Maibara, Shiga
Maibara (米原市, Maibara-shi) is a city in Shiga Prefecture, Japan. As of 1 September 2021, the city had an estimated population of 38,259 in 14761 households and a population density of 150 persons per km².[1] The total area of the city is 250.39 square kilometres (96.68 sq mi).
Maibara
米原市 | |
|---|---|
 | |
 Flag  Emblem | |
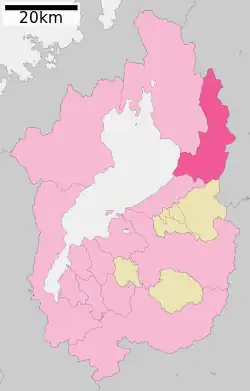 Location of Maibara in Shiga Prefecture | |
 Maibara Location in Japan | |
| Coordinates: 35°19′N 136°17′E | |
| Country | Japan |
| Region | Kansai |
| Prefecture | Shiga |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Michio Hirao |
| Area | |
| • Total | 250.39 km2 (96.68 sq mi) |
| Population (September 1, 2021) | |
| • Total | 38,259 |
| • Density | 150/km2 (400/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+09:00 (JST) |
| City hall address | 3-3 Shimotara, Maibara-shi, Shiga-ken 521-8501 |
| Climate | Cfa |
| Website | Official website |
.jpg.webp)
Geography
Maibara is located in northcentral Shiga Prefecture, on the eastern shore of Lake Biwa, and extending inland to the Ibuki Mountains and the border with Gifu Prefecture. Parts of the city are within the borders of the Biwako Quasi-National Park. Mount Ibuki is in the northeastern part of the prefecture. It is the highest peak in the prefecture. The Anegawa River and Amanogawa River pass through they city. About 70 percent of the city is forest.
Neighboring municipalities
Shiga Prefecture
Gifu Prefecture
Climate
Maibara has a Humid subtropical climate (Köppen Cfa) characterized by warm summers and cool winters with heavy snowfall. The average annual temperature in Maibara is 13.5 °C (56.3 °F). The average annual rainfall is 1,810 mm (71 in) with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 25.3 °C (77.5 °F), and lowest in January, at around 2.1 °C (35.8 °F).[2] The highest temperature ever recorded in Maibara was 36.2 °C (97.2 °F) on 14 July 2018.[3] The coldest temperature ever recorded was −12.2 °C (10.0 °F) on 4 February 2012.[3]
| Climate data for Maibara (2001−2020 normals, extremes 2001−present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 14.3 (57.7) |
18.9 (66.0) |
22.2 (72.0) |
28.0 (82.4) |
31.2 (88.2) |
33.2 (91.8) |
36.2 (97.2) |
35.9 (96.6) |
34.5 (94.1) |
31.5 (88.7) |
23.3 (73.9) |
19.3 (66.7) |
36.2 (97.2) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 5.8 (42.4) |
7.3 (45.1) |
11.3 (52.3) |
17.1 (62.8) |
22.0 (71.6) |
25.5 (77.9) |
29.1 (84.4) |
30.8 (87.4) |
27.0 (80.6) |
21.1 (70.0) |
14.9 (58.8) |
8.7 (47.7) |
18.4 (65.1) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 2.1 (35.8) |
3.1 (37.6) |
6.2 (43.2) |
11.7 (53.1) |
16.9 (62.4) |
21.0 (69.8) |
24.8 (76.6) |
26.0 (78.8) |
22.1 (71.8) |
16.0 (60.8) |
10.0 (50.0) |
4.7 (40.5) |
13.7 (56.7) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −1.7 (28.9) |
−1.2 (29.8) |
1.0 (33.8) |
5.9 (42.6) |
11.8 (53.2) |
16.9 (62.4) |
21.5 (70.7) |
22.2 (72.0) |
18.0 (64.4) |
11.1 (52.0) |
5.0 (41.0) |
0.7 (33.3) |
9.3 (48.7) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −11.9 (10.6) |
−12.2 (10.0) |
−7.6 (18.3) |
−3.8 (25.2) |
1.5 (34.7) |
8.5 (47.3) |
14.9 (58.8) |
13.7 (56.7) |
7.3 (45.1) |
1.7 (35.1) |
−2.7 (27.1) |
−7.5 (18.5) |
−12.2 (10.0) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 115.0 (4.53) |
93.5 (3.68) |
112.4 (4.43) |
115.1 (4.53) |
132.5 (5.22) |
168.5 (6.63) |
272.2 (10.72) |
153.2 (6.03) |
193.7 (7.63) |
149.6 (5.89) |
84.9 (3.34) |
129.5 (5.10) |
1,735.6 (68.33) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 87 (34) |
57 (22) |
14 (5.5) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
47 (19) |
200 (79) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 15.9 | 12.4 | 12.7 | 11.0 | 10.1 | 11.0 | 13.0 | 10.1 | 10.7 | 9.2 | 10.4 | 16.7 | 143.2 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 1 cm) | 9.2 | 5.6 | 1.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3.8 | 19.9 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 100.9 | 119.5 | 164.2 | 184.2 | 206.3 | 159.7 | 163.5 | 206.8 | 162.4 | 164.4 | 137.7 | 100.6 | 1,864.8 |
| Source: JMA[3][4] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
Per Japanese census data,[5] the population of Maibara has seen relatively little fluctuation over the past century.
