Mistra Battery
Mistra Battery (Maltese: Batterija tal-Mistra), formerly also known as Despirasse Battery (Maltese: Batterija ta' Despirasse),[1] is an artillery battery in Mistra Bay, Mellieħa, Malta. It was built by the Order of Saint John in the 18th century as one of a series of coastal fortifications around the coasts of the Maltese Islands.
| Mistra Battery | |
|---|---|
Batterija tal-Mistra | |
| Mellieħa, Malta | |
 Mistra Battery's redan and blockhouses | |
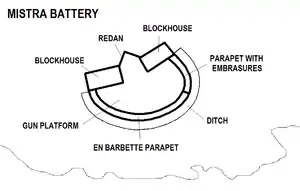 Map of Mistra Battery | |
| Coordinates | 35°57′30.48″N 14°23′41.86″E |
| Type | Artillery battery |
| Site information | |
| Owner | Government of Malta |
| Controlled by | Fondazzjoni Wirt Artna |
| Open to the public | No |
| Condition | Intact |
| Site history | |
| Built | c. 1761 |
| Built by | Order of Saint John |
| In use | c. 1761–1798 |
| Materials | Limestone |
The battery is considered as the best preserved of the Order's batteries in Malta, since it retains all of its original features. Many other batteries have been destroyed or otherwise modified, and very few have survived in their original state.[2]
History
The first plans to construct a battery at Mistra Bay were made in 1714, where the knight Mongontier donated 133 scudi for its construction. The battery does not appear in the 1715-1716 list of coastal fortifications, but possibly a gun platform was built some years later. However, the battery as it is today was built over forty years later in 1761 due to the insistence by the military engineer Bourlamaque, during the reign of Grand Master Manuel Pinto da Fonseca.

The battery has a roughly semi-circular gun platform, with its northern face having a parapet with three embrasures. There was no parapet around the rest of the platform. The battery is partially surrounded by a shallow rock hewn ditch that was left unfinished. The battery has two blockhouses, which are linked together by a redan with musketry loopholes. The redan also contains the main entrance, which is surmounted by the coats of arms of the Order, of Grand Master Pinto and of the Bailli de Montagnac.[3]
When completed in 1761, the battery had an armament of three 24-pounder and six 8-pounder iron cannons. By 1770, the armament was reduced to just a single 8-pounder cannon,[4] and all armaments were removed by 1785.[5] The battery was later rearmed once again with 18-pounder cannons. These were removed by Maltese insurgents during the French blockade of 1798-1800, and were taken to Għargħar Battery.[6]
Mistra Battery was included on the Antiquities List of 1925, and it was the only coastal battery to be specifically mentioned in this list.[7]
Present day

At some point, the battery's parapet with embrasures was demolished. The battery was used as a store by P2M Fisheries, and a number of alterations were made, in which some parts of the battery were destroyed.[8]
The fisheries company obtained new premises in 2012 and restored the battery before returning it to the government. Despite this, the battery and the surrounding area was vandalized repeatedly.[9]
Since then, more restoration works were undertaken by Fondazzjoni Wirt Artna. The destroyed embrasures and musketry loopholes were rebuilt, and layer of concrete over the gun platform was removed. The battery's ditch was also restored. Currently, work is being done to build replicas of the battery's cannons. The battery is currently closed to the public due to ongoing restoration works, however Fondazzjoni Wirt Artna plans to open it as a cultural attraction in 2015.[10] As of April 2016, the battery is at final stages of restoration, but not yet open to the public (as per sign on main entrance).
References
- de Boisgelin, Louis (1805). Ancient and Modern Malta: Containing a Full and Accurate Account of the Present State of the Islands of Malta and Goza, the History of the Knights of St. John of Jerusalem, Also a Narrative of the Events which Attended the Capture of These Islands by the French, and Their Conquest by the English: and an Appendix, Containing Authentic State Papers and Other Documents - Volume II. London: Richard Phillips. p. 189.
- Spiteri, Stephen C. (28 August 2012). "Campaigning for Rihama Battery". MilitaryArchitecture.com. Archived from the original on 2 October 2017. Retrieved 30 January 2015.
- "Mistra Battery - 1714". Fondazzjoni Wirt Artna. Archived from the original on 30 January 2015. Retrieved 30 January 2015.
- Debono, Charles. "Fortifications - Mistra Battery". Mellieha.com. Retrieved 30 January 2015.
- "Mistra Battery". Malta Military. Retrieved 30 January 2015.
- Spiteri, Stephen C. (May 2008). "Maltese 'siege' batteries of the blockade 1798-1800" (PDF). Arx - Online Journal of Military Architecture and Fortification (6): 39. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 November 2016. Retrieved 30 March 2015.
- "Protection of Antiquities Regulations 21st November, 1932 Government Notice 402 of 1932, as Amended by Government Notices 127 of 1935 and 338 of 1939". Malta Environment and Planning Authority. Archived from the original on 19 April 2016.
- Debono, James (22 June 2008). "From Pinto's battery to fish farm store". Malta Today. Retrieved 30 January 2015.
- Farrugia Randon, Stanley (11 August 2013). "The Mistra coastal battery". Times of Malta. Retrieved 30 January 2015.
- "Special heritage day at Mistra Battery". Times of Malta. 29 January 2015. Retrieved 30 January 2015.