Heritability
Heritability is a statistic used in the fields of breeding and genetics that estimates the degree of variation in a phenotypic trait in a population that is due to genetic variation between individuals in that population.[1] The concept of heritability can be expressed in the form of the following question: "What is the proportion of the variation in a given trait within a population that is not explained by the environment or random chance?"[2]

Other causes of measured variation in a trait are characterized as environmental factors, including observational error. In human studies of heritability these are often apportioned into factors from "shared environment" and "non-shared environment" based on whether they tend to result in persons brought up in the same household being more or less similar to persons who were not.
Heritability is estimated by comparing individual phenotypic variation among related individuals in a population, by examining the association between individual phenotype and genotype data,[3][4] or even by modeling summary-level data from genome-wide association studies (GWAS).[5] Heritability is an important concept in quantitative genetics, particularly in selective breeding and behavior genetics (for instance, twin studies). It is the source of much confusion due to the fact that its technical definition is different from its commonly-understood folk definition. Therefore, its use conveys the incorrect impression that behavioral traits are "inherited" or specifically passed down through the genes.[6] Behavioral geneticists also conduct heritability analyses based on the assumption that genes and environments contribute in a separate, additive manner to behavioral traits.[7]
Overview
Heritability measures the fraction of phenotype variability that can be attributed to genetic variation. This is not the same as saying that this fraction of an individual phenotype is caused by genetics. For example, it is incorrect to say that since the heritability of personality traits is about 0.6, that means that 60% of your personality is inherited from your parents and 40% comes from the environment. In addition, heritability can change without any genetic change occurring, such as when the environment starts contributing to more variation. As a case in point, consider that both genes and environment have the potential to influence intelligence. Heritability could increase if genetic variation increases, causing individuals to show more phenotypic variation, like showing different levels of intelligence. On the other hand, heritability might also increase if the environmental variation decreases, causing individuals to show less phenotypic variation, like showing more similar levels of intelligence. Heritability increases when genetics are contributing more variation or because non-genetic factors are contributing less variation; what matters is the relative contribution. Heritability is specific to a particular population in a particular environment. High heritability of a trait, consequently, does not necessarily mean that the trait is not very susceptible to environmental influences.[8] Heritability can also change as a result of changes in the environment, migration, inbreeding, or the way in which heritability itself is measured in the population under study.[9] The heritability of a trait should not be interpreted as a measure of the extent to which said trait is genetically determined in an individual.[10][11]
The extent of dependence of phenotype on environment can also be a function of the genes involved. Matters of heritability are complicated because genes may canalize a phenotype, making its expression almost inevitable in all occurring environments. Individuals with the same genotype can also exhibit different phenotypes through a mechanism called phenotypic plasticity, which makes heritability difficult to measure in some cases. Recent insights in molecular biology have identified changes in transcriptional activity of individual genes associated with environmental changes. However, there are a large number of genes whose transcription is not affected by the environment.[12]
Estimates of heritability use statistical analyses to help to identify the causes of differences between individuals. Since heritability is concerned with variance, it is necessarily an account of the differences between individuals in a population. Heritability can be univariate – examining a single trait – or multivariate – examining the genetic and environmental associations between multiple traits at once. This allows a test of the genetic overlap between different phenotypes: for instance hair color and eye color. Environment and genetics may also interact, and heritability analyses can test for and examine these interactions (GxE models).
A prerequisite for heritability analyses is that there is some population variation to account for. This last point highlights the fact that heritability cannot take into account the effect of factors which are invariant in the population. Factors may be invariant if they are absent and do not exist in the population, such as no one having access to a particular antibiotic, or because they are omni-present, like if everyone is drinking coffee. In practice, all human behavioral traits vary and almost all traits show some heritability.[13]
Definition
Any particular phenotype can be modeled as the sum of genetic and environmental effects:[14]
- Phenotype (P) = Genotype (G) + Environment (E).
Likewise the phenotypic variance in the trait – Var (P) – is the sum of effects as follows:
- Var(P) = Var(G) + Var(E) + 2 Cov(G,E).
