Methylmalonic acidemia
Methylmalonic acidemia, also called methylmalonic aciduria,[note 1] is an autosomal recessive[1] metabolic disorder that disrupts normal amino acid metabolism.[2] It is a classical type of organic acidemia.[3] The result of this condition is the inability to properly digest specific fats and proteins, which in turn leads to a buildup of a toxic level of methylmalonic acid in the blood.[4]
| Methylmalonic acidemia | |
|---|---|
| Other names | MMA |
 | |
| Methylmalonic acid | |
| Specialty | Endocrinology |
Methylmalonic acidemia stems from several genotypes,[5] all forms of the disorder usually diagnosed in the early neonatal period, presenting progressive encephalopathy, and secondary hyperammonemia. The disorder can result in death if undiagnosed or left untreated. It is estimated that this disorder has a frequency of 1 in 48,000 births, though the high mortality rate in diagnosed cases make exact determination difficult.[4] Methylmalonic acidemias are found with an equal frequency across ethnic boundaries.[6]
Symptoms and signs
Depending on the affected gene(s), this disorder may present symptoms that range from mild to life-threatening.
- Stroke[4]
- Progressive encephalopathy[4]
- Seizure[4][7]
- Kidney failure[4][8]
- Vomiting[4][7][8]
- Dehydration[4][7][8]
- Failure to thrive and developmental delays[4][7][8]
- Lethargy[4][7][8]
- Repeated yeast infections[4]
- Acidosis[7]
- Hepatomegaly[7][8]
- Hypotonia[7][8]
- Pancreatitis[8]
- Respiratory distress[7]
- Ketonemia[7]
- Ketonuria[7]
- Hyperammonemia[7]
- Hyperglycinemia[7]
- Hyperglycinuria[7]
- Hypoglycemia[7]
- Low red blood cell, white blood cell, and platelet concentrations[7]
Cause
Genetic

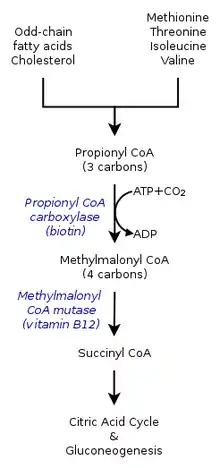
The inherited forms of methylmalonic acidemia cause defects in the metabolic pathway where methylmalonyl-coenzyme A (CoA) is converted into succinyl-CoA by the enzyme methylmalonyl-CoA mutase.[9]
Vitamin B12 is also needed for the conversion of methylmalonyl-CoA to succinyl-CoA. Mutations leading to defects in vitamin B12 metabolism or in its transport frequently result in the development of methylmalonic acidemia.
This disorder has an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern, which means the defective gene is located on an autosome, and two copies of the gene—one from each parent—must be inherited to be affected by the disorder. The parents of a child with an autosomal recessive disorder are carriers of one copy of the defective gene, but are usually not affected by the disorder.
