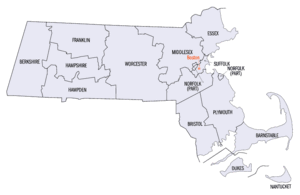
List of counties in Massachusetts
The U.S. state of Massachusetts has 14 counties, though eight[1] of these fourteen county governments were abolished between 1997 and 2000. The counties in the southeastern portion of the state retain county-level local government (Barnstable, Bristol, Dukes, Norfolk, Plymouth) or, in one case, (Nantucket County) consolidated city-county government.[2][3] Vestigial judicial and law enforcement districts still follow county boundaries even in the counties whose county-level government has been disestablished, and the counties are still generally recognized as geographic entities if not political ones.[4] Three counties (Hampshire, Barnstable, and Franklin) have formed new county regional compacts to serve as a form of regional governance.
| Counties of Massachusetts | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Location | Commonwealth of Massachusetts |
| Number | 14 |
| Populations | 14,421 (Nantucket) – 1,617,105 (Middlesex) |
| Areas | 48 square miles (120 km2) (Nantucket) – 1,513 square miles (3,920 km2) (Worcester) |
| Government | |
| Subdivisions |
|
Abolitions of some county governments

Mismanagement of Middlesex County's public hospital in the mid-1990s left that county on the brink of insolvency, and in 1997 the Massachusetts legislature stepped in by assuming all assets and obligations of the county. The government of Middlesex County was officially abolished on July 11, 1997.[1] Later that year, the Franklin County Commission voted itself out of existence. The law abolishing Middlesex County also provided for the elimination of Hampden County and Worcester County on July 1, 1998.[1] This law was later amended to abolish Hampshire County on January 1, 1999; Essex County and Suffolk County on July 1 of that same year; and Berkshire County on July 1, 2000.[1] State law allows other counties either to abolish themselves, or to reorganize as a "regional council of governments",[1] as Hampshire and Franklin Counties have done. The governments of Bristol, Plymouth, and Norfolk Counties remain substantially unchanged. Barnstable and Dukes Counties have adopted modern county charters, enabling them to act as efficient regional governments. Dukes County in particular has a strong regional planning agency known as the Martha's Vineyard Commission.[5]
District Attorneys
Jurisdictional areas for District Attorneys are created by state law and while some follow traditional county boundaries, names and geographic areas covered are often different. Criminal matters in Essex County are handled by the District Attorney for the Eastern District; in Middlesex County by the District Attorney for the Northern District; in Worcester County by the District Attorney for the Middle District; in Dukes, Barnstable and Nantucket counties by the District Attorney for the Cape and Islands District and in Franklin and Hampshire counties by the District Attorney for the Northwestern District. The districts for the counties of Berkshire, Bristol, Hampden, Norfolk, Plymouth and Suffolk are the same in geography and nomenclature as the respective counties,[6] and the District Attorneys for the Eastern, Middle, and Northern Districts are commonly known as the Essex County,[7] Worcester County,[8] and Middlesex County District Attorneys,[9] respectively.
Historical counties
Eleven other historical counties have existed in Massachusetts, most becoming defunct when their lands were absorbed into the colony of New Hampshire or the state of Maine, both of which were created out of territory originally claimed by Massachusetts colonists. The oldest counties still in Massachusetts are Essex County, Middlesex County, and Suffolk County, created in 1643 with the original Norfolk County which was absorbed by New Hampshire and bears no relation to the modern Norfolk County. When these counties were created, they were a part of the Massachusetts Bay Colony, which would remain separate from the Plymouth Colony and that colony's counties until 1691. Hampden County, created in 1812, is the most recently created county still in Massachusetts, although Penobscot County, Maine bore that distinction until Maine broke off from Massachusetts in 1820.[10] The majority of Massachusetts counties are named in honor of English place names, reflecting Massachusetts' colonial heritage.[11]
Shire town
The term shire town is the statutory term for the Massachusetts town having a county court and administration offices; a county can have multiple shire towns.[12] County seat is the standard term used in general communications by the Massachusetts government.
