Musqueam Indian Band
The Musqueam Indian Band (English: /ˈmʌskwiəm/ ⓘ MUS-kwee-əm; Halkomelem: xʷməθkʷəy̓əm) is a First Nations band government in the Canadian province of British Columbia. It is the only First Nations band whose reserve community lies within the boundaries of the City of Vancouver.
Musqueam
xʷməθkʷəy̓əm | |
|---|---|
 Seal | |
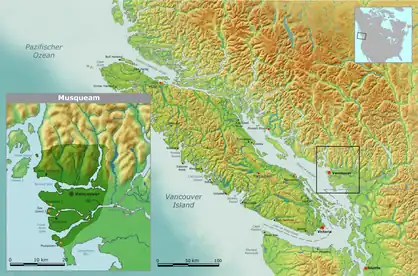 Territory of the Musqueam Indian Band | |
| Country | Canada |
| Province | British Columbia |
| Government | |
| • Type | Band council |
| • Chief | Wayne Sparrow |
| • Councillors | Full list (10): |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1,448.88 km2 (559.42 sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC-8 (PST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-7 (PDT) |
| Postal code span | V3H, V3J–N, V3V V4C, V4K, V4G V5- to V7- |
| Area code(s) | 604, 778 |
| Ethnic groups | Coast Salish |
| Languages | Halkomelem, English |
| Website | www |
| Person | xʷməθkʷəy̓əm |
|---|---|
| People | xʷməθkʷəy̓əm |
| Language | hən̓q̓əmin̓əm̓ |
| Country | šxʷməθkʷəy̓əmaɁɬ təməxʷ |

History
The Musqueam people are one of the three host nations of the Vancouver area, and have shared territory with the Squamish and Tsleil-Waututh Nations. The Great Marpole Midden[2][3] (also known as the Eburne Site, or Great Fraser Midden), is an ancient Musqueam village and burial site located in what has been developed as the Marpole neighbourhood of Vancouver, British Columbia.
This area was also known as the Great Fraser Midden. The midden is a thousands-year-old site from which as many as seventy-five human skeletal remains of Musqueam ancestors were excavated.[4] Additionally, Musqueam ancestral belongings (commonly referred to as "artifacts") were also found in the area such as: stone and wooden tools, artwork, and biofacts such as shells and other animal remains.[5] The village was known as c̓əsnaʔəm.[5] Formerly there was a second residential area near the current one, maləy̓, known in English as Mahlie.[6]
The Musqueam's ancestors, the Coast Salish, have lived in the Fraser River estuary for thousands of years. Musqueam describes their traditional territory in their Musqueam Declaration, which was ratified by Musqueam community leaders on June 10, 1976.[7]
The Musqueam Declaration describes their traditional territory as follows:
The lands, lakes and streams defined and included by a line commencing at Harvey Creek in Howe Sound and proceeding Eastward to the height of land and continuing on the height of land around the entire watershed draining into English Bay, Burrard Inlet and Indian Arm; South along the height of land between Coquitlam River and Brunette River to the Fraser River, across to the South or left bank of the Fraser River and proceeding downstream taking in the left Bank of the main stream and the South Arm to the sea, including all those intervening lands, islands and waters back along the sea shore to Harvey Creek, AND, the sea, its reefs, flats, tidal lands and islands adjacent to the above described land and out to the centre of Georgia Strait.
— Council & Chief & Musqueam Community, Musqueam Declaration[7]
The area of the Musqueam Reserve is the closest that Hudson's Bay Company explorer Simon Fraser reached to the Strait of Georgia; he was driven back by hostile Musqueam who had had bad experiences with Europeans on ships just prior. Chief Whattlekainum of the Kwantlen warned Fraser of an impending attack, thereby saving his life.
Language
Their traditional language is hən̓q̓əmin̓əm̓, the Downriver Dialect of the Salishan language Halkomelem; they are closely related to neighbouring peoples of the lower Fraser River. The nearby Kwantlen and Katzie peoples just upriver share the same hən̓q̓əmin̓əm̓ dialect, while the upriver Sto:lo people speak another dialect, Halq’əméyləm (known as the Upriver Dialect). The Cowichan, Chemainus, Snuneymuxw and neighbouring Coast Salish peoples of Vancouver Island and the parts of the Gulf Islands of the southern Gulf of Georgia speak another dialect, Hul'qumi'num' (usually spelled Hulquminum), often called the Straits dialect, or Island Halkomelem. It is not to be confused with North Straits Salish, which is a group of related dialects to the south.
In early 2018 the University of British Columbia installed at its main Vancouver campus 54 street signs in the Musqueam language, written in Americanist phonetic notation. (In 2010, UBC’s Okanagan satellite campus had put up signs in Nsyilxcen, the language of the Okanagan Nation. Before the 2010 Olympic Games, the British Columbia government installed road signs in Squamish, Lil’wat and English on the Sea-to-Sky Highway between Whistler and Vancouver, BC.)[8]
The xʷməθkʷəy̓əm Musqueam dialect, hən̓q̓əmin̓əm is from the Hul’q’umi’num’/Halq'eméyle/hən̓q̓əmin̓əm language family.[9]
Indian Reserves
Indian Reserves under the administration of the band are:[10]
- Musqueam Indian Reserve No. 2, at the mouth of the Fraser River to the north of Sea Island, 190.40 ha.[11] 49°14′00″N 123°13′00″W
- Musqueam Indian Reserve No. 4, to the east of Canoe Passage near Westham Island, 57.30 ha.[12] 49°04′00″N 123°07′30″W
- Sea Island Indian Reserve 3 (Halkomelem: sqʷsaθən), on the northwest corner of Sea Island, 6.50 ha.[13] 49°12′35″N 123°12′00″W
References
Citations
- "Chief & Council".
- Parks Canada 2010.
- Klashinsky, Dena (October 17, 2018). "Portion of c̓əsnaʔəm village and burial site returned to Musqueam".
- Smith, Harlan Ingersoll. Memoirs of the American Museum of Natural History; v. 4, pt. 4; Publications of the Jesup North Pacific Expedition ; v. 2, pt. 4 1903, p. 187.
- Musqueam Indian Band 2011.
- Early Vancouver, Vol. 1, Maj. J. S. Mathews, Vancouver Archives
- "Musqueam Declaration" (PDF). Retrieved August 18, 2023.
- Seal, Andrew (April 4, 2018). "UBC adds Musqueam language to street signs on campus". The Globe and Mail. Retrieved February 25, 2019.
- FPHLCC 2011–2012.
- Indian and Northern Affairs Canada – Reserves/Villages/Settlements detail
- "Musqueam 2". BC Geographical Names.
- "Musqueam 4". BC Geographical Names.
- "Sea Island 3". BC Geographical Names.
Sources
- "c̓əsnaʔəm", Musqueam: a living culture, Vancouver, BC: Musqueam Indian Band, 2011, archived from the original on December 7, 2013, retrieved December 2, 2013
- "Marpole Midden National Historic Site of Canada at Parks Canada". Parks Canada.
- "xʷməθkʷəy̓əm (Musqueam)", First Peoples Language Map, Aboriginal Languages Initiative (ALI), First Peoples' Heritage Language and Culture Council (FPHLCC), 2011–2012, retrieved December 4, 2013
- "Canada's Historic Places: Marpole Midden National Historic Site of Canada", Canadian Register, Parks Canada, 2010
- Roy, Susan (Winter 2006–2007). ""Who Were These Mysterious People?" – ç¢sna:m, the Marpole Midden, and the Dispossession of Aboriginal Lands in British Columbia". BC Studies (152): 67–95. Archived from the original on December 11, 2013. Retrieved December 6, 2013.
- These Mysterious People Shaping History and Archaeology in a Northwest Coast Community, McGill/Queen's University Press, October 2010, p. 240, ISBN 9780773537217
Further reading
- Dunkley, Katharine. Indian Rights and Federal Responsibilities: Supreme Court Musqueam Decision. [Ottawa]: Library of Parliament, Research Branch, 1985.
- Guerin, Arnold, and J. V. Powell. Hunq̓umỉn̉um ̉= Musqueam Language. Book 1. [Vancouver, B.C.?]: Musqueam Band, 1975.
- Johnson, Elizabeth Lominska, and Kathryn N. Bernick. Hands of Our Ancestors: The Revival of Salish Weaving at Musqueam. [Vancouver?]: University of British Columbia, Museum of Anthropology, 1986. ISBN 0-88865-108-2
- Suttles, Wayne P. Musqueam Reference Grammar. First Nations languages. Vancouver: UBC Press, 2004. ISBN 0-7748-1002-5
- Weightman, Barbara Ann. The Musqueam Reserve: A Case Study of the Indian Social Milieu in an Urban Environment. Seattle, Wash: University of Washington, 1978.