In a planned experiment Cov(G,E) can be controlled and held at 0. In this case, heritability, is defined as[15]
H2 is the broad-sense heritability. This reflects all the genetic contributions to a population's phenotypic variance including additive, dominant, and epistatic (multi-genic interactions), as well as maternal and paternal effects, where individuals are directly affected by their parents' phenotype, such as with milk production in mammals.
A particularly important component of the genetic variance is the additive variance, Var(A), which is the variance due to the average effects (additive effects) of the alleles. Since each parent passes a single allele per locus to each offspring, parent-offspring resemblance depends upon the average effect of single alleles. Additive variance represents, therefore, the genetic component of variance responsible for parent-offspring resemblance. The additive genetic portion of the phenotypic variance is known as Narrow-sense heritability and is defined as
An upper case H2 is used to denote broad sense, and lower case h2 for narrow sense.
For traits which are not continuous but dichotomous such as an additional toe or certain diseases, the contribution of the various alleles can be considered to be a sum, which past a threshold, manifests itself as the trait, giving the liability threshold model in which heritability can be estimated and selection modeled.
Additive variance is important for selection. If a selective pressure such as improving livestock is exerted, the response of the trait is directly related to narrow-sense heritability. The mean of the trait will increase in the next generation as a function of how much the mean of the selected parents differs from the mean of the population from which the selected parents were chosen. The observed response to selection leads to an estimate of the narrow-sense heritability (called realized heritability). This is the principle underlying artificial selection or breeding.
Example
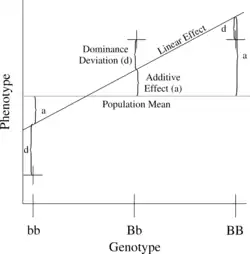
The simplest genetic model involves a single locus with two alleles (b and B) affecting one quantitative phenotype.
The number of B alleles can be 0, 1, or 2. For any genotype, (Bi,Bj), where Bi and Bj are either 0 or 1, the expected phenotype can then be written as the sum of the overall mean, a linear effect, and a dominance deviation (one can think of the dominance term as an interaction between Bi and Bj):
The additive genetic variance at this locus is the weighted average of the squares of the additive effects:
where
There is a similar relationship for the variance of dominance deviations:
where
The linear regression of phenotype on genotype is shown in Figure 1.
Assumptions
Estimates of the total heritability of human traits assume the absence of epistasis, which has been called the "assumption of additivity". Although some researchers have cited such estimates in support of the existence of "missing heritability" unaccounted for by known genetic loci, the assumption of additivity may render these estimates invalid.[16] There is also some empirical evidence that the additivity assumption is frequently violated in behavior genetic studies of adolescent intelligence and academic achievement.[17]
Estimating heritability
Since only P can be observed or measured directly, heritability must be estimated from the similarities observed in subjects varying in their level of genetic or environmental similarity. The statistical analyses required to estimate the genetic and environmental components of variance depend on the sample characteristics. Briefly, better estimates are obtained using data from individuals with widely varying levels of genetic relationship - such as twins, siblings, parents and offspring, rather than from more distantly related (and therefore less similar) subjects. The standard error for heritability estimates is improved with large sample sizes.
In non-human populations it is often possible to collect information in a controlled way. For example, among farm animals it is easy to arrange for a bull to produce offspring from a large number of cows and to control environments. Such experimental control is generally not possible when gathering human data, relying on naturally occurring relationships and environments.
In classical quantitative genetics, there were two schools of thought regarding estimation of heritability.
One school of thought was developed by Sewall Wright at The University of Chicago, and further popularized by C. C. Li (University of Chicago) and J. L. Lush (Iowa State University). It is based on the analysis of correlations and, by extension, regression. Path Analysis was developed by Sewall Wright as a way of estimating heritability.
The second was originally developed by R. A. Fisher and expanded at The University of Edinburgh, Iowa State University, and North Carolina State University, as well as other schools. It is based on the analysis of variance of breeding studies, using the intraclass correlation of relatives. Various methods of estimating components of variance (and, hence, heritability) from ANOVA are used in these analyses.
Today, heritability can be estimated from general pedigrees using linear mixed models and from genomic relatedness estimated from genetic markers.