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1920 | 34,839 | — |
| 1930 | 35,839 | +2.9% |
| 1940 | 34,860 | −2.7% |
| 1950 | 43,369 | +24.4% |
| 1960 | 42,214 | −2.7% |
| 1970 | 39,128 | −7.3% |
| 1980 | 39,355 | +0.6% |
| 1990 | 39,600 | +0.6% |
| 2000 | 41,251 | +4.2% |
| 2010 | 40,060 | −2.9% |
| 2020 | 37,225 | −7.1% |
History
Maibara is part of ancient Ōmi Province and the route of the Tōsandō (later the Nakasendō) highway connecting Heian-kyō with the eastern provinces passed through the area. Maibara is home to three former post stations: Banba-juku, Samegai-juku and Kashiwabara-juku, and was the location of a port on Lake Biwa where travelers could shorten their journey by taking boat to Ōtsu-juku. During the Muromachi and Sengoku periods, the Kyōgoku clan domained most of Ōmi Province from their base in what is now Maibara. Most of the area came under the control of Hikone Domain during the Edo period.
With the establishment of the modern municipalities system on April 1,1889, the village of Irie was established. It was raised to town status on November 15, 1923, becoming the town of Maihara. On February 14, 2005 Maihara merged with the neighboring towns of Santō and Ibuki (all from Sakata District) and was raised to city status, changing its name from "Maihara" to "Maibara" at that time. The new city name was based on the name of Japan Railways' Maibara Station which many people in Japan knew as a station on the Tōkaidō Shinkansen Line.
The adjacent town of Ōmi was merged into Maibara on October 1, 2005. Maibara was struck by an F2 tornado on June 29, 2018. The tornado caused major damage to homes and injured 8 people.
Government
Maibara has a mayor-council form of government with a directly elected mayor and a unicameral city council of 18 members. Maibara contributes two members to the Shiga Prefectural Assembly. In terms of national politics, the city is part of Shiga 2nd district of the lower house of the Diet of Japan.
Economy
The economy of Maibara is centered on agriculture and light manufacturing. There are several industrial parks in the city.
Education
Maibara has ten public elementary schools and seven public middle schools operated by the city government. There are two public high schools operated by the Shiga Prefectural Department of Education. The prefecture also operates one special education school for the handicapped.
Transportation
Railway
- Kashiwabara - Ōmi-Nagaoka - Samegai - Maibara
Local attractions
- Mount Ibuki — With an elevation of 1,377.4 meters, Mount Ibuki is Shiga Prefecture's tallest mountain and a popular spot for skiing in winter and camping and hiking in the warmer months. A gondola and ski lifts carry visitors to the top which affords fine views of Lake Biwa and the surrounding area. The nearest station is Omi-Nagaoka Station.
- Samegai Trout Farm — Established over a century ago, this is the largest trout farm in Asia and with many ponds. There is a shallow pond where children can try catch (and release) the trout. Riverside restaurants serve fresh trout.
- Nakasendō stage towns — The Nakasendō was an old highway linking Kyoto with Edo (present-day Tokyo). The highway had 67 stages and the three in Shiga were Kashiwabara-juku, Samegai-juku and Banba-juku in Maibara city. Even today, you can see remnants of these stage towns established for highway travelers to lodge and trade.
- Amanogawa River — In June, fireflies come out at night. Parts of the river are designated as a protected areas for fireflies.
- Lake Biwa — The lakeshore road is very scenic on fine days.
- Kamaha Castle ruins, National Historic Site
- Tokugen-in, bodaiji of the Kyōgoku clan, rulers of most of Ōmi province in the Muromachi period, and National Historic Site
- Kyōgoku clan ruins, sites related to the Sengoku-period Kyōgoku clan, a National Historic Site
Festivals and events
- Samegai Baikamo Flowers — Underwater flowers which bloom in Jizogawa River
- Maibara Hikiyama Festival — Parade of ornate floats which have a small stage featuring kabuki performed by children. Early October.
References
- "Maibara city official statistics" (in Japanese). Japan.
- Maibara climate data
- 観測史上1~10位の値(年間を通じての値). JMA. Retrieved February 27, 2022.
- 気象庁 / 平年値(年・月ごとの値). JMA. Retrieved February 27, 2022.
- Maibara population statistics
External links
- Maibara City official website (in Japanese)