Nutritional
Though not always grouped together with the inherited versions, a severe nutritional deficiency of vitamin B12 can also result in syndrome with identical symptoms and treatments as the genetic methylmalonic acidemias.[10] Methylmalonyl-CoA requires vitamin B12 to form succinyl-CoA. When the amount of B12 is insufficient for the conversion of cofactor methylmalonyl-CoA into succinyl-CoA, the buildup of unused methylmalonyl-CoA eventually leads to methylmalonic acidemia. This diagnosis is often used as an indicator of vitamin B12 deficiency in serum.[11]
Mechanism
Pathophysiology
In methylmalonic acidemia, the body is unable to break down the amino acids methionine, threonine, isoleucine and valine; as a result methylmalonic acid builds up in the blood and tissues. Those afflicted with this disorder are either lacking functional copies or adequate levels of one or more of the following enzymes: methylmalonyl-CoA mutase, methylmalonyl-CoA epimerase, or those involved in adenosylcobalamin synthesis.[7][8]
Methylmalonyl-CoA mutase
It is estimated that as many as 60% of cases are the result of a mutated MUT gene which encodes the protein methylmalonyl-CoA mutase. This enzyme is responsible for the digestion of potentially toxic derivatives of the breakdown of the above-mentioned amino acids and fats, primarily cholesterol,[8] particularly this enzyme converts methylmalonyl-CoA into succinyl-CoA.[12] Without this enzyme, the body has no means to neutralize or remove methylmalonic acid and related compounds. The action of this enzyme can also be crippled by mutations in the MMAA, MMAB, and MMADHC genes, each of which encodes a protein required for normal functioning of methylmalonyl-CoA mutase.[8]
Methylmalonyl-CoA epimerase
Mutations in the MCEE gene, which encodes the methylmalonyl-CoA epimerase protein, also referred to as methylmalonyl racemase, will cause a much more mild form of the disorder than the related methylmalonyl-CoA mutase variant. Like the mutase, the epimerase also functions in breaking down the same substances, but to a significantly lesser extent than the mutase does.[8] The phenotypic differences caused by a deficiency of the epimerase as opposed to the mutase are so mild that there is debate within the medical community as to whether or not this genetic deficiency can be considered a disorder or clinical syndrome.[13]
Adenosylcobalamin
Also known as vitamin B12, this form of cobalamin is a required cofactor of methylmalonyl-CoA mutase. Even with a functional version of the enzyme at physiologically normal levels, if B12 cannot be converted to this active form, the mutase will be unable to function.[8]
Progression
Though there are not distinct stages of the disease, methylmalonic acidemia is a progressive condition; the symptoms of this disorder are compounded as the concentration of methylmalonic acid increases. If the triggering proteins and fats are not removed from the diet, this buildup can lead to irreparable kidney or liver damage and eventually death.[4]
Diagnosis
One of, if not the most common form of organic acidemia,[14] methylmalonic acidemia is not apparent at birth as symptoms usually do not present themselves until proteins are added to the infant's diet.[4] Because of this, symptoms typically manifest anytime within the first year of life.[14] Due to the severity and rapidity in which this disorder can cause complications when left undiagnosed, screening for methylmalonic acidemia is often included in the newborn screening exam.[4][15]
Because of the inability to properly break down amino acids completely, the byproduct of protein digestion, the compound methylmalonic acid, is found in a disproportionate concentration in the blood and urine of those afflicted. These abnormal levels are used as the main diagnostic criteria for diagnosing the disorder. This disorder is typically determined through the use of a urine analysis or blood panel.[14] The presence of methylmalonic acidemia can also be suspected through the use of a CT or MRI scan or ammonia test, however these tests are by no means specific and require clinical and metabolic/correlation.[4] Elevated levels of ammonia, glycine, and ketone bodies may also be present in the blood and urine.[7]
Types
Methylmalonic acidemia has varying diagnoses, treatment requirements and prognoses, which are determined by the specific genetic mutation causing the inherited form of the disorder.[5] The following are the known genotypes responsible for methylmalonic acidemia:
| OMIM | Name | Gene |
|---|---|---|
| 251100 | cblA type | MMAA |
| 251110 | cblB type | MMAB |
| 277400 | cblC type | MMACHC |
| 277410 | cblD type | MMADHC[16] |
| 277380 | cblF type | LMBRD1[17] |
| 251000 | mut type | MUT |
The mut type can further be divided into mut0 and mut- subtypes, with mut0 characterized by a complete lack of methylmalonyl-CoA mutase and more severe symptoms and mut- characterized by a decreased amount of mutase activity.[6]
Mut-, cblB, and cblA versions of methylmalonic acidemia have been found to be cobalamin responsive. Mut0 is a nonresponsive variant.[6]
Combined malonic and methylmalonic aciduria (CMAMMA)
With regard to elevated methylmalonic acid levels, methylmalonic acidemia can be quickly laboratory differentiated from combined malonic and methylmalonic aciduria (CMAMMA) by calculating the ratio of malonic acid to methylmalonic acid in blood plasma, whereas calculation with values from urine is unsuitable.[18] The ratio can then also be used to determine whether CMAMMA is due to ACSF3 deficiency (MA<MMA) or malonyl-CoA decarboxylase deficiency (MA>MMA).[18][19][20]