Studies of human heritability often utilize adoption study designs, often with identical twins who have been separated early in life and raised in different environments. Such individuals have identical genotypes and can be used to separate the effects of genotype and environment. A limit of this design is the common prenatal environment and the relatively low numbers of twins reared apart. A second and more common design is the twin study in which the similarity of identical and fraternal twins is used to estimate heritability. These studies can be limited by the fact that identical twins are not completely genetically identical, potentially resulting in an underestimation of heritability.
In observational studies, or because of evocative effects (where a genome evokes environments by its effect on them), G and E may covary: gene environment correlation. Depending on the methods used to estimate heritability, correlations between genetic factors and shared or non-shared environments may or may not be confounded with heritability.[18]
Regression/correlation methods of estimation
The first school of estimation uses regression and correlation to estimate heritability.
Comparison of close relatives
In the comparison of relatives, we find that in general,
where r can be thought of as the coefficient of relatedness, b is the coefficient of regression and t is the coefficient of correlation.
Parent-offspring regression
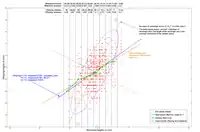
Heritability may be estimated by comparing parent and offspring traits (as in Fig. 2). The slope of the line (0.57) approximates the heritability of the trait when offspring values are regressed against the average trait in the parents. If only one parent's value is used then heritability is twice the slope. (Note that this is the source of the term "regression," since the offspring values always tend to regress to the mean value for the population, i.e., the slope is always less than one). This regression effect also underlies the DeFries–Fulker method for analyzing twins selected for one member being affected.[19]
Sibling comparison
A basic approach to heritability can be taken using full-Sib designs: comparing similarity between siblings who share both a biological mother and a father.[20] When there is only additive gene action, this sibling phenotypic correlation is an index of familiarity – the sum of half the additive genetic variance plus full effect of the common environment. It thus places an upper limit on additive heritability of twice the full-Sib phenotypic correlation. Half-Sib designs compare phenotypic traits of siblings that share one parent with other sibling groups.
Twin studies
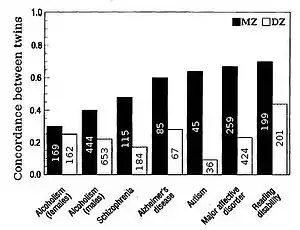
Heritability for traits in humans is most frequently estimated by comparing resemblances between twins. "The advantage of twin studies, is that the total variance can be split up into genetic, shared or common environmental, and unique environmental components, enabling an accurate estimation of heritability".[21] Fraternal or dizygotic (DZ) twins on average share half their genes (assuming there is no assortative mating for the trait), and so identical or monozygotic (MZ) twins on average are twice as genetically similar as DZ twins. A crude estimate of heritability, then, is approximately twice the difference in correlation between MZ and DZ twins, i.e. Falconer's formula H2=2(r(MZ)-r(DZ)).
The effect of shared environment, c2, contributes to similarity between siblings due to the commonality of the environment they are raised in. Shared environment is approximated by the DZ correlation minus half heritability, which is the degree to which DZ twins share the same genes, c2=DZ-1/2h2. Unique environmental variance, e2, reflects the degree to which identical twins raised together are dissimilar, e2=1-r(MZ).
Analysis of variance methods of estimation
The second set of methods of estimation of heritability involves ANOVA and estimation of variance components.
Basic model
We use the basic discussion of Kempthorne.[14] Considering only the most basic of genetic models, we can look at the quantitative contribution of a single locus with genotype Gi as
where is the effect of genotype Gi and is the environmental effect.
Consider an experiment with a group of sires and their progeny from random dams. Since the progeny get half of their genes from the father and half from their (random) mother, the progeny equation is
Intraclass correlations
Consider the experiment above. We have two groups of progeny we can compare. The first is comparing the various progeny for an individual sire (called within sire group). The variance will include terms for genetic variance (since they did not all get the same genotype) and environmental variance. This is thought of as an error term.
The second group of progeny are comparisons of means of half sibs with each other (called among sire group). In addition to the error term as in the within sire groups, we have an addition term due to the differences among different means of half sibs. The intraclass correlation is
- ,
since environmental effects are independent of each other.