FIPS code
The Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) code, used by the United States government to uniquely identify counties, is provided with each entry. FIPS codes are five-digit numbers; for Massachusetts the codes start with 25 and are completed with the three-digit county code. The FIPS code for each county in the table links to census data for that county.[13]
List of current counties
| County |
FIPS code[14] | County seat[15] | Est.[16] | Origin[10] | Etymology[11] | Population[17] | Area[16] | Map |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Barnstable County | 001 | Barnstable | 1685 | One of three original counties created in the Plymouth Colony | After its county seat of Barnstable, which is named after the English town of Barnstaple | 232,457 | 396 sq mi (1,026 km2) |  |
| Berkshire County | 003 | Pittsfield | 1761 | From part of Hampshire County. Government abolished in 2000.[4] | For the English county of Berkshire | 127,859 | 931 sq mi (2,411 km2) |  |
| Bristol County | 005 | Taunton | 1685 | One of three original counties created in the Plymouth Colony | For its original county seat of Bristol, Massachusetts, which is named for the English port city of Bristol – when the Town of Bristol joined Rhode Island, the name of the county was kept | 580,068 | 556 sq mi (1,440 km2) |  |
| Dukes County | 007 | Edgartown | 1695 | From Martha's Vineyard and the Elizabeth Islands, which had been part of Dukes County, New York until Massachusetts gained it in 1691 | Formerly a part of Dukes County, New York until 1691, the land at one time was the possession of the Duke of York | 20,868 | 104 sq mi (269 km2) |  |
| Essex County | 009 | Salem, Lawrence | 1643 | One of four original counties created in the Massachusetts Bay Colony. Government abolished in 1999.[4] | For the English county of Essex | 806,765 | 498 sq mi (1,290 km2) |  |
| Franklin County | 011 | Greenfield | 1811 | From part of Hampshire County. Government abolished in 1997.[4] | For Benjamin Franklin (1706–1790), early American scientist, diplomat, and politician | 70,894 | 702 sq mi (1,818 km2) | 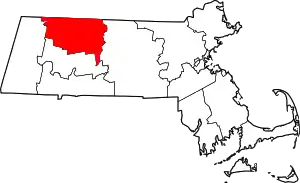 |
| Hampden County | 013 | Springfield | 1812 | From part of Hampshire County. Government abolished in 1998.[4] | John Hampden (1595—1643), the famous 17th century English parliamentarian | 461,041 | 618 sq mi (1,601 km2) |  |
| Hampshire County | 015 | Northampton | 1662 | From unorganized territory in the western part of the Massachusetts Bay Colony. Government abolished 1999.[4] | For the English county of Hampshire | 162,588 | 529 sq mi (1,370 km2) |  |
| Middlesex County | 017 | Lowell, Cambridge | 1643 | One of four original counties created in the Massachusetts Bay Colony. Government abolished in 1997.[4] | For the English county of Middlesex | 1,617,105 | 824 sq mi (2,134 km2) |  |
| Nantucket County | 019 | Nantucket | 1695 | From Nantucket Island which had been part of Dukes County, New York until Massachusetts gained it in 1691. | The Town of Nantucket, itself derived from a Wampanoag word meaning "place of peace" | 14,421 | 48 sq mi (124 km2) | 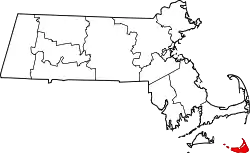 |
| Norfolk County | 021 | Dedham | 1793 | From part of Suffolk County. | For the English county of Norfolk | 725,531 | 400 sq mi (1,036 km2) |  |
| Plymouth County | 023 | Brockton, Plymouth | 1685 | One of three original counties created in the Plymouth Colony. | For its seat of Plymouth, which is named for the English port city of Plymouth | 533,069 | 661 sq mi (1,712 km2) |  |
| Suffolk County | 025 | Boston | 1643 | One of four original counties created in the Massachusetts Bay Colony. Government abolished in 1999.[4] | For the English county of Suffolk | 766,381 | 58 sq mi (150 km2) |  |
| Worcester County | 027 | Worcester | 1731 | From parts of Hampshire County, Middlesex County and Suffolk County. Government abolished in 1998.[4] | For its county seat of Worcester, which is named in honor of the English city of Worcester and the English Civil War Battle of Worcester in 1651, a Parliamentarian victory | 862,927 | 1,513 sq mi (3,919 km2) |  |