Treatment
Dietary
Treatment for all forms of this condition primarily relies on a low-protein diet, and depending on what variant of the disorder the individual suffers from, various dietary supplements. All variants respond to the levo isomer of carnitine as the improper breakdown of the affected substances results in sufferers developing a carnitine deficiency. The carnitine also assists in the removal of acyl-CoA, buildup of which is common in low-protein diets by converting it into acyl-carnitine which can be excreted in urine. Some forms of methylmalonyl acidemia are responsive to cobalamin although cyanocobalamin supplements could prove detrimental to some forms. [21] If the individual proves responsive to both cobalamin and carnitine supplements, then it may be possible for them to ingest substances that include small amounts of the problematic amino acids isoleucine, threonine, methionine, and valine without causing an attack.[4]
Surgical
A more extreme treatment includes kidney or liver transplant from a donor without the condition. The foreign organs will produce a functional version of the defective enzymes and digest the methylmalonic acid, however all of the disadvantages of organ transplantation are of course applicable in this situation.[4] There is evidence to suggest that the central nervous system may metabolize methylmalonyl-CoA in a system isolated from the rest of the body. If this is the case, transplantation may not reverse the neurological effects of methylmalonic acid previous to the transplant or prevent further damage to the brain by continued build up.[22][12]
Prognosis
The prognosis will vary depending on the severity of the condition and the individual's response to treatment. Prognosis is typically better for those with cobalamin-responsive variants and not promising in those suffering from noncobalamin-responsive variants.[12] Milder variants have a higher frequency of appearance in the population than the more severe ones.[14] Even with dietary modification and continued medical care, it may not be possible to prevent neurological damage in those with a nonresponsive acidemia.[12] Without proper treatment or diagnosis, it is not uncommon for the first acidemic attack to be fatal.[4]
Despite these challenges, since it was first identified in 1967, treatment and understanding of the condition has improved to the point where it is not unheard of for even those with unresponsive forms of methylmalonic acidemia to be able to reach adulthood and even carry and deliver children safely.[22]
Research
Neurologic effects
That MMA can have disastrous effects on the nervous system has been long reported; however, the mechanism by which this occurs has never been determined. Published on June 15, 2015, research performed on the effects of methylmalonic acid on neurons isolated from fetal rats in an in vitro setting using a control group of neurons treated with an alternate acid of similar pH. These tests have suggested that methylmalonic acid causes decreases in cellular size and increase in the rate of cellular apoptosis in a concentration dependent manner with more extreme effects being seen at higher concentrations. Furthermore, micro-array analysis of these treated neurons have also suggested that on an epigenetic-level methylmalonic acid alters the transcription rate of 564 genes, notably including those involved in the apoptosis, p53, and MAPK signaling pathways.[24]
Mitochondrial dysfunction
As the conversion of methylmalonyl-CoA to succinyl-CoA takes place inside the mitochondria, mitochondrial dysfunction as a result of diminished electron transport chain function has long been suspected as a feature in MMA. Recent research has found that in rat models mitochondria of rats affected by the disorder grow to unusual size, dubbed megamitochondria. These megamitochondria also appear to have deformed internal structures and a loss in electron richness in their internal matrix. These megamitochondria also showed signs of decreased respiratory chain function, particularly in respiratory complex IV which only functioned at about 50% efficiency. Similar changes were identified in the mitochondria of a liver sample removed during transplant from a 5-year-old boy suffering from MMA.[25]
Benign mut phenotype
Recent case studies in several patients presenting nonresponsive mut0 MMA with a specific mutation designated p.P86L have suggest the possibility of further subdivision in mut type MMA might exist. Though currently unclear if this is due to the specific mutation or early detection and treatment, despite complete nonresponse to cobalamin supplements, these individuals appeared to develop a largely benign and near completely asymptomatic version of MMA. Despite consistently showing elevated methylmalonic acid in the blood and urine, these individuals appeared for the large part developmentally normal.[26]
Notable cases
- Ryan Stallings, a St. Louis infant, was mistakenly diagnosed with ethylene glycol poisoning instead of MMA in 1989, leading to a wrongful murder conviction and life sentence for his mother, Patricia Stallings.[22]
Notes
- The names methylmalonic acidemia and methylmalonic aciduria, which are also sometimes written as solid compounds (methylmalonicacidemia and methylmalonicaciduria), use the suffixes -emia and -uria and literally mean "[excess] methylmalonic acid in the blood" and "[excess] methylmalonic acid in the urine", respectively; they are used to label both the fluid analysis findings and the disease entity that causes them.
References
- Radmanesh A, Zaman T, Ghanaati H, Molaei S, Robertson RL, Zamani AA (October 2008). "Methylmalonic acidemia: brain imaging findings in 52 children and a review of the literature". Pediatric Radiology. 38 (10): 1054–1061. doi:10.1007/s00247-008-0940-8. PMID 18636250. S2CID 24915585.
- "Clinical and Basic Investigations of Methylmalonic Acidemia Study". National Human Genome Research Institute. U.S. National Institutes of Health. Retrieved April 26, 2016.
- Dionisi-Vici C, Deodato F, Röschinger W, Rhead W, Wilcken B (2006). "'Classical' organic acidurias, propionic aciduria, methylmalonic aciduria and isovaleric aciduria: long-term outcome and effects of expanded newborn screening using tandem mass spectrometry". Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease. 29 (2–3): 383–389. doi:10.1007/s10545-006-0278-z. PMID 16763906. S2CID 19710669.
- "Methylmalonic acidemia". MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia. US National Library of Medicine. Retrieved 2015-10-27.
- Matsui SM, Mahoney MJ, Rosenberg LE (April 1983). "The natural history of the inherited methylmalonic acidemias". The New England Journal of Medicine. 308 (15): 857–861. doi:10.1056/NEJM198304143081501. PMID 6132336.
- "About Methylmalonic Acidemia". National Human Genome Research Institute. U.S. National Institutes of Health. Retrieved 2015-11-03.
- "Acidemia, Methylmalonic". NORD (National Organization for Rare Disorders). Retrieved 2015-10-29.
- "Methylmalonic acidemia". Genetics Home Reference. US National Library of Medecine. 2015-10-26. Retrieved 2015-11-02.
- Sakamoto O, Ohura T, Matsubara Y, Takayanagi M, Tsuchiya S (2007). "Mutation and haplotype analyses of the MUT gene in Japanese patients with methylmalonic acidemia". Journal of Human Genetics. 52 (1): 48–55. doi:10.1007/s10038-006-0077-2. PMID 17075691.
- Higginbottom MC, Sweetman L, Nyhan WL (August 1978). "A syndrome of methylmalonic aciduria, homocystinuria, megaloblastic anemia and neurologic abnormalities in a vitamin B12-deficient breast-fed infant of a strict vegetarian". The New England Journal of Medicine. 299 (7): 317–323. doi:10.1056/NEJM197808172990701. PMID 683264.
- "Vitamin B12 deficiency - The methylmalonic aciduria connection". The Biology Project. Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biophysics, The University of Arizona. 31 January 2000. Archived from the original on 15 June 2018.
- Kumbham P, Mandava P, Zweifler RM, Kent TA, Nelson Jr SL, Gerstein BY (19 September 2022). Talavera F, Kirshner HS, Lutsep HL (eds.). "Methylmalonic Acidemia". EMedicine.
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM): Methylmalonyl-CoA Epimerase Deficiency - 251120
- Saini N, Malhotra A, Chhabra S, Chhabra S (March 2015). "Methylmalonic acidemia mimicking diabetic ketoacidosis and septic shock in infants". Indian Journal of Critical Care Medicine. 19 (3): 183–185. doi:10.4103/0972-5229.152776. PMC 4366921. PMID 25810618.
