Marc Antoine de Beaumont
Marc-Antoine de Beaumont (French pronunciation: [maʁk ɑ̃twan də bomɔ̃]; 23 September 1763 – 4 February 1830) a French nobleman, became a page to the king and joined the army of the Old Regime. He stayed in the army during the French Revolution and narrowly escaped being executed. During the French Revolutionary Wars he fought in the 1796 Italian campaign under Napoleon Bonaparte, leading the cavalry at Lodi and Castiglione. In 1799 he was wounded in Italy but fought there again in late 1800.
Marc Antoine de Beaumont | |
|---|---|
 General of Division Marc Antoine de Beaumont | |
| Born | 23 September 1763 Beaumont-la-Ronce, France |
| Died | 4 February 1830 (aged 66) France |
| Allegiance | |
| Service/ | Cavalry |
| Rank | General of Division |
| Battles/wars | French Revolutionary Wars Napoleonic Wars |
| Awards | Légion d'Honneur, 1803 Order of the Iron Crown, 1808 Military Order of Max Joseph, 1808 Order of Saint Louis, 1814 |
| Other work | Senator, 1807 Count of the Empire, 1808 |
After Napoleon became emperor, Beaumont led the 3rd Dragoon Division in two major campaigns during the Napoleonic Wars. He led his cavalrymen against Habsburg Austria and Russia in several actions during the War of the Third Coalition in 1805. In the War of the Fourth Coalition, he was present at Jena and fought at Prenzlau and Eylau. In 1809, he commanded a reserve formation. His brother-in-law was Marshal Louis-Nicolas Davout. Beaumont is one of the names inscribed under the Arc de Triomphe.
Early career
Born into a noble family from the province of Touraine, Beaumont became a page in the household of King Louis XVI of France on 31 December 1777. After attaining the position of first page, he was nominated captain in the Lorraine Dragoon Regiment on 2 June 1784. He received the brevet rank of lieutenant colonel on 22 July 1792 and colonel on 7 August. While his regiment was posted at Lyon during the Reign of Terror, he came under suspicion, was arrested, and condemned to die. His dragoons turned out fully armed and promised to use violence if the sentence was carried out. In the face of this threat, the authorities had a change of heart and Beaumont was posted to the Army of Italy instead. While in Italy, he served under André Masséna and Barthélemy Louis Joseph Schérer. He became a general of brigade on 25 March 1795.[1]

On 26 March 1796, a youthful commander named Napoleon Bonaparte arrived in Nice to assume command of the Army of Italy.[2] At that time, Beaumont was a brigadier in the 3,090-man 1st Cavalry Division under the overall command of Henri Christian Michel de Stengel. The division included the 1st Hussar Regiment, the 10th, 22nd, and 25th Chasseurs à Cheval, and the 5th and 20th Dragoon Regiments. In April, Beaumont fought in the Montenotte Campaign,[3] in which Stengel was mortally wounded at the Battle of Mondovì.[4]
On 2 May, while leading part of the cavalry, Beaumont sent out patrols to find where the Austrian forces were located.[5] At the Battle of Lodi on 10 May, Bonaparte directed him to take his cavalry to ford the Adda River and flank the Austrians out of position. A ford was located 800 meters upstream but it was hard to move significant numbers of horsemen across because the river banks were a tangle of trees. At 6:00 PM Bonaparte ordered a frontal attack, which was a success. Though the horsemen were not directly involved, the knowledge that enemy cavalry were crossing the river helped to unnerve the Austrian defenders.[6]
An eyewitness described an incident during the pursuit of the Austrians. As the French cavalry advance guard approached Crema in a cloud of dust, the observer made out the leading horseman yelling at the Austrian stragglers whom he encountered on the road. It was Beaumont. The general dismounted his men, who were on their best behavior, and requested refreshment for his unit. At the time much of the army was on a plundering rampage, looting everything in sight.[7]
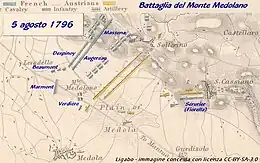
At the Battle of Castiglione on 5 August 1796, a powerful redoubt crowned a small hill on the Austrian left flank near the village of Medole. To take the Monte Medolano position, Bonaparte assigned Beaumont's cavalry, Auguste Marmont's 15 to 18 artillery pieces, and the 4th Line Infantry Demi-Brigade under Jean-Antoine Verdier. After an hour and a half of combat, the position fell to the 4th Line and Beaumont's cavalry supports. Though the French tried to cut off the retreat of Dagobert Sigmund von Wurmser's army, it was able to escape across the Mincio River.[8][9]