Former counties
| County |
Created [10] |
Abolished [10] |
Fate [10] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cumberland County | 1760 | 1820 | Transferred to Maine |
| Devonshire County | 1674 | 1675 | Abolished and then absorbed into Maine |
| Hancock County | 1789 | 1820 | Transferred to Maine |
| Kennebec County | 1799 | 1820 | Transferred to Maine |
| Lincoln County | 1760 | 1820 | Transferred to Maine |
| Norfolk County | 1643 | 1679 | Abolished – most of its territory was absorbed into New Hampshire; towns remaining in Massachusetts were absorbed into Essex County. One of four original counties created in the Massachusetts Bay Colony. |
| Oxford County | 1805 | 1820 | Transferred to Maine |
| Penobscot County | 1816 | 1820 | Transferred to Maine |
| Somerset County | 1809 | 1820 | Transferred to Maine |
| Washington County | 1789 | 1820 | Transferred to Maine |
| York County | 1652 | 1820 | Transferred to Maine – there were two periods when York County was abolished, 1664 to 1668 and 1680 to 1691 |
See also
- Administrative divisions of Massachusetts
- Government of Massachusetts – section on local government
- List of former United States counties
References
- Mass. Gen. L. c. 34B
"General Laws of Massachusetts, Chapter 34B. Abolition of County Government". Massachusetts General Court. Archived from the original on February 5, 2010. Retrieved January 24, 2010. - "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Archived from the original on 8 June 2007. Retrieved 19 July 2007.
- "Find A County". National Association of Counties. Archived from the original on 2014-01-13. Retrieved 2012-04-07.
- "Historical Data Relating to the Incorporation of and Abolishment of Counties in the Commonwealth of Massachusetts". Secretary of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. Archived from the original on 17 June 2018. Retrieved 14 January 2007.
- "Martha's Vineyard Commission - mvcommission.org". www.mvcommission.org. Archived from the original on 8 April 2018. Retrieved 16 April 2018.
- "Elections: Massachusetts District Attorney – Districts". www.sec.state.ma.us. August 23, 2004. Archived from the original on 2004-08-23.
- "Essex District Attorney's Office | Mass.gov". www.mass.gov. Archived from the original on 2021-10-13. Retrieved 2021-10-24.
- "Worcester County District Attorney Joseph D. Early, Jr". The Office of the Worcester County District Attorney. Archived from the original on 2021-07-28. Retrieved 2021-10-24.
- "Middlesex District Attorney". Archived from the original on 2017-03-08. Retrieved 2017-03-08.
- Brown, Richard & Tager, Jack (2000). Massachusetts: A Concise History. University of Massachusetts Press. ISBN 1-55849-249-6.
- Beatty, Michael (2001). County Name Origins of the United States. McFarland Press. ISBN 0-7864-1025-6.
- Part III, Title I, Chapter 213, §7 Archived 2008-07-19 at the Wayback Machine, Massachusetts General Laws. Accessed 24 January 2008.
- "County FIPS Code Listing for the Commonwealth of Massachusetts". US Environmental Protection Agency. Retrieved September 27, 2017.
- "EPA County FIPS Code Listing". EPA.gov. Archived from the original on 2011-05-14. Retrieved 2008-02-23.
- "U.S. Census Bureau QuickFacts: Massachusetts". Archived from the original on 2021-01-27. Retrieved 2020-08-21.
- "NACo – Find a county". National Association of Counties. Archived from the original on 2010-06-01. Retrieved 30 April 2008.
- "U.S. Census Bureau QuickFacts: Massachusetts". U.S. Census Bureau. Archived from the original on 27 January 2021. Retrieved 5 April 2023.
External links
- Historical Data Relating to the Incorporation of and Abolishment of Counties in the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, Secretary of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts