MK-2206
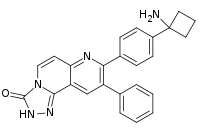
MK-2206 is a drug candidate being investigated to help treat cancer. Its chemical formula is C25H21N5O.[1] It acts as an allosteric AKT inhibitor.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
8-[4-(1-Aminocyclobutyl)phenyl]-9-phenyl[1,2,4]triazolo[3,4-f] [1,6]naphthyridin-3(2H)-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.207.435 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C25H21N5O | |
| Molar mass | 407.477 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
It is a highly selective inhibitor of pan-Akt, namely, of all three Akt isoforms Akt1, Akt2, and Akt3.[1]
It is intended to be used with other cancer therapies that advanced tumours may become resistant to.[3]
Clinical trials
2011: A phase 1 clinical trial of MK-2206 alone has reported it was well tolerated.[4]
2014: A phase 1 clinical trial of MK-2206 with a variety of other agents in 72 patients with advanced cancer reported acceptable side-effects.[3]
2016: MK-2206 is one of the treatments in the I-SPY2 Adaptive clinical trial for breast cancer that had been selected for later stage trials.[5]
As of August 2017 31 phase II clinical trials are registered, many completed.[6] e.g. in colorectal cancer, breast cancer, and many others.
MK-2206 and COVID-19
Data shown in a study preprint suggest that SARS-CoV-2 infection decreases cellular autophagy and that MK-2206, which induces autophagy, reduced virus replication by up to 88% in vitro. The study's authors propose that MK-2206 should be tested in clinical trials as a potential treatment for COVID-19.[7]
References
- MK-2206 dihydrochloride (CAS 1032350-13-2) inc structure diagram
- MK-2206, an Allosteric Akt Inhibitor, Enhances Antitumor Efficacy by Standard Chemotherapeutic Agents or Molecular Targeted Drugs In vitro and In vivo. Hirai et al. 2010
- A trial of MK-2206 with chemotherapy or erlotinib for advanced cancer
- Yap TA, Yan L, Patnaik A, Fearen I, Olmos D, Papadopoulos K, et al. (December 2011). "First-in-man clinical trial of the oral pan-AKT inhibitor MK-2206 in patients with advanced solid tumors". Journal of Clinical Oncology. 29 (35): 4688–4695. doi:10.1200/JCO.2011.35.5263. PMID 22025163.
- Novel Agents are Targeting Drivers of TNBC - Several drug candidates in I-SPY2 have 'graduated' to later-phase studies. June 2016
- MK-2206 phase=2 trials
- Gassen NC, Papies J, Bajaj T, Emanuel J, Dethloff F, Chua RL, et al. (June 2021). "SARS-CoV-2-mediated dysregulation of metabolism and autophagy uncovers host-targeting antivirals". Nature Communications. 12 (1): 3818. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-24007-w. PMC 8217552. PMID 34155207.