Basque Parliament
The Basque Parliament (Basque: Eusko Legebiltzarra, Spanish: Parlamento Vasco) is the legislative body of the Basque Autonomous Community of Spain and the elected assembly to which the Basque Government is responsible.
Basque Parliament Eusko Legebiltzarra Parlamento Vasco | |
|---|---|
| 12th Basque Parliament | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| Leadership | |
Vice President | |
Second Vice President | |
Secretary | |
Vice Secretary | |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 75 |
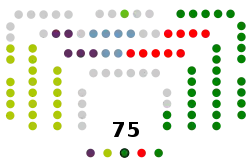 | |
Political groups | Government (41)
Opposition (34) |
| Elections | |
| Closed party lists in three 25-seat constituencies, with seats allocated using the D'Hondt method | |
Last election | 12 July 2020 |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| Vitoria-Gasteiz, Álava | |
| Website | |
| Website | |
The Parliament meets in the Basque capital, Vitoria-Gasteiz, although the first session of the modern assembly, as constituted by the Statute of Autonomy of the Basque Country, was held in Guernica – the symbolic centre of Basque freedoms – on 31 March 1980.[1] Later in 1980 it started meeting at the premises of the Council of Álava. In 1982, it got its own site in a former high school. The symbol of the Parliament is an oaken sculpture by Nestor Basterretxea representing a stylized tree, an allusion to the tradition of Basque political assemblies meeting under a tree, as in Guernica.
It is composed of seventy-five deputies representing citizens from the three provinces of the Basque autonomous community. Each province (Álava, Gipuzkoa and Biscay) elects the same number of deputies, despite their having very different levels of population. This was chosen to earn support from Álava and Navarre, less populated territories. Still, Navarre did not join the autonomous community.
The elections are held using closed list proportional representation with seats allocated on a Provincial basis using the D'Hondt method of allocation. To qualify for seats in a particular province, electoral lists must receive at least 3% of the votes cast in that province, including votes "en blanco" for "none of the above." From 1984 to 2001, the election threshold was 5% in each province. Sessions of the Basque Parliament are conducted in both Basque and Spanish, with translation services.
The Parliament consists of 75 deputies elected by universal adult suffrage under a system of proportional representation.
Current composition
The last elections, held 12 July 2020, resulted in the following distribution of seats:[2]
- Partido Nacionalista Vasco (EAJ-PNV): 31 deputies (39.12% of popular vote)
- Euskal Herria Bildu (EH Bildu): 21 deputies (27.84% of popular vote)
- Partido Socialista de Euskadi-Euskadiko Ezkerra (PSE-EE / PSOE): 10 deputies (13.64% of popular vote)
- Podemos-Izquierda Unida (Podemos-IU): 6 deputies (8.03% of popular vote)
- Partido Popular + Ciudadanos (PP+Cs): 6 deputies (6.75% of popular vote)
- Vox (Vox): 1 deputy (1.96% of popular vote)
 |
|---|

See also
- List of Basque presidents (known as Lehendakari), heads of the Basque government
- List of presidents of the Basque Parliament
References
- Parlamento Vasco - Servicios > Conócenos > La sede Archived 2012-09-06 at archive.today (in Spanish)
- Bello, Carlos Medina (2020-07-12). "12J: Urkullu gana en el País Vasco y Feijoó suma su cuarta mayoría absoluta en Galicia". espanadiario.net (in Spanish). Retrieved 2020-07-14.