The ANOVA
In an experiment with sires and progeny per sire, we can calculate the following ANOVA, using as the genetic variance and as the environmental variance:
| Source | d.f. | Mean Square | Expected Mean Square |
|---|---|---|---|
| Between sire groups | |||
| Within sire groups |
The term is the intraclass correlation between half sibs. We can easily calculate . The expected mean square is calculated from the relationship of the individuals (progeny within a sire are all half-sibs, for example), and an understanding of intraclass correlations.
The use of ANOVA to calculate heritability often fails to account for the presence of gene–-environment interactions, because ANOVA has a much lower statistical power for testing for interaction effects than for direct effects.[22]
Model with additive and dominance terms
For a model with additive and dominance terms, but not others, the equation for a single locus is
where
is the additive effect of the ith allele, is the additive effect of the jth allele, is the dominance deviation for the ijth genotype, and is the environment.
Experiments can be run with a similar setup to the one given in Table 1. Using different relationship groups, we can evaluate different intraclass correlations. Using as the additive genetic variance and as the dominance deviation variance, intraclass correlations become linear functions of these parameters. In general,
- Intraclass correlation
where and are found as
P[ alleles drawn at random from the relationship pair are identical by descent], and
P[ genotypes drawn at random from the relationship pair are identical by descent].
Some common relationships and their coefficients are given in Table 2.
| Relationship | ||
|---|---|---|
| Identical Twins | ||
| Parent-Offspring | ||
| Half Siblings | ||
| Full Siblings | ||
| First Cousins | ||
| Double First Cousins |
Linear mixed models
A wide variety of approaches using linear mixed models have been reported in literature. Via these methods, phenotypic variance is partitioned into genetic, environmental and experimental design variances to estimate heritability. Environmental variance can be explicitly modeled by studying individuals across a broad range of environments, although inference of genetic variance from phenotypic and environmental variance may lead to underestimation of heritability due to the challenge of capturing the full range of environmental influence affecting a trait. Other methods for calculating heritability use data from genome-wide association studies to estimate the influence on a trait by genetic factors, which is reflected by the rate and influence of putatively associated genetic loci (usually single-nucleotide polymorphisms) on the trait. This can lead to underestimation of heritability, however. This discrepancy is referred to as "missing heritability" and reflects the challenge of accurately modeling both genetic and environmental variance in heritability models.[23]
When a large, complex pedigree or another aforementioned type of data is available, heritability and other quantitative genetic parameters can be estimated by restricted maximum likelihood (REML) or Bayesian methods. The raw data will usually have three or more data points for each individual: a code for the sire, a code for the dam and one or several trait values. Different trait values may be for different traits or for different time points of measurement.
The currently popular methodology relies on high degrees of certainty over the identities of the sire and dam; it is not common to treat the sire identity probabilistically. This is not usually a problem, since the methodology is rarely applied to wild populations (although it has been used for several wild ungulate and bird populations), and sires are invariably known with a very high degree of certainty in breeding programmes. There are also algorithms that account for uncertain paternity.
The pedigrees can be viewed using programs such as Pedigree Viewer , and analyzed with programs such as ASReml, VCE , WOMBAT , MCMCglmm within the R environment or the BLUPF90 family of programs .
Pedigree models are helpful for untangling confounds such as reverse causality, maternal effects such as the prenatal environment, and confounding of genetic dominance, shared environment, and maternal gene effects.[24][9]
Genomic heritability
When genome-wide genotype data and phenotypes from large population samples are available, one can estimate the relationships between individuals based on their genotypes and use a linear mixed model to estimate the variance explained by the genetic markers. This gives a genomic heritability estimate based on the variance captured by common genetic variants.[4] There are multiple methods that make different adjustments for allele frequency and linkage disequilibrium. Particularly, the method called High-Definition Likelihood (HDL) can estimate genomic heritability using only GWAS summary statistics,[5] making it easier to incorporate large sample size available in various GWAS meta-analysis.
