McCreary County, Kentucky
McCreary County is a county located in the U.S. state of Kentucky. As of the 2020 census, the population was 16,888.[1] Its county seat is Whitley City.[2] The county is named for James B. McCreary, a Confederate war soldier and two-time Governor of Kentucky (1875–1879, 1911–1915). During his second term as governor, McCreary County was created by the Legislature and was named in his honor.
McCreary County | |
|---|---|
 McCreary County courthouse in Whitley City | |
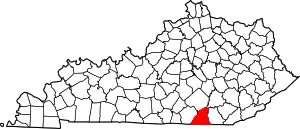 Location within the U.S. state of Kentucky | |
 Kentucky's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 36°44′N 84°29′W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | March 12, 1912 |
| Named for | James B. McCreary |
| Seat | Whitley City |
| Largest community | Pine Knot |
| Area | |
| • Total | 431 sq mi (1,120 km2) |
| • Land | 427 sq mi (1,110 km2) |
| • Water | 4.1 sq mi (11 km2) 1.0% |
| Population (2020) | |
| • Total | 16,888 |
| • Estimate (2022) | 16,701 |
| • Density | 39/sq mi (15/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) |
| Congressional district | 5th |
| Website | www |
History
McCreary County is the only Kentucky county without an incorporated city. Because of this, county government is the sole local government agency for the entire county. Attractions in McCreary County include the Big South Fork National River and Recreation Area, Cumberland Falls State Park, and the Big South Fork Scenic Railway, which tours several former coal camps. In popular culture, McCreary County is mentioned in the FX drama Justified, for it is home to USP McCreary, near Pine Knot.
The majority of the county is controlled by the federal government. 43% is managed by the Daniel Boone National Forest, and 18% managed by the National Park Service as the Big South Fork National River and Recreation Area.
The area now encompassed by Kentucky's McCreary County was first bounded in 1772, when all of what is now the state of Kentucky was in the frontier county of Fincastle County, Virginia. Fincastle was divided in 1776, with the western portion named Kentucky County, Virginia. In 1780, the Virginia legislature set aside all land in Kentucky County for soldiers who had served in the Revolutionary War. In 1780, Kentucky County was divided into three counties: Jefferson, Fayette, and Lincoln. In 1784, a portion of Jefferson County was partitioned off to create Nelson County, and in 1792 a portion of Lincoln County was partitioned off to create Green County. In 1798, a further portion of Lincoln County was partitioned off, and combined with parts of Green County, to create Pulaski and Cumberland Counties. The following year yet another portion of Lincoln County was partitioned off to create Knox County, and in 1800 the new Cumberland County was sectioned off to create Wayne County. In 1818, Whitley County was created from a portion of Knox County.
In 1912, the Kentucky Legislature partitioned parts of Pulaski, Wayne, and Whitley Counties, to create McCreary County. Its boundaries have remained unchanged since that time.[3] It is the 120th and final county in order of formation. The present county boundaries contain 427.7 square miles (1,107.7 km2) of land area. The majority of the county was carved out of Wayne and Whitley Counties, with a large center strip following the rail line and roadway from Pulaski County. The early history of the area is that of those counties, and is related in the historic perspectives for them. The map to the left shows the network of roadways that had been established by the 1860s. A dotted blue line and settlement names have been added for reference.
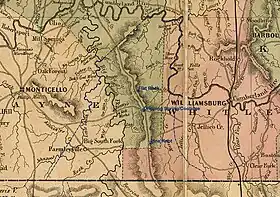
The most significant early feature of the future county was the Jacksboro Road. Running from Jacksboro, Tennessee, to Point Isabel and Somerset, this pioneer road was simply an enlargement of the Tellico Trail, an Indian route that had been used for thousands of years. Several other trails intersected this road, and led to the settlement of villages such as Pine Knot, Dripping Springs/Coolidge, and Flat Rock. Other settlement occurred in sequestered hollows. The economy of the times was based upon small-scale subsistence agriculture, timber products such as railroad ties and barrel staves, and small coal mines.
Beginning in the early 19th century, Cumberland Falls gained attention as a tourism destination. Later development increased visitation, and the Brunsen Inn was a popular destination for seasonal visitors. Until a road was built from Whitley County in 1931, the primary access to the Falls was through McCreary. With a generous contribution from one of the DuPont family heirs, the Falls joined the state park system in 1930.
