich |
| In office 17 August 1803 – 5 February 1806 | |
| Prime Minister | |
| Preceded by | The Lord Pelham |
| Succeeded by | The Lord Grenville |
| Home Secretary | |
| In office 25 March 1807 – 1 November 1809 | |
| Prime Minister | The Duke of Portland |
| Preceded by | The Earl Spencer |
| Succeeded by | Richard Ryder |
| In office 12 May 1804 – 5 February 1806 | |
| Prime Minister | William Pitt the Younger |
| Preceded by | Charles Philip Yorke |
| Succeeded by | The Earl Spencer |
| Secretary of State for Foreign Affairs | |
| In office 20 February 1801 – 14 May 1804 | |
| Prime Minister | Henry Addington |
| Preceded by | The Lord Grenville |
| Succeeded by | The Lord Harrowby |
| Personal details | |
| Born | Robert Banks Jenkinson 7 June 1770 London, England |
| Died | 4 December 1828 (aged 58) Kingston upon Thames, Surrey, England |
| Resting place | Hawkesbury Parish Church, Gloucestershire, England |
| Political party | Tory |
| Spouses | |
| Parent | Charles Jenkinson (father) |
| Education | Charterhouse School |
| Alma mater | Christ Church, Oxford |
| Signature | |
As prime minister, Liverpool called for repressive measures at domestic level to maintain order after the Peterloo Massacre of 1819. He dealt smoothly with the Prince Regent when King George III was incapacitated. He also steered the country through the period of radicalism and unrest that followed the Napoleonic Wars. He favoured commercial and manufacturing interests as well as the landed interest. He sought a compromise of the heated issue of Catholic emancipation. The revival of the economy strengthened his political position. By the 1820s, he was the leader of a reform faction of "Liberal Tories" who lowered the tariff, abolished the death penalty for many offences, and reformed the criminal law. By the time of his death, however, the Tory party, which had dominated the House of Commons for over 40 years, was ripping itself apart.
Derry says he was:
[A] capable and intelligent statesman, whose skill in building up his party, leading the country to victory in the war against Napoleon, and laying the foundations for prosperity outweighed his unpopularity in the immediate post-Waterloo years.[1]
Important events during his tenure as prime minister included the War of 1812 with the United States, the Sixth and Seventh Coalitions against the French Empire, the conclusion of the Napoleonic Wars at the Congress of Vienna, the Corn Laws, the Peterloo Massacre, the Trinitarian Act 1812 and the emerging issue of Catholic emancipation. Scholars rank him highly among all British prime ministers, but he was also called "the Arch-mediocrity" by a later Conservative prime minister, the Earl of Beaconsfield (Benjamin Disraeli).[2]
Early life: 1770-1790
Jenkinson was baptised on 29 June 1770 at St. Margaret's, Westminster, the son of George III's close adviser Charles Jenkinson, later the first Earl of Liverpool, and his first wife, Amelia Watts. Jenkinson's 19-year-old mother, who was the daughter of a senior East India Company official, William Watts, and of his wife Begum Johnson, died from the effects of childbirth one month after his birth.[3] Through his mother's grandmother, Isabella Beizor, Jenkinson was descended from Portuguese settlers in India; he may also have been one-sixteenth Indian in ancestry.[4][5][6]
From an early age, Jenkinson had a strong influential training in economics and politics from his father, who was at the time, a leading politician and adviser to King George III.[7] To give his son the highest education possible, Jenkinson was sent to be educated at Charterhouse School, whose education was broader than that of the prestigious Eton College, to which many sons of noblemen were sent be educated.[7] While at Charterhouse, Jenkinson's father insisted that he study political economy and read current politics. Jenkinson later matriculated at Christ Church, Oxford, in 1787.[8][9]

While learning at Oxford, he went on the tradition “Grand Tour” of Europe, which was undertaken by most wealthy students to travel abroad.[7] In the summer of 1789, he took his Grand Tour, first travelling to Italy and then to Paris, France.[7] In Paris, Jenkinson spent four months there to perfect his French and enlarge his social experience among Parisian Society.[10] While there, he witnessed the storming of the Bastille during the early stages of the French Revolution and before the revolution took place, he was able to safely return to England and in time for his last year at Oxford.[7] He spent next the three months in Oxford to complete his terms of residence, and in May 1790 was created Master of Arts.
Early career: 1790-1801
Member of Parliament
He won election to the House of Commons in 1790 for Rye, a seat he would hold until 1803; at the time, however, he was below the age of assent to Parliament, so he refrained from taking his seat and spent the following winter and early spring in an extended tour of the continent. This tour took in the Netherlands and Italy; at its conclusion he was old enough to take his seat in Parliament. It is not clear exactly when he entered the Commons, but as his twenty-first birthday was not reached until almost the end of the 1791 session, it is possible that he waited until the following year.
House of Commons
With the help of his father's influence and his political talent, he rose relatively fast in the Tory government. In February 1792, he gave the reply to Samuel Whitbread's critical motion on the government's Russian policy. He delivered several other speeches during the session, and was a strong opposer of abolitionism and William Wilberforce. He served as a member of the Board of Control for India from 1793 to 1796.
In the defence movement that followed the outbreak of hostilities with France, Jenkinson, was one of the first of the ministers of the government to enlist in the militia. He became a colonel in the Cinque Ports Fencibles in 1794, and his military duties led to frequent absences from the Commons. His regiment was sent to Scotland in 1796, and he was quartered for a time in Dumfries.
In 1797, the then Lord Hawkesbury was the cavalry commander of the Cinque Ports Light Dragoons who ran amok following a protest against the Militia Act at Tranent in East Lothian; twelve civilians were killed. Author James Miller wrote in 1844 that "His lordship was blamed for remaining at Haddington, as his presence might have prevented the outrages of the soldiery."[11]
His parliamentary attendance also suffered from his reaction when his father angrily opposed his projected marriage with Lady Louisa Hervey, daughter of the Earl of Bristol. After Pitt and the King had intervened on his behalf, the wedding finally took place at Wimbledon on 25 March 1795. In May 1796, when his father was created Earl of Liverpool, he took the courtesy title of Lord Hawkesbury and remained in the Commons. He became Baron Hawkesbury in his own right and was elevated to the House of Lords in November 1803, as recognition of his work as Foreign Secretary. He also served as Master of the Mint (1799–1801).[8]
Foreign Secretary: 1801-1804
Entry
As the question of Catholic emancipation came apparent and as the King refused to pass on to law, in response, Pitt resigned as prime minister as a result. This departure left the King to choose a successor and so appointed one of Pitt's prominent allies, Henry Addington, as the new prime minister. When Addington's government came to power, the young Liverpool entered the cabinet in 1801 as Secretary of State for Foreign Affairs.[8] Addington's main political agenda was peace and promised that as prime minister that, he will negotiate with the French. In this capacity he was entrusted by Addington negotiate with the France and pursue an immediate peace deal, which he set to do, as his first duty.[12]
Treaty of Amiens
The French Revolutionary Wars begun as a direct result of the French Revolution, of which the aftermath saw a growing sentiment of radicalism and a shock wave of political turmoil being send across Europe. At the beginning of the Revolution, the British government led by William Pitt opposed its ideology and the belief that it would undermine the principles of Britain's established constitutional monarchy. Also the French revolutionary ideology heavily opposed such forms of government containing a monarchy, while favouring a republican form of government, which Britain and other countries in Europe opposed and wished to end such ideologies from spreading elsewhere. What followed was a decade long series of wars, known as the Coalition wars that resulted in Britain and its allies being defeated or being pushed to the position of economic crisis and so many opted to peace.[13]
As Foreign Secretary, Liverpool has to face the crisis war in Europe and negotiate peace as soon as possible. As Britain and its allies in the continent were unable to defeat France in any way and the long duration of the war itself, led to a period of instability as the British war effort has been over overwhelmed by nearly a decade of war without any results. As per Addington's wishes, Liverpool opened negotiations with France. Liverpool immediately, first, communicated with the French commissary for prisoners of war in London, Louis Guillaume Otto, through whom he could contact and agree to Napoleon Bonaparte’s earlier proposals.[13]
Liverpool stated that he “wanted to open discussions on terms for a peace agreement”, but Otto, who was under direct and strict orders from Bonaparte, begun to open negotiations by mid-September. Despite his efforts, negotiations seemed fruitless with Otto and unhappy with this result, Liverpool sent diplomat Anthony Merry to Paris to open a second round of negotiations with his own French counterpart, French Foreign Minister Talleyrand by mid-September. By this time, written negotiations followed and progressed to the point Otto met shaft a preliminary agreement on 30 September and finally in London, which was finally published the next day. Thus signing the Treaty of Amiens and concluding the end of the War of the Second Coalition.[13]