Response to selection
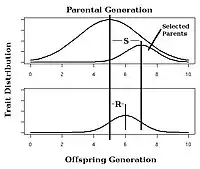
In selective breeding of plants and animals, the expected response to selection of a trait with known narrow-sense heritability can be estimated using the breeder's equation:[25]
In this equation, the Response to Selection (R) is defined as the realized average difference between the parent generation and the next generation, and the Selection Differential (S) is defined as the average difference between the parent generation and the selected parents.[14]: 1957 [26]
For example, imagine that a plant breeder is involved in a selective breeding project with the aim of increasing the number of kernels per ear of corn. For the sake of argument, let us assume that the average ear of corn in the parent generation has 100 kernels. Let us also assume that the selected parents produce corn with an average of 120 kernels per ear. If h2 equals 0.5, then the next generation will produce corn with an average of 0.5(120-100) = 10 additional kernels per ear. Therefore, the total number of kernels per ear of corn will equal, on average, 110.
Observing the response to selection in an artificial selection experiment will allow calculation of realized heritability as in Fig. 4.
Note that heritability in the above equation is equal to the ratio only if the genotype and the environmental noise follow Gaussian distributions.
Controversies
Heritability estimates' prominent critics, such as Steven Rose,[27] Jay Joseph,[28] and Richard Bentall, focus largely on heritability estimates in behavioral sciences and social sciences. Bentall has claimed that such heritability scores are typically calculated counterintuitively to derive numerically high scores, that heritability is misinterpreted as genetic determination, and that this alleged bias distracts from other factors that researches have found more causally important, such as childhood abuse causing later psychosis.[29][30] Heritability estimates are also inherently limited because they do not convey any information regarding whether genes or environment play a larger role in the development of the trait under study. For this reason, David Moore and David Shenk describe the term "heritability" in the context of behavior genetics as "...one of the most misleading in the history of science" and argue that it has no value except in very rare cases.[31] When studying complex human traits, it is impossible to use heritability analysis to determine the relative contributions of genes and environment, as such traits result from multiple causes interacting.[32] In particular, Feldman and Lewontin emphasize that heritability is itself a function of environmental variation.[33] However, some researchers argue that it is possible to disentangle the two.[34]
The controversy over heritability estimates is largely via their basis in twin studies. The scarce success of molecular-genetic studies to corroborate such population-genetic studies' conclusions is the missing heritability problem.[35] Eric Turkheimer has argued that newer molecular methods have vindicated the conventional interpretation of twin studies,[35] although it remains mostly unclear how to explain the relations between genes and behaviors.[36] According to Turkheimer, both genes and environment are heritable, genetic contribution varies by environment, and a focus on heritability distracts from other important factors.[37] Overall, however, heritability is a concept widely applicable.[9]
References
- Wray N, Visscher P (2008). "Estimating Trait Heritability". Nature Education. 1 (1): 29. Archived from the original on 2 August 2015. Retrieved 24 July 2015.
- Gazzaniga MS, Heatherton TF, Halpern DF (February 2015). Psychological science (5th ed.). New York. ISBN 978-0-393-26313-8. OCLC 908409996.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Yang J, Lee SH, Goddard ME, Visscher PM (January 2011). "GCTA: a tool for genome-wide complex trait analysis". American Journal of Human Genetics. 88 (1): 76–82. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.11.011. PMC 3014363. PMID 21167468.
- Yang J, Zeng J, Goddard ME, Wray NR, Visscher PM (August 2017). "Concepts, estimation and interpretation of SNP-based heritability" (PDF). Nature Genetics. 49 (9): 1304–1310. doi:10.1038/ng.3941. PMID 28854176. S2CID 8790524. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2020-10-05. Retrieved 2020-09-06.
- Ning Z, Pawitan Y, Shen X (June 2020). "High-definition likelihood inference of genetic correlations across human complex traits" (PDF). Nature Genetics. 52 (8): 859–864. doi:10.1038/s41588-020-0653-y. hdl:10616/47311. PMID 32601477. S2CID 220260262. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2021-04-15. Retrieved 2021-02-08.
- Stoltenberg SF (June 1997). "Coming to terms with heritability". Genetica. 99 (2–3): 89–96. doi:10.1007/BF02259512. hdl:2027.42/42804. PMID 9463077. S2CID 18212219. Archived from the original on 2020-12-02. Retrieved 2020-12-24.