The completion of the Cincinnati Southern Railway line through the county in 1880 changed its economic characteristics. Access to distant markets for timber and coal caused the emergence of many small mining and logging companies. The greatest impact came from the Justus S. Stearns enterprises. From 1903 through the rest of the century, the territory of McCreary County was dominated and controlled by Stearns company interests.
Attempting to avoid financial losses during the Great Depression of the 1930s, the Stearns cluster of companies sold vast quantities of land to the U.S. Government, becoming part of what was to become the Cumberland National Forest in 1937. This forest reserve was subsequently renamed Daniel Boone National Forest. In the 1970s, legislative action acquired additional lands in southern McCreary and Tennessee, creating the Big South Fork National River and Recreation Area in the mid-1970s.
Government
- Judge Executive — Hon. Jimmie "Bevo" Greene (R)
- Deputy Judge Executive — Hon.Nathan Nevels (R)
- County Magistrates:
- Magistrate Dist. 1 — William "Bill" Hale Jr. (R)
- Magistrate Dist. 2 — Roger Phillips (R)
- Magistrate Dist. 3 — Bobbie Strunk (R)
- Magistrate Dist. 4 — Vacant
- County Clerk — Eric Haynes (R)
- Sheriff — Randy Waters (D)
- Jailer — Jesse Hatfield (R)
- Coroner — Timothy L. Corder (R)
- Tourism Director
- Economic Development Director
- Property Valuation Administrator — Dwight Ross
- McCreary County Attorney — Austin Price
The Federal Bureau of Prisons U.S. Penitentiary, McCreary is in the county, near Pine Knot.[4][5]
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 431 square miles (1,120 km2), of which 427 square miles (1,110 km2) is land and 4.1 square miles (11 km2) (1.0%) is water.[6]
Geology

McCreary County lies on the western edge of the Cumberland Plateau, which constitutes the East Kentucky Coal Field. It is located entirely within the proclamation boundary of the Daniel Boone National Forest. The county's bedrock is deeply incised by the Big South Fork of the Cumberland River and its tributaries, creating sheer cliffs, gorges, waterfalls, rock shelters, and natural stone arches. Most of the geological underpinning of this region is capped with thick sandstone, and formidable coal seams are common in this formation. Limited lands suitable for large-scale conventional agriculture exist, so the economy of the area has historically been centered upon extractive industries such as timber and mining.
Adjacent counties
- Pulaski County (north)
- Laurel County (northeast)
- Whitley County (east)
- Campbell County, Tennessee (southeast)
- Scott County, Tennessee (south)
- Wayne County (west)
National protected areas
Demographics
| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1920 | 11,676 | — | |
| 1930 | 14,627 | 25.3% | |
| 1940 | 16,451 | 12.5% | |
| 1950 | 16,660 | 1.3% | |
| 1960 | 12,463 | −25.2% | |
| 1970 | 12,548 | 0.7% | |
| 1980 | 15,634 | 24.6% | |
| 1990 | 15,603 | −0.2% | |
| 2000 | 17,080 | 9.5% | |
| 2010 | 18,306 | 7.2% | |
| 2020 | 16,888 | −7.7% | |
| 2022 (est.) | 16,701 | [7] | −1.1% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[8] 1790–1960[9] 1900–1990[10] 1990–2000[11] 2010–2020[1] | |||
As of the census of 2000, there were 17,080 people, 6,520 households, and 4,753 families residing in the county. The population density was 40 per square mile (15/km2). There were 7,405 housing units at an average density of 17 per square mile (6.6/km2). The racial makeup of the county was 97.99% White, 0.63% Black or African American, 0.42% Native American, 0.02% Asian, 0.01% Pacific Islander, 0.20% from other races, and 0.73% from two or more races. 0.62% of the population were Hispanics or Latinos of any race.
There were 6,520 households, out of which 35.70% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 54.50% were married couples living together, 13.80% had a female householder with no husband present, and 27.10% were non-families. 24.70% of all households were made up of individuals, and 8.40% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.55 and the average family size was 3.03.