Resignation
Most of his time as Foreign Secretary was spent dealing with the nations of France and the United States. But this was cut short, as shortly afterwards, the Addington government came under attack from the opposition and was criticised for its lack of credibility when war resumed yet again in 1803 and the start of the War of the Third Coalition. Soon the government fell into disarray and quickly led to the reappointment of Pitt as prime minister.[13]
Home Secretary: 1804-1809
When Pitt came to power for the second time, he reappointed the former Foreign secretary and he was soon continued to serve in the cabinet as Home Secretary in Pitt the Younger's second government.
Soon after taking the role of Prime Minister, Pitt fell ill and was sick during 1805. Despite a terminal illness, he managed the out-going war in Europe and was able to hold together his Cabinet and his country against the will-power of the French. While Pitt was seriously ill, Liverpool was in charge of the cabinet and drew up the King's Speech for the official opening of Parliament. When William Pitt died in 1806, the King needed choose a successor to office and asked the Home Secretary Liverpool to accept the post of Prime Minister, but he refused, as he believed he lacked a governing majority.[8]
He was then became Leader of the Opposition during Lord Grenville's ministry. This was the second only time that Liverpool did not hold government office between 1793 and after his retirement. In 1807, after an year in opposition, he resumed office as Home Secretary in the Duke of Portland's new ministry.[8]
War Secretary: 1809-1812
Lord Hawkesbury, by this point, assumed the title of Lord Liverpool, as he had now become by the death of his father in December 1808. After the fall of the Whig Portland ministry, saw the sudden rise of Spencer Perceval to the office of prime minister. Perceval was reluctant appoint a fellow Tory to his cabinet, as the Whigs were splintered and unified, which would allow the Tories to govern opposed and asked Liverpool to join his new cabinet. Liverpool accepted the position of Secretary of State for War and the Colonies in Perceval's new government in 1809. Liverpool's first step on taking up his new post was to elicit from General Arthur Wellesley (the future Duke of Wellington) a strong enough statement of his ability to resist a French attack to persuade the cabinet to commit themselves to the maintenance of his small force in Portugal. In 1810 Liverpool was made a colonel of militia.[14]
War finance
By 1809 the political situation in Europe have changed dramatically. Napoleon has conquered most, if not almost, all of Europe except for Russia, Austria, Eastern Europe and Northern Europe. The war against Napoleonic France did not improve for Britain's war effort and is by this point, Five coalitions have failed to defeat Napoleon or bring down France. This did not help Britain overcome the Continental System, issued by the 1806 Berlin Decree, which forbade most countries of Europe from Engaging in trade and commerce with the British and prevented them from trading British goods. This not only effected Britain and all countries as they were dependent on British supplies, mainly British allies. But to prevent Britain falling to an economic crisis, Liverpool as War Secretary has raised loans to help the Britain win the war and also help Britain's allies in need. At home, with a combination of strong government finances and sustain financial attrition was able to save Britain from falling behind the economic fallout. And by using the Royal Navy to undermine French naval activities, a blockade across the English Channel and with persistent but moderate military pressure on France would ultimately bear fruit and will win the war.[13]
Prime Minister: 1812-1827
Appointment
When Perceval was assassinated in May 1812, George, the Prince Regent, successively tried to appoint four men to succeed him, but failed; Liverpool, the fifth choice for the post, reluctantly accepted office on 8 June 1812.[15][8] The cabinet proposed Liverpool as his successor with Lord Castlereagh as leader in the Commons but after an adverse vote in the Lower House, they subsequently both gave their resignations. The Prince Regent, however, found it impossible to form a different coalition and confirmed Liverpool as prime minister on 8 June. No successor, in over 200 years, has been younger. Liverpool's government contained some of the future great leaders of Britain, such as Lord Castlereagh, George Canning, the Duke of Wellington, Robert Peel and William Huskisson. Liverpool is considered a skilled politician, and held together the liberal and reactionary wings of the Tory party, which his successors, Canning, Goderich and Wellington, had great difficulty with.
