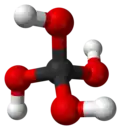
Orthocarbonic acid
Orthocarbonic acid, carbon hydroxide or methanetetrol is the name given to a hypothetical compound with the chemical formula H4CO4 or C(OH)4. Its molecular structure consists of a single carbon atom bonded to four hydroxy groups. It would be therefore a fourfold alcohol. In theory it could lose four protons to give the hypothetical oxocarbon anion orthocarbonate CO4−4, and is therefore considered an oxoacid of carbon.
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Methanetetrol[1] | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
Orthocarbonic acid | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID |
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| CH4O4 | |||
| Molar mass | 80.039 g·mol−1 | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Other cations |
|||
Related compounds |
| ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |||
Orthocarbonic acid is highly unstable. Calculations show that it decomposes spontaneously into carbonic acid and water:[2][3]
Orthocarbonic acid is one of the group of ortho acids that have the general structure of RC(OH)3.The term ortho acid is also used to refer to the most hydroxylated acid in a set of oxoacids.
Researchers predict that orthocarbonic acid is stable at high pressure; hence it may form in the interior of the ice giant planets Uranus and Neptune, where water and methane are common.[4]
Orthocarbonate anions
By loss of one through four protons, orthocarbonic acid could yield four anions: H3CO−4, H2CO2−4, HCO3−4, and CO4−4.
Numerous salts of fully deprotonated CO4−4, such as Ca2CO4 or Sr2CO4, have been synthesized under high pressure conditions and structurally characterized by X-ray diffraction.[5][6][7] Strontium orthocarbonate, Sr2CO4, is stable at atmospheric pressure. Orthocarbonate is tetrahedral in shape, and is isoelectronic to orthonitrate. The C-O distance is 1.41 Å.[8] Sr3[CO4]O is an oxide orthocarbonate, also stable at atmospheric pressure.[9]
Orthocarbonate esters
The tetravalent moiety CO4 is found in stable organic compounds; they are formally esters of orthocarbonic acid, and therefore are called orthocarbonates. For example, tetraethoxymethane can be prepared by the reaction between chloropicrin and sodium ethoxide in ethanol.[10] Polyorthocarbonates are stable polymers that might have applications in absorbing organic solvents in waste treatment processes,[11] or in dental restorative materials.[12] The explosive trinitroethylorthocarbonate possesses an orthocarbonate core.
See also
- Pentaerythritol
- Silicic acid or Si(OH)
4 - Carbonic acid or H
2CO
3
References
- "Methanetetrol - PubChem Public Chemical Database". The PubChem Project. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information.
- Bohm S.; Antipova D.; Kuthan J. (1997). "A Study of Methanetetraol Dehydration to Carbonic Acid". International Journal of Quantum Chemistry. 62 (3): 315–322. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-461X(1997)62:3<315::AID-QUA10>3.0.CO;2-8.
- Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives Archived 2017-09-13 at the Wayback Machine IUPAC Recommendations on Organic & Biochemical Nomenclature
- G. Saleh; A. R. Oganov (2016). "Novel Stable Compounds in the C-H-O Ternary System at High Pressure". Scientific Reports. 6: 32486. Bibcode:2016NatSR...632486S. doi:10.1038/srep32486. PMC 5007508. PMID 27580525.
- Sagatova, Dinara; Shatskiy, Anton; Sagatov, Nursultan; Gavryushkin, Pavel N.; Litasov, Konstantin D. (2020). "Calcium orthocarbonate, Ca2CO4-Pnma: A potential host for subducting carbon in the transition zone and lower mantle". Lithos. 370–371: 105637. Bibcode:2020Litho.37005637S. doi:10.1016/j.lithos.2020.105637. ISSN 0024-4937. S2CID 224909120.
- Binck, Jannes; Laniel, Dominique; Bayarjargal, Lkhamsuren; Khandarkhaeva, Saiana; Fedotenko, Timofey; Aslandukov, Andrey; Milman, Victor; Glazyrin, Konstantin; Milman, Victor; Chariton, Stella; Prakapenka, Vitali B.; Dubrovinskaia, Natalia; Dubrovinsky, Leonid; Winkler, Björn (2022). "Synthesis of calcium orthocarbonate, Ca2CO4-Pnma at P-T conditions of Earth's transition zone and lower mantle". American Mineralogist. 107 (3): 336–342. Bibcode:2022AmMin.107..336B. doi:10.2138/am-2021-7872. S2CID 242847474.
- Laniel, Dominique; Binck, Jannes; Winkler, Björn; Vogel, Sebastian; Fedotenko, Timofey; Chariton, Stella; Prakapenka, Vitali; Milman, Victor; Schnick, Wolfgang; Dubrovinsky, Leonid; Dubrovinskaia, Natalia (2021). "Synthesis, crystal structure and structure–property relations of strontium orthocarbonate, Sr2CO4". Acta Crystallographica Section B. 77 (1): 131–137. doi:10.1107/S2052520620016650. ISSN 2052-5206. PMC 7941283.
- Spahr, Dominik; Binck, Jannes; Bayarjargal, Lkhamsuren; Luchitskaia, Rita; Morgenroth, Wolfgang; Comboni, Davide; Milman, Victor; Winkler, Björn (4 April 2021). "Tetrahedrally Coordinated sp3-Hybridized Carbon in Sr2CO4 Orthocarbonate at Ambient Conditions". Inorganic Chemistry. 60 (8): 5419–5422. doi:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.1c00159. PMID 33813824.
- Spahr, Dominik; König, Jannes; Bayarjargal, Lkhamsuren; Gavryushkin, Pavel N.; Milman, Victor; Liermann, Hanns-Peter; Winkler, Björn (4 October 2021). "Sr 3 [CO 4 ]O Antiperovskite with Tetrahedrally Coordinated sp 3 -Hybridized Carbon and OSr 6 Octahedra". Inorganic Chemistry. 60 (19): 14504–14508. doi:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.1c01900. PMID 34520201. S2CID 237514625.
- Orthocarbonic acid, tetraethyl ester Archived 2012-09-20 at the Wayback Machine Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 4, p. 457 (1963); Vol. 32, p. 68 (1952).
- Sonmez, H.B.; Wudl, F. (2005). "Cross-linked poly(orthocarbonate)s as organic solvent sorbents". Macromolecules. 38 (5): 1623–1626. Bibcode:2005MaMol..38.1623S. doi:10.1021/ma048731x.
- Stansbury, J.W. (1992). "Synthesis and evaluation of new oxaspiro monomers for double ring-opening polymerization". Journal of Dental Research. 71 (7): 1408–1412. doi:10.1177/00220345920710070901. PMID 1629456. S2CID 24589493. Archived from the original on 2008-07-08. Retrieved 2008-06-19.