- Wahlsten D (1994). "The intelligence of heritability" (PDF). Canadian Psychology. 35 (3): 244–260. doi:10.1037/0708-5591.35.3.244. ISSN 1878-7304. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2018-10-24. Retrieved 2019-12-05.
- Maccoby EE (February 2000). "Parenting and its effects on children: on reading and misreading behavior genetics". Annual Review of Psychology. 51 (1): 1–27. doi:10.1146/annurev.psych.51.1.1. PMID 10751963. S2CID 43435035.
- Visscher PM, Hill WG, Wray NR (April 2008). "Heritability in the genomics era--concepts and misconceptions" (PDF). Nature Reviews. Genetics. 9 (4): 255–66. doi:10.1038/nrg2322. PMID 18319743. S2CID 690431. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2016-03-24. Retrieved 2015-08-28.
- Sauce B, Matzel LD (January 2018). "The paradox of intelligence: Heritability and malleability coexist in hidden gene-environment interplay". Psychological Bulletin. 144 (1): 26–47. doi:10.1037/bul0000131. PMC 5754247. PMID 29083200.
- Block N (August 1995). "How heritability misleads about race". Cognition. 56 (2): 99–128. doi:10.1016/0010-0277(95)00678-r. PMID 7554794. S2CID 204981536.
- Wills C (2007). "Principles of Population Genetics, 4th edition". Journal of Heredity (Book Review). 98 (4): 382. doi:10.1093/jhered/esm035.
- review of: Hartl DL, Clark AG (2007). Principles of Population Genetics. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer and Associates. pp. xv + 652. ISBN 978-0-87893-308-2.
- Turkheimer E (October 2000). "Three Laws of Behavior Genetics and What They Mean" (PDF). Current Directions in Psychological Science. 9 (5): 160–164. doi:10.1111/1467-8721.00084. ISSN 0963-7214. S2CID 2861437. Archived (PDF) from the original on 19 October 2013. Retrieved 29 October 2013.
- Kempthorne O (1957). An introduction to genetic statistics (1st ed.). Ames, Iowa: Iowa State Univ. Press. OCLC 422371269.
- Stephen Downes and Lucas Matthews. "Heritability". Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Stanford University. Archived from the original on 2020-02-25. Retrieved 2020-02-20.
- Zuk O, Hechter E, Sunyaev SR, Lander ES (January 2012). "The mystery of missing heritability: Genetic interactions create phantom heritability". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 109 (4): 1193–8. Bibcode:2012PNAS..109.1193Z. doi:10.1073/pnas.1119675109. PMC 3268279. PMID 22223662.
- Daw J, Guo G, Harris KM (July 2015). "Nurture net of nature: Re-evaluating the role of shared environments in academic achievement and verbal intelligence". Social Science Research. 52: 422–39. doi:10.1016/j.ssresearch.2015.02.011. PMC 4888873. PMID 26004471.
- Cattell RB (November 1960). "The multiple abstract variance analysis equations and solutions: for nature-nurture research on continuous variables". Psychological Review. 67 (6): 353–72. doi:10.1037/h0043487. PMID 13691636.
- DeFries JC, Fulker DW (September 1985). "Multiple regression analysis of twin data". Behavior Genetics. 15 (5): 467–73. doi:10.1007/BF01066239. PMID 4074272. S2CID 1172312.
- Falconer DS, Mackay TF (December 1995). Introduction to Quantitative Genetics (4th ed.). Longman. ISBN 978-0582243026.
- Gielen M, Lindsey PJ, Derom C, Smeets HJ, Souren NY, Paulussen AD, Derom R, Nijhuis JG (January 2008). "Modeling genetic and environmental factors to increase heritability and ease the identification of candidate genes for birth weight: a twin study". Behavior Genetics. 38 (1): 44–54. doi:10.1007/s10519-007-9170-3. PMC 2226023. PMID 18157630.
- Wahlsten, Douglas (March 1990). "Insensitivity of the analysis of variance to heredity-environment interaction" (PDF). Behavioral and Brain Sciences. 13 (1): 109–120. doi:10.1017/S0140525X00077797. ISSN 1469-1825. S2CID 143217984. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2020-10-05. Retrieved 2020-09-06.