War
At the beginging of his premiership, Liverpool was faced directly with conflict, the War of 1812 with the United States and the final campaigns of the Napoleonic Wars were fought during his governance. The Peninsular Campaigns saw the British army led by the Duke of Wellington drive the French out of Spain and Portugal. At the peace negotiations that followed, Liverpool's main concern was to obtain a European settlement that would ensure the independence of the Netherlands, Spain and Portugal, and confine France inside its pre-war frontiers without damaging its national integrity. To achieve this, he was ready to return all British colonial conquests. Within this broad framework, he gave Castlereagh discretion at the Congress of Vienna, the next most important event of his ministry. At the congress he gave prompt approval for Castlereagh's bold initiative in making the defensive alliance with Austria and France in January 1815. In the aftermath of the defeat of Napoleon – who had briefly been exiled to the island Elba and escaped exile and returned to rule France. The allies immediately begun mobilizing their armies to fight the escaped emperor and an combined Anglo-Allied army was send under the command of Wellington to assist Britain's allies. Within few months, Napoleon was decisively defeated at the Battle of Waterloo and peace followed through the now exhausted continent.
Congress of Vienna
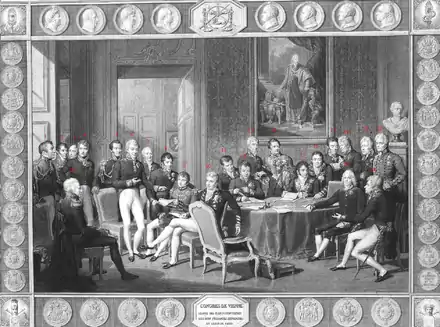
After the Battle of Waterloo saw the conclusion of the War of the Seventh Coalition and the ushering in of peace in Europe, after the continuous decade-long wars that were fought as a direct aftermath of the French Revolution in 1789, now ceased. Despite this, Napoleon's conquests left a defining situation in Europe and all countries of Europe to fill or reconstruct many of its cracks. Soon after the victory at Waterloo and peace was secured, the nations of Europe came together to talk of securing peace. The Austrian Foreign Minister Klemens Von Metternich, a skilled diplomat and capable politician, called on European countries to gather at Vienna to negotiate a peacekeeping effort, with the aim of establishing a lasting peace. The main powers: Britain,Austria, Prussia, Russia and last the defeated France all met at Vienna for negotiations and representing their perspective countries. Lord Liverpool, as prime minister, decided to a send one of his most skilled ministers to attend the peace assembly in France, and so appointed his Foreign Secretary, Lord Castlereagh, to be sent to Vienna. The gathering of nations at the Austrian city, is known as the Congress of Vienna and was attended by some of Europe's most influential diplomats and politicians and the result of this congressional meeting was the establishment of a peaceful Europe. So, as a direct result, it saw the maps of Europe being redrawn to the previous borders there before the war, opposing or eradicating radicalism and liberal ideals, such as that of the French Revolution, from spreading across the continent and securing a lasting peace that would see no major conflict being ever fought between the nations of Europe. This became known as the Concert of Europe and its ideals of a longstanding peace and political landscape would endure to the early 20th Century until the start of the First World War in 1914.[13]
Colonial expansion
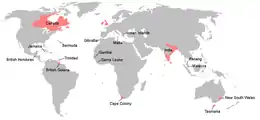
The British Empire in 1815 and throughout Liverpool's premiership was thriving and expanding across the globe and was raising as greatest colonial empire of all time. As the 20-year long war in Europe ended with peace being established in Europe, Britain finally established itself as a main power, alongside Austria, Russia and France. But by this point, Britain proved itself to be a far more superior power than any other nation in Europe. Through its vast empire, strong economy and military might, it made Britain one of the earliest known world power with establishing a hegemony over the globe. Through trade and commerce, Britain accumulated large amounts of wealth and through its industrialisation, mass production of cotton, iron, wheat increased dramatically. Britain's colonial endeavours saw British armies conquering and subjugating new territories. In South Asia, saw British territories gradually