Mitsubishi Ki-21
The Mitsubishi Ki-21, formal designation "Type 97 Heavy Bomber" (九七式重爆撃機, Kyūnana-shiki jūbakugekiki) was a Japanese heavy bomber during World War II. It began operations during the Second Sino-Japanese War participating in the Nomonhan Incident, and in the first stages of the Pacific War, including the Malayan, Burmese, Dutch East Indies and New Guinea Campaigns. It was also used to attack targets as far-flung as western China, India and northern Australia. The Allies designated it under the reporting names "Sally" /"Gwen".
| Ki-21 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Mitsubishi Ki-21 | |
| Role | Heavy bomber |
| Manufacturer | Mitsubishi Heavy Industries |
| First flight | 18 December 1936 |
| Introduction | 1938 |
| Retired | 1945 |
| Primary users | Imperial Japanese Army Air Service Royal Thai Air Force |
| Number built | 2,064 units (excluding Ki-57) |
| Variants | Mitsubishi Ki-57 |
Design and development
In 1936, the Imperial Japanese Army Air Service issued a requirement for a new heavy bomber to replace both the Ki-20 (Army Type 92 Heavy Bomber) and the Ki-1 (Army Type 93 Heavy Bomber).[1] The design called for a crew of at least four, top speed of 400 km/h (250 mph), endurance of at least five hours, and a bombload of 750 kg (1,650 lb). The design parameters were very ambitious, and few twin-engine bombers anywhere in the world could exceed such performance at that time.[2]
Both Mitsubishi and Nakajima were asked to build two prototypes each, a further proposal from Kawasaki was rejected. The Mitsubishi design was an all-metal mid-wing cantilever monoplane with retractable landing gear, ventral bomb bay and two radial engines.[3] The first prototype flew on 18 December 1936, with the second prototype, which differed in replacing the dorsal turret of the first prototype with a long greenhouse canopy, following later in the month.[4] In the resulting competition Mitsubishi's Ki-21 and Nakajima's Ki-19 were found to be similar, with the Ki-21 having better performance while the Nakajima design was a better bombing platform and had more reliable engines. In order to make a final decision, two further prototype were ordered from both Mitsubishi and Nakajima, with Mitsubishi instructed to change its own 615 kW (825 hp) Mitsubishi Ha-6 radial engines for the Nakajima Ha-5 engines used by the Nakajima design and vice versa, while the Ki-21 gained a revised glazed nose similar to that of the Ki-19 and revised tail surfaces. Thus modified, the Ki-21 proved superior and was ordered into production as the "Army Type 97 Heavy Bomber Model 1A", being ordered into production in November 1937.[5]
Production aircraft began to enter service in August 1938, supplementing and then replacing the Fiat BR.20 bombers which had been purchased as an interim measure.[6]
Several improved versions followed (see below) before the production of the type ended in September 1944. A total of 2,064 aircraft were built, 1,713 by Mitsubishi and 351 by Nakajima.[7]
Operational history
The Ki-21-Ia was used in combat in the war with China by the 60th Sentai from autumn 1938, carrying out long-range unescorted bombing missions in conjunction with the BR.20 equipped 12th and 98th Sentais. The Ki-21 proved to be more successful than the BR.20, having a longer range and being more robust and reliable. Two more Sentais, the 58th and 61st deployed to Manchuria in the summer of 1939 for operations against China, with aircraft from the 61st also being heavily used against Russian and Mongolian Forces during the Nomonhan Incident in June–July 1939.[6]
Losses were high during early combat operations, with weaknesses including a lack of armament and self-sealing fuel tanks, while the aircraft's oxygen system also proved unreliable. The Ki-21-Ib was an improved version designed to address the armament issue by increasing the number of 7.7 mm (.303 in) Type 89 machine guns to five, and incorporating improvements to the horizontal tail surfaces and trailing edge flaps. In addition, the bomb bay was enlarged. The tail gun was a 'stinger' installation and was remotely controlled. Also, the fuel tanks were partially protected with laminated rubber sheets.[8][9]
This was followed in production by the Ki-21-Ic with provision for a 500 L (130 US gal) auxiliary fuel tank, fitted in the rear weapons bay and one more 7.7 mm (.303 in) machine gun, bringing the total to six. Four 50 kg (110 lb) bombs were carried externally. To offset the increase in weight the main wheels of the Ki-21-IC were increased in size.[10][9]
However, by the attack on Pearl Harbor and the start of the Pacific War, improvements in the ROC Air Force caused losses to mount, and most Ki-21-1a, -1b and -1c were relegated to training or second-line duties.
Front line units from mid-1940 were equipped with the Ki-21-IIa ("Army Type 97 Heavy Bomber Model 2A") with the more powerful 1,118 kW (1,500 hp) Mitsubishi Ha-101 air-cooled engines and larger horizontal tail surfaces. This became the main version operated by most IJAAF heavy bomber squadrons at the beginning of the Pacific War and played a major role in many early campaigns. For operations over the Philippines the JAAF's 5th, 14th and 62nd Air Groups, based in Taiwan, attacked American targets at Aparri, Tuguegarao, Vigan and other targets in Luzon on 8 December 1941. The 3rd, 12th, 60th, and 98th Air Groups, based in French Indochina, struck British and Australian targets in Thailand and Malaya, bombing Alor Star, Sungai Petani and Butterworth under escort by Nakajima Ki-27 and Ki-43 fighters. However, starting from operations over Burma in December 1941 and early 1942, the Ki-21 began to suffer heavy casualties from Curtiss P-40s and Hawker Hurricanes.
To partially compensate, the IJAAF introduced the Ki-21-IIb, with a pedal-operated upper turret with one 12.7 mm (0.50 in) Type 1 machine gun, redesigned cockpit canopies and increased fuel capacity. Although used in all fronts in the Pacific theater, it became clear by 1942 that the design was rapidly becoming obsolete, and was increasingly shifted away from front-line service.
In spite of its shortcomings, the Ki-21 remained in service until the end of the war, being utilized as transport (along with the civil transport version MC-21), bomber crew and paratrooper trainer, for liaison and communications, special commando and secret missions, and kamikaze operations.
Nine Ki-21-Ia/b's were sold by Japan to Thailand in 1940 for use by the Royal Thai Air Force against Vichy French forces in French Indochina but did not participate in the French-Thai War as its crews had not completed training.[11]

Towards the end of the war, remaining Ki-21s were used by Giretsu Special Forces in strikes against American forces in Okinawa and the Ryūkyū Islands. One of the noted operations was an attack on the Allied-held Yontan airfield and Kadena airfield on the night of 24 May 1945. Twelve Ki-21-IIb's of the Daisan Dokuritsu Hikōtai were dispatched for a strike, each with 14 commandos. Five managed to crash-land on the Yontan airfield. Only one plane landed successfully. The surviving raiders, armed with submachine guns and explosives, then wrought havoc on the supplies and nearby aircraft, destroyed 70,000 US gallons (260,000 L) of fuel and nine aircraft, and damaged 26 more.[12]
A number of Ki-21-Ia were modified to serve as military transports for use by Greater Japan Airways, which was under contract by the Japanese Army in China for transportation. Designated "MC-21", these aircraft had all armament and military equipment removed. Used primarily as cargo transports, each could also seat nine paratroopers. Aircraft built from the start as transports were given the separate designation of Mitsubishi Ki-57, with equivalent civil aircraft being designated MC-20.
Code Names
The Ki-21 had more than one Allied codename. Initially called "Jane", the name was quickly changed to "Sally" when General Douglas MacArthur objected that the name was the same as that of his wife. When the Ki-21-IIb entered service, the absence of the long dorsal "greenhouse" led Allied observers to mistake it for a completely new type, which was designated "Gwen". However, when it was realized that "Gwen" was a new version of the Ki-21, it was renamed "Sally 3", with "Sally 1" referring to the earlier Ha-5 powered models, and "Sally 2" referring to the Ha-101 powered Ki-21-IIa.[13]
Variants
- Ki-21
- Prototype models with various engines and armament combinations for evaluation. Final version with Nakajima Ha-5 engine. 8 built
- Ki-21-Ia (Army Type 97 Heavy Bomber, Model IA)
- First production model, with 634 kW (850 hp) Nakajima Ha-5-kai engines. Most were built by Mitsubishi, 143 manufactured by Nakajima
- Ki-21-Ib (Army Type 97 Heavy Bomber, Model IB)
- Improved version with additional 7.7 mm (.303 in) machine guns, larger bomb compartment and flaps, redesigned tail. 120 built by Mitsubishi, 351 (including Ki-21 Ib and Ic) by Nakajima
- Ki-21-Ic (Army Type 97 Heavy Bomber, Model IC)
- Improved type with one additional 7.7 mm (.303 in) machine gun, increased fuel capacity, 160 built by Mitsubishi
- Ki-21-II
- Evaluation model with more powerful engines, 4 built
- Ki-21-IIa (Army Type 97 Heavy Bomber, Model IIA)
- Production model based on Ki-21-II, 590 built
- Ki-21-IIb (Army Type 97 Heavy Bomber, Model IIB)
- Final production version based on Ki-21-IIa with modified canopy, clear upper cabin replaced by rotating turret, 688 built.
- MC-20-I (Army Type 100 Transport, Model I)
- Unarmed civilian transport version, converted from Ki-21-Ia; approximately 100 aircraft were converted
Operators
- Imperial Japanese Army Air Service
- Imperial Japanese Airways (Dai Nippon Kōkū)
- 6 operated by the Manchukuo Imperial Air Force
- Royal Thai Air Force operated nine Ki-21-I Nagoya
Postwar
- French Air Force (Armée de l'Air) operated at least one Ki-21 as a transport in Indochina.[14]
Specifications (Ki-21-IIb)
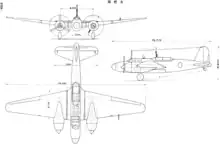
Data from The Concise Guide to Axis Aircraft of World War II[15]
General characteristics
- Crew: 5-7
- Length: 16 m (52 ft 6 in)
- Wingspan: 22.5 m (73 ft 10 in)
- Height: 4.85 m (15 ft 11 in)
- Wing area: 69.9 m2 (752 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 6,070 kg (13,382 lb)
- Gross weight: 10,600 kg (23,369 lb)
- Powerplant: 2 × Mitsubishi Ha101 14-cylinder air-cooled radial piston engine, 1,100 kW (1,500 hp) each (long designation Army Type 100 1,450hp Air Cooled Radial)
- Propellers: 3-bladed variable-pitch propellers
Performance
- Maximum speed: 485 km/h (301 mph, 262 kn)
- Cruise speed: 380 km/h (240 mph, 210 kn)
- Range: 2,700 km (1,700 mi, 1,500 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 10,000 m (33,000 ft)
- Time to altitude: 6,000 m (19,685 ft) in 13 minutes 13 seconds
Armament
- Guns:
- 5× 7.7 mm (.303 in) flexible Type 89 machine guns in nose, ventral, beam and tail positions
- 1× 12.7 mm (.50 in) Ho-103 machine gun in dorsal turret
- Bombs:
- 1,000 kg (2,200 lb) of bombs
See also
Related development
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration, and era
- Bristol Beaufort
- Dornier Do 17
- Douglas B-18 Bolo
- Fiat BR.20 Cicogna
- Heinkel He 111
- Ilyushin Il-4
- Mitsubishi G3M
- Savoia-Marchetti SM.79
Related lists
Notes
- Francillon 1979, pp. 155–156
- Air International August 1986, pp. 74–75
- Air International August 1986, p. 75
- Francillon 1979, p. 156
- Air International August 1986, pp. 75–76
- Air International August 1986, p. 77
- Francillon 1979, p. 164
- Air International August 1986, pp. 77–78
- Francillon 1970, p. 158
- Air International August 1986, p. 79
- Young 1984, p. 23
- Jowett 2002, p. 20.
- Francillon 1970, pp. 160–161
- Pelletier 1995, pp. 21, 23.
- Mondey 1996, p. 208
Bibliography
- Francillon, René J. (1970). Japanese Aircraft of the Pacific War. London: Putnam & Company Ltd. ISBN 0370000331.
- Francillon, René J. (1979). Japanese Aircraft of the Pacific War (2nd ed.). London: Putnam. ISBN 0-370-30251-6..
- Jowett, Philip (2002). The Japanese Army 1931–1945, Volume 2. Botley, Oxfordshire, UK: Osprey Publishing. ISBN 1-84176-354-3.
- "Mitsubishi Ki-21...Stalwart of the Imperial Army Air Force". Air International. Vol. 31, no. 2. August 1986. pp. 74–80, 100–101. ISSN 0306-5634.
- Mondey, David (1996). The Concise Guide to Axis Aircraft of World War II. London: Chancellor Press. ISBN 1-85152-966-7.
- Pelletier, Alain (August 1995). "Les Avions japonais à Cocardes françaises". Le Fana de l'Aviation (in French). No. 309. pp. 14–23.
- Young, Edward M. (August–November 1984). "France's Forgotten Air War". Air Enthusiast. No. 25. ISSN 0143-5450.
Further reading
- Donald, David (editor). The Encyclopedia of World Aircraft. Prospero Books, 1997. ISBN 1-85605-375-X.
- Francillon, René J. The Mitsubishi Ki-21 (Aircraft in Profile number 172). Leatherhead, Surrey, UK: Profile Publications Ltd., 1967.
- Gunston, Bill. The Illustrated Directory of Fighting Aircraft of World War II. ISBN 0-86101-390-5.
- Lake, Jon. Great Book of Bombers. London: Zenith Press, 2002. ISBN 0-7603-1347-4.
- Mikesh, Robert and Shorzoe Abe. Japanese Aircraft 1910–1941. Annapolis, MD: Naval Institute Press, 1990. ISBN 1-55750-563-2.
- Ministry of Defense Japan. Senshi Sosho Volume 36: Rikugun Koku Sakusen(means,Army Air Operation),Okinawa etc. Asagumo Shimbunsha 1970.
- Soumille, Jean-Claude (September 1999). "Les avions japonais aux coleurs françaises" [Japanese Aircraft in French Colors]. Avions (in French) (78): 6–17. ISSN 1243-8650.