In the War of the Second Coalition, Beaumont served in Italy again. On 5 April 1799, he was shot through the right shoulder at the Battle of Magnano. He recovered from his wound in time to fight at the Battle of the Mincio on 25 December 1800. He received promotion to general of division sometime in 1802 or 1803. On 11 December 1803 he became a member of the Légion d'Honneur.[1]
Napoleonic Wars

In the War of the Third Coalition, Beaumont led the 3rd Dragoon Division, which included 18 squadrons in the 5th, 8th, 9th, 12th, and 16th Dragoon Regiments, and a horse artillery battery. His brigadiers were Charles Joseph Boyé and Nicolas-Joseph Scalfort. Under the overall leadership of Marshal Joachim Murat, he led his 2,400 troopers into action at the Battle of Wertingen on 8 October 1805. The French cavalry, including Beaumont's division, Louis Klein's 1st Dragoon Division, Anne-François-Charles Trelliard's Light Cavalry Brigade,[10] and Étienne Marie Antoine Champion de Nansouty's 1st Cuirassier Division, marched from Rain early that morning. Moving south along the Lech River to Nordendorf, they turned west and appeared before Franz Xavier Auffenburg's 5,400 Austrians at Wertingen.[11]

Klein's division marched south and west to flank the Austrians, while Beaumont and Trelliard attacked in front.[12] Major Rémi Joseph Isidore Exelmans led an attack by 200 dismounted dragoons which cleared the Austrians out of an outlying village. The French found the nine enemy battalions drawn up behind Wertingen in one large square. The formation was attacked with the help of Nicolas Oudinot's infantry division and driven back in increasing confusion. Finally, the Austrians fled, leaving 2,000 prisoners in French hands.[13]
After the Austrians surrendered at the Battle of Ulm, Napoleon's army pursued a rear guard led by Maximilian, Count of Merveldt to the east. Murat's cavalry attacked between 4,000 and 6,000 Austrians near Ried im Innkreis on 30 October. A portion of the rear guard was driven into a defile. Murat sent in chasseurs à cheval and dismounted dragoons to crush this force, capturing 500 to 600 prisoners.[14] The next day, 4,000 troops from Merveldt's rear guard under Emmanuel von Schustekh-Herve made a stand at Lambach on the Traun River. Three battalions of the Ignaz Gyulai Infantry Regiment, two squadrons of the Kaiser Dragoons # 1, and eight squadrons of the Kaiser Hussars # 1 were supported by four Russian jager battalions and a squadron of hussars. Murat ordered Beaumont's 3rd Dragoon Division and Baptiste Pierre Bisson's 1st Division of Davout's III Corps to attack. The Allies were driven back, with the Russians suffering 100 killed and less than 50 wounded. French losses were "slight" though Bisson was wounded.[15][16] Beaumont fought at the Battle of Austerlitz, leading the 5th, 8th, 12th, 16th, and 21st Dragoon Regiments.[17] He was named a Grand Officer of the Légion d'Honneur on 10 February 1806.[1]


Beaumont led the 3rd Dragoon Division at the Battle of Jena on 14 October 1806 in the War of the Fourth Coalition.[18] His division was one of the three present with Marshal Joachim Murat at the Capitulation of Erfurt.[19] The 3rd Division included the 5th, 8th, 12th, 16th, 19th, and 21st Dragoon Regiments.[20] He was active in the pursuit of Prince Hohenlohe's Prussian corps. He was present in the action of Zehdenick on 26 October.[21] Beaumont played a prominent role at the Battle of Prenzlau on 28 October. After the Prussian rear guard under Prince Augustus of Prussia became separated from the marching column, Beaumont charged it repeatedly, driving it northward. He finally pinned the rear guard against the Uecker River, forcing it to surrender. Hohenlohe capitulated with his main body soon afterward.[22] He was present at the Battle of Czarnowo on 23 December 1806.[1]
Emperor Napoleon named Beaumont a Senator on 14 August 1807 and a Count of the Empire in March 1808. That year he was also awarded the Order of the Iron Crown, the Military Order of Max Joseph of Bavaria, and the Order of Fidelity of Baden.[1]
In 1809 Beaumont commanded the Reserve Division under Marshal François Christophe de Kellermann. Based at Frankfurt-on-the-Main, the all-arms unit consisted of 826 men from elite companies of line and light infantry regiments, 1,251 Württemberg infantry, 527 Bavarian infantry, a 160-man foot artillery company with eight guns, and the following provisional dragoon regiments, 1st - 697 sabers, 2nd - 669 sabers, 3rd - 515 sabers, 4th - 771 sabers, and 5th - 792 sabers. This force did not fight at the Battle of Wagram.[23]
In 1814, the Senate officially passed laws deposing Napoleon. King Louis XVIII of France bestowed the Order of Saint Louis on Beaumont in June 1814. He was not employed during the Hundred Days. After the Bourbon Restoration he commanded a division in the Army of Paris.