expanded far and beyond. The annexation of Nepal during the Anglo-Nepalese War saw it incorporated to British India as a result. Britain also expanded its borders within the Indian frontiers during the Third Anglo-Maratha War against the long-time British enemy of the Maratha Confederacy. In modern-day Myanmar, conflict with the Third Burmese Empire led to the First Anglo-Burmese War, which saw the strategic weakening of the Burma and led to the cessation of territories in Assam, Manipur, Arakan and other territories south of the Salween River as a result. Furthermore, in South Africa, the complete integration of the Cape Colony in South Africa and victory over the Xhosa tribes in the Fourth Xhosa War in which the Colony were able to push the tribes beyond the Fish River and reverse many of the Xhosa's past success. During Liverpool's tenure as Prime Minister, saw the establishment of a permanent penal colony in Australia and new settlements in New Zealand.[13]
Home trouble
Inevitably taxes rose to compensate for borrowing and to pay off the national debt, which led to widespread disturbance between 1812 and 1822. Around this time, the group known as Luddites began industrial action. Throughout the period 1811–1816, there was a series of incidents of machine-breaking and many of those convicted faced execution.[12]
Corn Laws
Agriculture remained a problem because good harvests between 1819 and 1822 had brought down prices and evoked a cry for greater protection. When the powerful agricultural lobby in Parliament demanded protection in the aftermath, Liverpool gave in to political necessity. Under governmental supervision the notorious Corn Laws of 1815 were passed prohibiting the import of foreign wheat until the domestic price reached a minimum accepted level. Liverpool, however, was in principle a free-trader, but had to accept the bill as a temporary measure to ease the transition to peacetime conditions. His chief economic problem during his time as Prime Minister was that of the nation's finances.
The interest on the national debt, massively swollen by the enormous expenditure of the final war years, together with the war pensions, absorbed the greater part of normal government revenue. The refusal of the House of Commons in 1816 to continue the wartime income tax left ministers with no immediate alternative but to go on with the ruinous system of borrowing to meet necessary annual expenditure. Liverpool eventually facilitated a return to the gold standard in 1819.
Liverpool argued for the abolition of the wider slave trade at the Congress of Vienna, and at home he supported the repeal of the Combination Laws banning workers from combining into trade unions in 1824.[16] In the latter year the newly formed Royal National Institution for the Preservation of Life from Shipwreck, later the RNLI, obtained Liverpool as its first president.[17]
Assassination attempt

The reports of the secret committees he obtained in 1817 pointed to the existence of an organised network of disaffected political societies, especially in the manufacturing areas. Liverpool told Peel that the disaffection in the country seemed even worse than in 1794. Because of a largely perceived threat to the government, temporary legislation was introduced. He suspended habeas corpus in both Great Britain (1817) and Ireland (1822). Following the Peterloo Massacre in 1819, his government imposed the repressive Six Acts legislation which limited, among other things, free speech and the right to gather for peaceful demonstration. In 1820, as a result of these measures, Liverpool and other cabinet ministers were targeted for assassination. They escaped harm when the Cato Street conspiracy was foiled.[18]
Catholic emancipation
During the 19th century, and, in particular, during Liverpool's time in office, Catholic emancipation was a source of great conflict. In 1805, in his first important statement of his views on the subject, Liverpool had argued that the special relationship of the monarch with the Church of England, and the refusal of Roman Catholics to take the oath of supremacy, justified their exclusion from political power. Throughout his career, he remained opposed to the idea of Catholic emancipation, though he did see marginal concessions as important to the stability of the nation.