The age distribution was 27.70% under the age of 18, 9.80% from 18 to 24, 28.20% from 25 to 44, 23.70% from 45 to 64, and 10.60% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 34 years. For every 100 females there were 96.90 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 93.80 males.
The median income for a household in the county was $19,348, and the median income for a family was $22,261. Males had a median income of $20,823 versus $15,575 for females. The per capita income for the county was $9,896. About 26.10% of families and 32.20% of the population were below the poverty line, including 40.50% of those under age 18 and 27.30% of those age 65 or over. The county's per-capita income makes it one of the poorest counties in the United States, and second in poverty only to another county in the same Kentucky region, Clay County, among counties with a majority non-Hispanic white population.
Politics
McCreary County has only once voted for a non-Republican for president, in the year of its formation, when it voted for Theodore Roosevelt of the Progressive Party, with President William Howard Taft second and Democrat Woodrow Wilson a distant third at 18.1%.[12] This trend has only strengthened in recent elections, with Republican Donald Trump winning 88.0% of the vote in 2020, the highest vote share for a Republican in the county since Herbert Hoover in 1928.
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third party | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | |
| 2020 | 5,664 | 87.98% | 725 | 11.26% | 49 | 0.76% |
| 2016 | 5,012 | 86.77% | 664 | 11.50% | 100 | 1.73% |
| 2012 | 4,564 | 79.97% | 1,069 | 18.73% | 74 | 1.30% |
| 2008 | 4,078 | 75.42% | 1,258 | 23.27% | 71 | 1.31% |
| 2004 | 4,121 | 72.39% | 1,530 | 26.88% | 42 | 0.74% |
| 2000 | 3,321 | 69.20% | 1,418 | 29.55% | 60 | 1.25% |
| 1996 | 2,527 | 52.70% | 1,710 | 35.66% | 558 | 11.64% |
| 1992 | 3,588 | 57.78% | 1,934 | 31.14% | 688 | 11.08% |
| 1988 | 3,477 | 66.96% | 1,644 | 31.66% | 72 | 1.39% |
| 1984 | 4,028 | 70.58% | 1,609 | 28.19% | 70 | 1.23% |
| 1980 | 3,786 | 71.27% | 1,377 | 25.92% | 149 | 2.80% |
| 1976 | 3,272 | 63.63% | 1,827 | 35.53% | 43 | 0.84% |
| 1972 | 3,203 | 80.56% | 684 | 17.20% | 89 | 2.24% |
| 1968 | 2,670 | 67.61% | 759 | 19.22% | 520 | 13.17% |
| 1964 | 2,230 | 60.55% | 1,428 | 38.77% | 25 | 0.68% |
| 1960 | 3,671 | 79.89% | 924 | 20.11% | 0 | 0.00% |
| 1956 | 3,812 | 82.33% | 814 | 17.58% | 4 | 0.09% |
| 1952 | 3,360 | 77.98% | 937 | 21.75% | 12 | 0.28% |
| 1948 | 3,031 | 75.93% | 933 | 23.37% | 28 | 0.70% |
| 1944 | 3,419 | 79.49% | 880 | 20.46% | 2 | 0.05% |
| 1940 | 3,172 | 71.62% | 1,248 | 28.18% | 9 | 0.20% |
| 1936 | 2,953 | 72.57% | 1,105 | 27.16% | 11 | 0.27% |
| 1932 | 3,360 | 73.43% | 1,194 | 26.09% | 22 | 0.48% |
| 1928 | 3,622 | 89.10% | 435 | 10.70% | 8 | 0.20% |
| 1924 | 2,317 | 74.98% | 533 | 17.25% | 240 | 7.77% |
| 1920 | 2,889 | 84.01% | 525 | 15.27% | 25 | 0.73% |
| 1916 | 1,630 | 82.28% | 324 | 16.36% | 27 | 1.36% |
| 1912 | 411 | 33.36% | 225 | 18.26% | 596 | 48.38% |
Economy
The economic history of McCreary County has been one of boom and bust, based upon the extractive resources of coal mining and timber. The Stearns interests sold the last of their mining operations to Blue Diamond Coal in the 1980s, and the county's last operating mine closed in 1994. A resurgence of the coal industry does not seem possible, as the local coal is high in sulfur, and drainage from coal mining would adversely affect a number of outstanding and special waters in the county.