- Heckerman D, Gurdasani D, Kadie C, Pomilla C, Carstensen T, Martin H, Ekoru K, Nsubuga RN, Ssenyomo G, Kamali A, Kaleebu P, Widmer C, Sandhu MS (July 2016). "Linear mixed model for heritability estimation that explicitly addresses environmental variation". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 113 (27): 7377–82. Bibcode:2016PNAS..113.7377H. doi:10.1073/pnas.1510497113. PMC 4941438. PMID 27382152.
- Hill WG, Goddard ME, Visscher PM (February 2008). MacKay TF, Goddard ME (eds.). "Data and theory point to mainly additive genetic variance for complex traits". PLOS Genetics. 4 (2): e1000008. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1000008. PMC 2265475. PMID 18454194.

- Plomin R, DeFries JC, McClearn GE, McGuffin P (2017). Behavioral Genetics: A Primer (2nd ed.). New York: W.H. Freeman. ISBN 978-0-7167-2056-0.
- Falconer DS, Mackay TF (1998). Introduction to quantitative genetics (4th ed.). Essex: Longman. ISBN 978-0-582-24302-6.
- Rose SP (June 2006). "Commentary: heritability estimates--long past their sell-by date". International Journal of Epidemiology. 35 (3): 525–7. doi:10.1093/ije/dyl064. PMID 16645027.
- Joseph J (2004). "Chapter 5". The Gene Illusion. New York: Algora. p. 141. ISBN 978-1-898059-47-9. Archived from the original on 2017-07-19. Retrieved 2016-04-02.
- Bentall RP (2009). Doctoring the Mind: Is Our Current Treatment of Mental Illness Really Any Good?. New York: New York University Press. pp. 123–127. ISBN 978-0-8147-8723-6. Archived from the original on 2020-10-05. Retrieved 2016-04-02.
- McGrath M (5 July 2009). "Doctoring the Mind: Review". The Telegraph. Archived from the original on 28 September 2011. Retrieved 4 April 2018.
- Moore DS, Shenk D (January 2017). "The heritability fallacy". Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Cognitive Science. 8 (1–2): e1400. doi:10.1002/wcs.1400. PMID 27906501.
- Feldman MW, Ramachandran S (April 2018). "Missing compared to what? Revisiting heritability, genes and culture". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences. 373 (1743): 20170064. doi:10.1098/rstb.2017.0064. PMC 5812976. PMID 29440529.
...all complex human traits result from a combination of causes. If these causes interact, it is impossible to assign quantitative values to the fraction of a trait due to each, just as we cannot say how much of the area of a rectangle is due, separately, to each of its two dimensions. Thus, in the analyses of complex human phenotypes...we cannot actually find 'the relative importance of genes and environment in the determination of phenotype'.
- Marcus W. Feldman; Richard C. Lewontin (1975). "The Heritability Hang–Up". Science. 190 (4220): 1163–1168. Bibcode:1975Sci...190.1163F. doi:10.1126/science.1198102. PMID 1198102. S2CID 6797128. Archived from the original on 20 May 2021. Retrieved 20 May 2021.
- Tredoux, Gavan. "The Nature and Nurture of Rectangles." (2019).
- Turkheimer E (2011). "Still missing". Research in Human Development. 8 (3–4): 227–241. doi:10.1080/15427609.2011.625321. S2CID 14737438.
- Turkheimer E (2015). "Genetic Prediction". The Hastings Center Report. 45 (5 Suppl): S32–8. doi:10.1002/hast.496. PMID 26413946.
- Joseph J (2014). The Trouble with Twin Studies: A Reassessment of Twin Research in the Social and Behavioral Sciences (PDF). New York: Routledge. p. 81. ISBN 978-1-317-60590-4. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2016-04-04. Retrieved 2016-04-02.
Further reading
- Lynch M, Walsh B (1998). Genetics and analysis of quantitative traits. Sunderland, Mass.: Sinauer Assoc. ISBN 978-0-87893-481-2.
- Johnson W, Penke L, Spinath FM (2011). "Understanding Heritability: What it is and What it is Not". European Journal of Personality. 25 (4): 287–294. doi:10.1002/per.835. ISSN 0890-2070. S2CID 41842465.