Legislative Assembly of El Salvador
The Legislative Assembly (Spanish: Asamblea Legislativa) is the legislative branch of the government of El Salvador.
Legislative Assembly of the Republic of El Salvador Asamblea Legislativa de la República de El Salvador | |
|---|---|
.svg.png.webp) | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| History | |
| Founded | 1824[1] |
| Leadership | |
| Structure | |
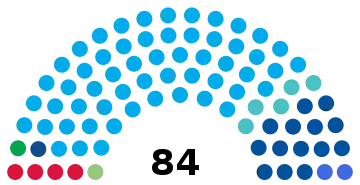
| Seats | 84 deputies |
 | |
Political groups | Government: (67)
Opposition: (17)
|
| Elections | |
Last election | 28 February 2021 |
Next election | 4 February 2024 |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| San Salvador | |
| Website | |
| www | |
 |
|---|
|
|
History
The organization was founded in 1824 as the Central American Congress (Spanish: Congreso Federal Centroamericano).[1]
Structure

The Salvadoran legislature is a unicameral body. It is made up of 84 deputies, all of whom are elected by direct popular vote according to open-list proportional representation to serve three-year terms and are eligible for immediate re-election. Of these, 64 are elected in 14 multi-seat constituencies, corresponding to the country's 14 departments, which return between 3 and 16 deputies each. The remaining 20 deputies are selected on the basis of a single national constituency.
To be eligible for election to the Assembly, candidates must be (Art. 126, Constitution):
- over 25;
- Salvadoran citizens by birth, born of at least one parent to be a Salvadoran citizen;
- of recognised honesty and education, and
- have not had the privilege of one's rights as a citizen cancelled in the previous five years.
On 1 June 2023, Salvadoran President Nayib Bukele issued a proposal to the Legislative Assembly to reduce the number of its seats from 84 to 60.[2] The proposal was passed by the Legislative Assembly on 7 June 2023.[3]
Current standing by party
| Party / Group | Deputies | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Nuevas Ideas (NI) | 56 | ||
| Nationalist Republican Alliance (ARENA) | 11 | ||
| Grand Alliance for National Unity (GANA) | 4 | ||
| Farabundo Martí National Liberation Front (FMLN) | 4 | ||
| National Coalition Party (PCN) | 2 | ||
| Nuestro Tiempo (NT) | 1 | ||
| Vamos (V) | 1 | ||
| Christian Democratic Party (PDC) | 1 | ||
| Independent | 4 | ||
| Source: Salvadoran Legislative Assembly | |||
XIII legislative composition
| Charge | Name | Party |
| President | Ernesto Castro | Nuevas Ideas |
| First Vice President | Suecy Callejas | Nuevas Ideas |
| Second Vice President | Rodrigo Ayala | Nuevas Ideas |
| Third Vice President | Guillermo Gallegos | GANA |
| First Secretary | Elisa Rosales | Nuevas Ideas |
| Second Secretary | Numan Salgado | GANA |
| Third Secretary | Serafín Orantes (2021-2022) Reynaldo Cardoza (2022-2024) | PCN |
| Fourth Secretary | Reinaldo Carballo | PDC |
Election results
Results
 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | |
| Nuevas Ideas | 1,430,578 | 54.67 | 46 | New | |
| Nuevas Ideas–GANA | 311,723 | 11.91 | 10 | – | |
| Nationalist Republican Alliance | 206,328 | 7.88 | 9 | −26 | |
| Farabundo Martí National Liberation Front | 180,808 | 6.91 | 4 | −14 | |
| Grand Alliance for National Unity | 135,223 | 5.17 | 5 | −5 | |
| ARENA–DS | 99,003 | 3.78 | 4 | – | |
| National Coalition Party | 85,548 | 3.27 | 1 | −8 | |
| Nuestro Tiempo | 44,401 | 1.70 | 1 | New | |
| Christian Democratic Party | 44,379 | 1.70 | 1 | −1 | |
| Vamos | 26,492 | 1.01 | 1 | New | |
| PCN–DS | 21,211 | 0.81 | 1 | – | |
| Democratic Change | 14,768 | 0.56 | 0 | −1 | |
| ARENA–National Coalition Party | 13,503 | 0.52 | 1 | –1 | |
| Independents | 2,783 | 0.11 | 0 | −1 | |
| Total | 2,616,748 | 100.00 | 84 | 0 | |
| Registered voters/turnout | 5,389,017 | – | |||
| Source: TSE | |||||
Other parliamentary bodies
El Salvador also returns 20 deputies to the supranational Central American Parliament, also elected according to closed-list proportional representation from a single national constituency.
Members of the Legislative Assembly
| Members of the Legislative Assembly 1928–present | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Election | Distribution | ||||||||
| 1928 |
| ||||||||
| 1932 | Election cancelled | ||||||||
| 1936 |
| ||||||||
| 1939 |
| ||||||||
| 1944 |
| ||||||||
| 1950 |
| ||||||||
| 1952 |
| ||||||||
| 1954 |
| ||||||||
| 1956 |
| ||||||||
| 1958 |
| ||||||||
| 1960 |
| ||||||||
| 1961 |
| ||||||||
| 1964 |
| ||||||||
| 1968 |
| ||||||||
| 1970 |
| ||||||||
| 1972 |
| ||||||||
| 1974 |
| ||||||||
| 1976 |
| ||||||||
| 1978 |
| ||||||||
| 1982 |
| ||||||||
| 1985 |
| ||||||||
| 1988 |
| ||||||||
| 1991 |
| ||||||||
| 1994 |
| ||||||||
| 1997 |
| ||||||||
| 2000 |
| ||||||||
| 2003 |
| ||||||||
| 2006 |
| ||||||||
| 2009 |
| ||||||||
| 2012 |
| ||||||||
| 2015 |
| ||||||||
| 2018 |
| ||||||||
| 2021 |
| ||||||||
See also
References
- "Breve historia de la Asamblea Legislativa de la República de El Salvador" (PDF). Retrieved 19 August 2023.
- Velásquez, Eugenia (1 June 2023). "En Vivo: En su Discurso del Cuarto Año de Gobierno Bukele Presenta Propuesta para Reducir de 262 a 44 Municipios y Diputados a 60" [Live: In His Speech of Four Years of Government Bukele Presents Proposal to Reduce from 262 to 44 Municipalities and Deputies to 60]. El Salvador.com (in Spanish). Retrieved 1 June 2023.
- Renteria, Nelson; Madry, Kylie (7 June 2023). Berkrot, Bill (ed.). "El Salvador Slashes Size of Congress Ahead of Elections". Reuters. San Salvador, El Salvador. Retrieved 7 June 2023.
.svg.png.webp)