Nuclear groove
A nuclear groove is an invagination of the nuclear envelope, in the longitudinal axis.[1] It can be present in:
- Thyroid neoplasms: It is a characteristic feature of papillary thyroid carcinoma, but has also been seen in other types of thyroid neoplasms, as well as in non-neoplastic thyroid lesions.[1]
- Ovarian tumors including Brenner tumors, adult granulosa cell tumors, and transitional cell tumors.[1]
- Breast carcinomas[1]
- Vaginal, cervical and/or endometrial neoplasms
- Papillary neoplasms of several organs: papillary transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder, papillary renal cell carcinoma, papillary endometrioid carcinoma of the prostate, in thymic carcinomas, and in non-epithelial tumors.
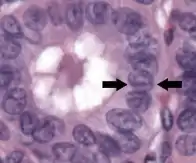
Nuclear grooves (arrows indicate one of them) in papillary thyroid cancer. H&E stain.
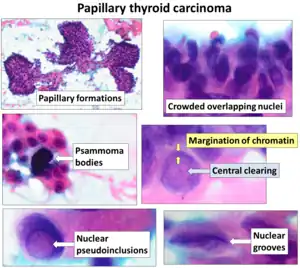
Cytopathology of papillary thyroid carcinoma, with typical features, with nuclear groove at bottom right. Pap stain.
References
- Batistatou, Anna; Scopa, Chrisoula D. (2008). "Review Articles: Pathogenesis and Diagnostic Significance of Nuclear Grooves in Thyroid and Other Sites". International Journal of Surgical Pathology. 17 (2): 107–110. doi:10.1177/1066896908316071. ISSN 1066-8969.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.