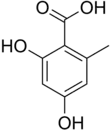
Orsellinic acid
Orsellinic acid, more specifically o-orsellinic acid, is a phenolic acid. It is of importance in the biochemistry of lichens, from which it can be extracted.[1] It is a common subunit of depsides.
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,4-Dihydroxy-6-methylbenzoic acid | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.115.964 | ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID |
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C8H8O4 | |||
| Molar mass | 168.148 g·mol−1 | ||
| Melting point | 175 °C (347 °F; 448 K) | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |||
Chemistry
It can be prepared by the oxidation of orsellaldehyde.[2]
This is also produced when everninic acid and ramalic acid is boiled with barium hydroxide. It forms colorless crystals in the form of needles which on rapid heating melt with decomposition in the neighborhood of 175 °C.[3]
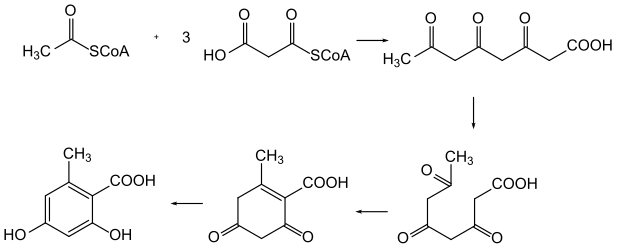
Biosynthesis of orsellinic acid from polyketides
References
- Nolan, T. J.; Keane, J.; Davidson, V. E. (1940). "Chemical constituents of the lichen Parmelia latissima Fee". Scientific Proceedings of the Royal Dublin Society, Series A. 22: 237–239.
- Kang, Ying; Mei, Yan; Du, Yuguo; Jin, Zhendong (2003). "Total Synthesis of the Highly Potent Anti-HIV Natural Product Daurichromenic Acid along with Its Two Chromane Derivatives, Rhododaurichromanic Acids A and B". Organic Letters. 5 (23): 4481–4484. doi:10.1021/ol030109m. PMID 14602030.
- Russell, R.; Kemmelmeier, C (1990). "Neutral, alkaline and difference ultraviolet spectra of secondary metabolites from Penicillium and other fungi, and comparisons to published maxima from gradient high-performance liquid chromatography with diode-array detection". Journal of Chromatography. 511: 195–221. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(01)93285-6. PMID 2211911.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.