Family
Beaumont married Louis-Nicolas Davout's sister Julie (1771–1846) in 1801. He died on 4 February 1830 and was buried in the same tomb as his brother-in-law Davout with whom he shared a long friendship. The name BEAUMONT is engraved on Column 17 of the Arc de Triomphe. The surname was shared with another French officer, Louis-Chrétien Carrière, Baron de Beaumont (1771–1813), who temporarily led a brigade under Beaumont at Prenzlau.[1]
Notes
- Mullié, Charles. Biographie des célébrités militaires des armées de terre et de mer de 1789 a 1850. 1852. Marc Antoine de Beaumont, 49
- Boycott-Brown, Martin. The Road to Rivoli. London: Cassell & Co., 2001. ISBN 0-304-35305-1. 144
- Smith, Digby. The Napoleonic Wars Data Book. London: Greenhill, 1998. ISBN 1-85367-276-9. 113. Smith lists the Army of Italy order of battle for April 1796 under the Battle of Borghetto, which occurred on 30 May.
- Boycott-Brown, 271
- Boycott-Brown, 289
- Boycott-Brown, 313-314
- Boycott-Brown, 319
- Boycott-Brown, 398-400
- Chandler, David. The Campaigns of Napoleon. New York: Macmillan, 1966. 198. Chandler writes that Marmont had 18 guns.
- Smith, 203
- Kagan, Frederick W. The End of the Old Order: Napoleon and Europe, 1801-1805. Cambridge, MA: Da Capo Press, 2006. ISBN 0-306-81137-5. 404
- Kagan, 404-405. Map information is included.
- Thiers, Adolphe. Histoire du Consulat et de Empire. Vol. 6. Paris, 1847. 89-91
- Kagan, 450-451
- Kagan, 451
- Smith, 210
- Duffy, Christopher. Austerlitz 1805. Hamden, Conn.: Archon Books, 1977. 179-180
- Smith, 224
- Petre, 194-196
- Smith, 227-228
- Petre, 239
- Petre, 244-246
- Bowden & Tarbox, 160
References
- Bowden, Scotty & Tarbox, Charlie. Armies on the Danube 1809. Arlington, Texas: Empire Games Press, 1980.
- Boycott-Brown, Martin. The Road to Rivoli. London: Cassell & Co., 2001. ISBN 0-304-35305-1
- Chandler, David. The Campaigns of Napoleon. New York: Macmillan, 1966.
- Duffy, Christopher. Austerlitz 1805. Hamden, Conn.: Archon Books, 1977.
- Kagan, Frederick W. The End of the Old Order: Napoleon and Europe, 1801-1805. Cambridge, MA: Da Capo Press, 2006. ISBN 0-306-81137-5
- (in French) Mullié, Charles. Biographie des célébrités militaires des armées de terre et de mer de 1789 a 1850. 1852.
- Petre, F. Loraine. Napoleon's Conquest of Prussia 1806. London: Lionel Leventhal Ltd., 1993 (1907). ISBN 1-85367-145-2
- Smith, Digby. The Napoleonic Wars Data Book. London: Greenhill, 1998. ISBN 1-85367-276-9
- (in French) Thiers, Adolphe. Histoire du Consulat et de Empire. Vol. 6. Paris, 1847.