MC21-B
MC21-B is an antibiotic isolated from the O-BC30T strain of a marine bacterium, Pseudoalteromonas phenolica.[1] MC21-B is cytotoxic to human leukaemia cells and human normal dermal fibroblasts.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
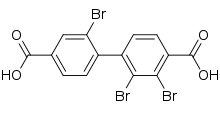
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,2′,3-Tribromo[1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-dicarboxylic acid | |
| Other names
2,2′,3-Tribromobiphenyl-4,4′-dicarboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H7Br3O4 | |
| Molar mass | 478.918 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White powder |
| Sol. MeOH, CHCl3 insol. H2O, hexane | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
See also
References
- Isnansetyo, A.; Kamei, Y. (2009). "Anti-methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) activity of MC21-B, an antibacterial compound produced by the marine bacterium Pseudoalteromonas phenolica O-BC30T". International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents. 34 (2): 131–135. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2009.02.009. PMID 19329285.
- Rahman, H.; Austin, B.; Mitchell, W. J.; Morris, P. C.; Jamieson, D. J.; Adams, D. R.; Spragg, A. M.; Schweizer, M. (2010). "Novel Anti-Infective Compounds from Marine Bacteria". Marine Drugs. 8 (3): 498–518. doi:10.3390/md8030498. PMC 2857357. PMID 20411112.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.