The decision of 1812 to remove the issue from collective cabinet policy, followed in 1813 by the defeat of Grattan's Roman Catholic Relief Bill, brought a period of calm. Liverpool supported marginal concessions such as the admittance of English Roman Catholics to the higher ranks of the armed forces, the magistracy, and the parliamentary franchise; but he remained opposed to their participation in parliament itself. In the 1820s, pressure from the liberal wing of the Commons and the rise of the Catholic Association in Ireland revived the controversy.
By the date of Sir Francis Burdett's Catholic Relief Bill in 1825, emancipation looked a likely success. Indeed, the success of the bill in the Commons in April, followed by Robert Peel's tender of resignation, finally persuaded Liverpool that he should retire. When Canning made a formal proposal that the cabinet should back the bill, Liverpool was convinced that his administration had come to its end. George Canning then succeeded him as Prime Minister. Catholic emancipation however was not fully implemented until the major changes of the Roman Catholic Relief Act 1829 under the leadership of the Duke of Wellington and Sir Robert Peel, and with the work of the Catholic Association established in 1823.[19]
Retirement and death
Liverpool's first wife, Louisa, died at 54. He soon married again, on 24 September 1822, to Lady Mary Chester, a long-time friend of Louisa.[20] Liverpool finally retired on 9 April 1827 after suffering a severe cerebral hemorrhage at his Fife House residence in Whitehall two months earlier,[21] and asked the King to seek a successor. He suffered another minor stroke in July, after which he lingered on at Coombe until a third attack on 4 December 1828 from which he died.[22] Having died childless, he was succeeded as Earl of Liverpool by his younger half-brother Charles. He was buried in Hawkesbury parish church, Gloucestershire, beside his father and his first wife. His personal estate was registered at under £120,000.
Legacy
Historian R. W. Seton-Watson sums up Liverpool's strengths and weaknesses:
No one would claim Liverpool as a man of genius, but he had qualities of tact, firmness and endurance to which historians have rarely done full justice: and thus it came about that he held the office of Premier over a period more than twice as long as any other successor of Pitt, long after peace had been restored to Europe. One reason for his ascendancy was that he had an unrivalled insight into the whole machinery of government, having filled successively every Secretaryship of State, and tested the efficiency and mutual relations of politicians and officials alike.... He had a much wider acquaintance with foreign affairs than many who have held his high office.[23]
Liverpool was the first British Prime Minister to regularly wear long trousers instead of knee breeches. He entered office at the age of 42 years and one day, making him younger than all of his successors. Liverpool served as Prime Minister for a total of 14 years and 305 days, making him the longest-serving Prime Minister of the 19th century. As of 2022, none of Liverpool's successors has served longer.
In London, Liverpool Street and Liverpool Road, Islington, are named after Lord Liverpool. The Canadian town of Hawkesbury, Ontario, the Hawkesbury River and the Liverpool Plains, New South Wales, Australia, Liverpool, New South Wales, and the Liverpool River in the Northern Territory of Australia were also named after Lord Liverpool.[24]
Lord Liverpool, as Prime Minister to whose government Nathan Mayer Rothschild was a lender, was portrayed by American actor Gilbert Emery in the 1934 movie, The House of Rothschild.