The county is poor. McCreary is one of the U.S. counties most dependent upon federal government assistance programs such as SNAP, SSI, SSDI, Social Security, Medicare/Medicaid, and other government assistance programs. 52.46 percent of the income of the residents of the county is derived from government assistance. The average resident received $11,022 in government assistance in 2009.[14]
Industrial development began in the 1970s, with new manufacturing concerns in the sewing industry. Changes in the global economy have shifted a substantial percentage of the consumer garment market to production facilities outside the United States. Those that remain in the county draw their work from military contracts, and the production of high-end consumer goods. Timber remains a factor in the economy, with logging and cut hardwood production. Since the 1970s, the county has attempted to develop three industrial parks with little success. The latest venture, on Kentucky Route 92 in Pine Knot, is building a "spec" building as a means of attracting new industry to the county.
Agriculture has never played a significant role in the county's economy. In 2002, 5% of the county was in farmland. Top products were livestock, hay and forage. Together this represented a total market value of $566,000, down 1% from 1997. These low numbers indicate that the county has never had a substantial agricultural industry, and that over 80% of the county lands are held by the federal government. McCreary County is ranked number 112 out of 120 counties in overall agricultural production.
The tourism industry in the county may trace its beginnings to the restoration of Historic Stearns, the development of the scenic railway, the interpretive work at Blue Heron, and the reconstruction of Barthell, the site of Stearns Company's first coal mine and town in 1903. Those resources may represent the largest interpretive collection of historic coal mining in America. The Big South Fork Scenic Railway is presently in a major development project to add a steam locomotive and to extend the line.
The Big South Fork NRRA represents 196 square miles (508 km2) of land, of which approximately one-third is located in McCreary County. The largest section of the park and its main Bandy Creek visitor center are located in Tennessee. In 2004, the park received 901,425 visitors, down 23% from 2002. Due to a lack of organized activities, events, and recreational tourism opportunities, visitation on the Kentucky side does not fare well. Similar issues exist for visitation in the Stearns district of the Daniel Boone National Forest.
Transportation
McCreary County Airport is near Pine Knot.[4]
US 27 splits the county north and south, and KY 92 runs east and west. US 27 and KY 92 run concurrent from Pine Knot to the traffic light at Stearns, where KY 92 splits off and heads west towards Wayne County. McCreary is also served by Norfolk Southern Railway, which has several industrial sidings in the area. NS also interchanges traffic with the Kentucky and Tennessee Railway in Stearns.
Communities
McCreary is the last remaining county in the Commonwealth of Kentucky that does not have any incorporated city or township. The following McCreary County communities are census-designated places:
- Pine Knot
- Stearns
- Whitley City (county seat)
Attractions
|
Notable people
- Wilburn K. Ross
- Allie Leggett
- Will Lavender[15]
See also
References
- "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved February 24, 2023.
- "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Archived from the original on May 31, 2011. Retrieved June 7, 2011.
- Steven A. Channing, Encyclopedia of Kentucky (3d.ed.) Somerset Publishers. (1999) p. 222
- "Pine Knot CDP, Kentucky ." U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved February 22, 2011.
- USP McCreary Contact Information Archived December 3, 2010, at the Wayback Machine. Federal Bureau of Prisons. Retrieved February 22, 2011. "USP MCCREARY U.S. PENITENTIARY 330 FEDERAL WAY PINE KNOT, KY 42635."
- "2010 Census Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. August 22, 2012. Archived from the original on August 12, 2014. Retrieved August 17, 2014.
- "Annual Estimates of the Resident Population for Counties: April 1, 2020 to July 1, 2022". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved April 2, 2023.
- "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved August 17, 2014.
- "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved August 17, 2014.
- "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved August 17, 2014.
- "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Archived (PDF) from the original on March 27, 2010. Retrieved August 17, 2014.
- The Chicago Daily News Almanac and Year Book for 1913, Vol. 29. Chicago: Chicago Daily News. 1913.
- Leip, David. "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved July 4, 2018.
- "The Geography of Government Dependence," The New York Times, , accessed September 8, 2019
- "Best-selling author Will Lavender credits his Whitley City roots | Lexington Herald Leader". Archived from the original on November 6, 2019.