- Kimberly G Lee. "Newborn screening tests". MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia. Division of Neonatology, Medical University of South Carolina. Retrieved April 26, 2016.
- Coelho D, Suormala T, Stucki M, Lerner-Ellis JP, Rosenblatt DS, Newbold RF, et al. (April 2008). "Gene identification for the cblD defect of vitamin B12 metabolism". The New England Journal of Medicine. 358 (14): 1454–1464. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa072200. PMID 18385497. S2CID 15107040.
- Rutsch F, Gailus S, Miousse IR, Suormala T, Sagné C, Toliat MR, et al. (February 2009). "Identification of a putative lysosomal cobalamin exporter altered in the cblF defect of vitamin B12 metabolism". Nature Genetics. 41 (2): 234–239. doi:10.1038/ng.294. PMID 19136951. S2CID 28006539.
- de Sain-van der Velden MG, van der Ham M, Jans JJ, Visser G, Prinsen HC, Verhoeven-Duif NM, et al. (2016). Morava E, Baumgartner M, Patterson M, Rahman S (eds.). "A New Approach for Fast Metabolic Diagnostics in CMAMMA". JIMD Reports. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg. 30: 15–22. doi:10.1007/8904_2016_531. ISBN 978-3-662-53680-3. PMC 5110436. PMID 26915364.
- Alfares A, Nunez LD, Al-Thihli K, Mitchell J, Melançon S, Anastasio N, et al. (September 2011). "Combined malonic and methylmalonic aciduria: exome sequencing reveals mutations in the ACSF3 gene in patients with a non-classic phenotype". Journal of Medical Genetics. 48 (9): 602–605. doi:10.1136/jmedgenet-2011-100230. PMID 21785126.
- de Wit MC, de Coo IF, Verbeek E, Schot R, Schoonderwoerd GC, Duran M, et al. (February 2006). "Brain abnormalities in a case of malonyl-CoA decarboxylase deficiency". Molecular Genetics and Metabolism. 87 (2): 102–106. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2005.09.009. PMID 16275149.
- Linnell JC, Matthews DM, England JM (November 1978). "Therapeutic misuse of cyanocobalamin". Lancet. 2 (8098): 1053–1054. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92379-6. PMID 82069. S2CID 29703726.
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM): Methylmalonic Aciduria due to Methylmalonyl-CoA Mutase deficiency - 251000
- Oberholzer VG, Levin B, Burgess EA, Young WF (October 1967). "Methylmalonic aciduria. An inborn error of metabolism leading to chronic metabolic acidosis". Archives of Disease in Childhood. 42 (225): 492–504. doi:10.1136/adc.42.225.492. PMC 2019805. PMID 6061291.
- Han L, Wu S, Han F, Gu X (Jun 15, 2015). "Insights into the molecular mechanisms of methylmalonic acidemia using microarray technology". International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine. 8 (6): 8866–8879. PMC 4538064. PMID 26309541.
- Chandler RJ, Zerfas PM, Shanske S, Sloan J, Hoffmann V, DiMauro S, Venditti CP (April 2009). "Mitochondrial dysfunction in mut methylmalonic acidemia". FASEB Journal. 23 (4): 1252–1261. doi:10.1096/fj.08-121848. PMC 2660647. PMID 19088183.
- Underhill HR, Hahn SH, Hale SL, Merritt JL (December 2013). "Asymptomatic methylmalonic acidemia in a homozygous MUT mutation (p.P86L)". Pediatrics International. 55 (6): e156–e158. doi:10.1111/ped.12195. PMID 24330302. S2CID 27495325.
Further reading
- Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Bean LJ, Gripp KW, Mirzaa GM, Amemiya A, eds. (2016). "Isolated Methylmalonic Acidemia". GeneReviews® [Internet]. University of Washington. PMID 20301409. NBK1231.
- Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Bean LJ, Gripp KW, Mirzaa GM, Amemiya A, eds. (2021). "Disorders of Intracellular Cobalamin Metabolism". GeneReviews® [Internet]. University of Washington. PMID 20301503. NBK1328.