Lord Liverpool's ministry (1812–1827)
- Lord Liverpool – First Lord of the Treasury and Leader of the House of Lords
- Lord Eldon – Lord Chancellor
- Lord Harrowby – Lord President of the Council
- Lord Westmorland – Lord Privy Seal
- Lord Sidmouth – Secretary of State for the Home Department
- Lord Castlereagh (Lord Londonderry after 1821) – Secretary of State for Foreign Affairs and Leader of the House of Commons
- Lord Bathurst – Secretary of State for War and the Colonies
- Lord Melville – First Lord of the Admiralty
- Nicholas Vansittart – Chancellor of the Exchequer
- Lord Mulgrave – Master-General of the Ordnance
- Lord Buckinghamshire – President of the Board of Control
- Charles Bathurst – Chancellor of the Duchy of Lancaster
- Lord Camden – minister without portfolio
Changes
- Late 1812 – Lord Camden leaves the Cabinet
- September 1814 – William Wellesley-Pole (Lord Maryborough from 1821), the Master of the Mint, enters the Cabinet
- February 1816 – George Canning succeeds Lord Buckinghamshire at the Board of Control
- January 1818 – F. J. Robinson, the President of the Board of Trade, enters the Cabinet
- January 1819 – The Duke of Wellington succeeds Lord Mulgrave as Master-General of the Ordnance. Lord Mulgrave becomes minister without portfolio
- 1820 – Lord Mulgrave leaves the cabinet
- January 1821 – Charles Bathurst succeeds Canning as President of the Board of Control, remaining also at the Duchy of Lancaster
- January 1822 – Robert Peel succeeds Lord Sidmouth as Home Secretary
- February 1822 – Charles Williams-Wynn succeeds Charles Bathurst at the Board of Control. Bathurst remains at the Duchy of Lancaster and in the Cabinet
- September 1822 – Following the suicide of Lord Londonderry, George Canning becomes Foreign Secretary and Leader of the House of Commons
- January 1823 – Vansittart, elevated to the peerage as Lord Bexley, succeeds Charles Bathurst as Chancellor of the Duchy of Lancaster. F. J. Robinson succeeds Vansittart as Chancellor of the Exchequer. He is succeeded at the Board of Trade by William Huskisson
- 1823 – Lord Maryborough, the Master of the Mint, leaves the Cabinet. His successor in the office is not a Cabinet member
Arms
 |
|
References
- John Cannon, ed. (2009). The Oxford Companion to British History. p. 582.
- Paul Strangio; Paul 't Hart; James Walter (2013). Understanding Prime-Ministerial Performance: Comparative Perspectives. Oxford UP. p. 225. ISBN 978-0199666423.
- D. Leonard 2008 Nineteenth-Century British Premiers: Pitt to Rosebery. Palgrave Macmillan: p. 82.
- Blake, Robert (18 October 1984). "Weathering the storm". London Review of Books. Vol. 6, no. 19. Retrieved 25 March 2020.
- "Edward Croke's wife, Isabella Beizor (c. 1710–80), was a Portuguese Indian creole, thus giving Liverpool a trace (probably about one sixteenth, but maybe less) of Indian blood." Hutchinson, Martin, Britain's Greatest Prime Minister: Lord Liverpool
- "It is true that [Lord Liverpool's] maternal grandmother was a Calcutta-born woman, Frances Croke ... there is no evidence that her half-Portuguese mother, Isabella Beizor, was Eurasian." Brendon, de Vyvyen, Children of the Raj
- https://www.cato.org/cato-journal/fall-2021/economic-policies-lord-liverpool#
- Chisholm 1911.
- Foster, Joseph (1888–1892). . Alumni Oxonienses: the Members of the University of Oxford, 1715–1886. Oxford: Parker and Co – via Wikisource.
- https://victorianweb.org/history/Liverpool.html
- Miller, James (1844). "(Chapter:) Dreadful Riot and Military Massacre at Tranent, on the First Balloting for the Scots Militia for the County of Haddington". (Book:)The Lamp of Lothian, or, The history of Haddington: in connection with the public affairs of East Lothian and of Scotland, from the earliest records to the present period.
{{cite book}}:|website=ignored (help) - "Lord Liverpool". Victorian Web. 4 March 2002.
- https://www.historic-uk.com/HistoryUK/HistoryofBritain/Lord-Liverpool/
- JENKINSON, Hon. Robert Banks (1770–1828), of Coombe Wood, nr. Kingston, Surr. | History of Parliament Online "The History of Parliament" article by R. G. Thorne
- Marjie Bloy (4 March 2002). "Lord Liverpool". The Victorian Web.
- W. R. Brock (1967). Lord Liverpool and Liberal Toryism 1820 to 1827. CUP Archive. p. 3.
- Lewis, Richard (1874). "History of the life-boat, and its work". MacMillan & Co. Retrieved 8 December 2020 – via Internet Archive.
- Ann Lyon (2003). Constitutional History of the UK. Routledge. p. 319. ISBN 9781135337001.
- Richard W. Davis, "Wellington and the 'Open Question': The Issue of Catholic Emancipation, 1821–1829", Albion, (1997) 29#1 pp 39–55. doi:10.2307/4051594
- Oxford Dictionary of National Biography, Volume 29. Oxford University Press. 2004. p. 988. ISBN 978-0-19-861379-4.Article by Norman Gash.
- "Robert Jenkinson, Lord Liverpool". Archived from the original on 30 March 2015. Retrieved 14 September 2015. Spartacus Educational article.
- "Robert Banks Jenkinson, 2nd Earl of Liverpool". Encyclopaedia Britannica. Edinburgh. Retrieved 11 April 2021.
- R. W. Seton-Watson, Britain in Europe (1789–1914): A Survey of Foreign Policy (1937) (1937), p. 29.
- "Place Names Register Extract – Liverpool River". NT Place Names Register. Northern Territory Government. Retrieved 2 May 2015.
Further reading
- Brock, W. R. (1943). Lord Liverpool and Liberal Toryism 1820 to 1827. CUP Archive. p. 2.
- Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 16 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 804. This contains an assessment of his character and achievements.
- Cookson, J. E. Lord Liverpool's administration: the crucial years, 1815–1822 (1975)
- Gash, Norman. Lord Liverpool: The Life and Political Career of Robert Banks Jenkinson, Second Earl of Liverpool 1770–1828 (1984)
- Gash, Norman. "Jenkinson, Robert Banks, second earl of Liverpool (1770–1828)", Oxford Dictionary of National Biography (Oxford University Press, 2004); online ed. 2008 accessed 20 June 2014 doi:10.1093/ref:odnb/14740
- Gash, Norman. "Lord Liverpool: a private view," History Today (1980) 30#5 pp 35–40
- Hay, William Anthony. Lord Liverpool: A Political Life (The Boydell Press, 2018).
- Hilton, Boyd. A Mad, Bad, and Dangerous People? England 1783–1846 (New Oxford History of England) (2006) scholarly survey
- Hilton, Boyd. "The Political Arts of Lord Liverpool." Transactions of the Royal Historical Society (Fifth Series) 38 (1988): 147–170. online
- Hutchinson, Martin. Britain's Greatest Prime Minister: Lord Liverpool (Cambridge, The Lutterworth Press, 2020).
- Petrie, Charles. Lord Liverpool and His Times (1954)
- Plowright, John. Regency England: The Age of Lord Liverpool (Routledge, 1996) "The Lancaster Pamphlets".
- Sack, James J. The Grenvillites, 1801–29: Party Politics and Factionalism in the Age of Pitt and Liverpool (1991)
- Seton-Watson, R. W. Britain in Europe (1789–1914): A Survey of Foreign Policy (1937) online free
External links
- Hansard 1803–2005: contributions in Parliament by the Earl of Liverpool
- Earl of Liverpool Prime Minister's Office
- "Earl of Liverpool" by Prime Minister's Office
- Portraits of Robert Jenkinson, 2nd Earl of Liverpool at the National Portrait Gallery, London
- "Archival material relating to Robert Jenkinson, 2nd Earl of Liverpool". UK National Archives.
_(2022).svg.png.webp)