Peace River Country
The Peace River Country (or Peace Country; French: Région de la Rivière-de-la-paix) is an aspen parkland region centring on the Peace River in Canada. It extends from northwestern Alberta to the Rocky Mountains in northeastern British Columbia, where a certain portion of the region is also referred to as the Peace River Block.
Peace River Country | |
|---|---|
 | |
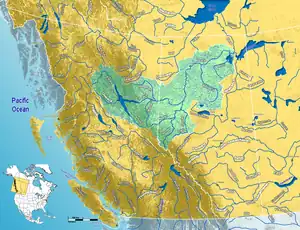 Peace River Country is closely associated with the watershed of the Peace River | |
| Coordinates: 56°30′N 122°00′W | |
| Country | Canada |
| Provinces | Alberta and British Columbia |
| Largest City | Grande Prairie |
Geography
The Peace River Country includes the incorporated communities of Fort St. John, Dawson Creek,[1] Tumbler Ridge and Chetwynd in British Columbia. Major communities in the Alberta portion of the Peace Country include Grande Prairie, Peace River, High Level and Fairview. It has no fixed boundaries but covers some 260,000 to 390,000 km² (100,000 to 150,000 square miles).[2]
In British Columbia, the area extends from Monkman Provincial Park and Tumbler Ridge in the south, to Hudson's Hope and the Williston Lake in the west, to Fort St. John and Charlie Lake in the north. The term is used also in a broader sense to mean the whole of the Northeastern Interior past the Rockies, including Fort Nelson and other parts of the Liard drainage, and before W.A.C. Bennett Dam included the upper Peace River through its canyon between Finlay Forks and Hudson's Hope. In Alberta, the region stretches from Grande Prairie and Valleyview in the south, to High Prairie and Lesser Slave Lake in the east, to Fort Vermilion, High Level and Rainbow Lake in the north.[3]
History

The first European to explore the area was Sir Alexander MacKenzie, who travelled down the Peace in 1789 and eventually reached the Mackenzie River and the Arctic Ocean. In 1793 he used the same route to reach the Pacific Ocean.[4] Subsequently, the region saw a surge in the fur trade, with forts [5] built along the river from Fort Vermilion to Hudson's Hope.
At the beginning of the 20th century, the farming potential of the area was advertised by the federal government, but a settlement was scarce because of difficult travel conditions through the muskeg. With the arrival of the railway in 1916, and following the opening of land for homesteaders in 1910, farming and ranching took off in the fertile Peace Country. The settlement of the British Columbia portion of the agricultural area, known as the Peace River Block, originated as a railway grant which wound up for a time under Dominion jurisdiction and managed by offices in Alberta until returned to British Columbia following ongoing jurisdictional conflicts.[6]
Forestry plays a large role in the Peace Country economy. Pulp mills were built in Chetwynd, Peace River and Grande Prairie beginning in the 1970s.
The economy received another boost when oil and gas were found in the region. In 1952, gas was struck in the Fort St. John No. 1 well, and the first refinery was built in 1957 at Taylor. The massive Elmworth natural gas field in northwestern Alberta was discovered in the mid-70s along with other major gas fields in British Columbia and Alberta. Both Fort St. John and Grande Prairie experienced rapid economic and population growth as a result.
Economy


Peace Country contains Canada's northernmost lands suitable for agriculture. Crops raised include canola, oats, peas, and barley. Some cattle ranching and beekeeping is also done in the area. In 2006, the region accounted for 14.4% of Canada's total bison-producing herd.[7]
Other industries include oil and gas extraction and forestry. Lumber, oriented strand board, and pulp are produced in many forestry mills throughout the region.
Infrastructure
Peace Country is crossed by the southern leg of the Alaska Highway, the western extremity of Alberta Highway 43 and the southern portion of the Mackenzie Highway. Other important transportation routes include the northern part of Alberta Highway 2, Alberta Highway 35, British Columbia Highway 29, British Columbia Highway 97, and Alberta Highway 49.[3]
Regional air transport hubs are Grande Prairie Airport and Peace River Airport in Alberta and Fort St. John Airport in British Columbia.
Health care is provided through British Columbia's Northern Health and through Alberta Health Services, on behalf of Alberta's Ministry of Health.
References
- Clare, Gerald R., Dawson Creek: An Illustrated History, 2008
- Henry M. Leppard (January 1935). "The Settlement of the Peace River Country" Geographical Review, Vol. 25, No. 1, pp. 62-78
- Discover the Peace Country. "Peace Country Map". Retrieved 2006-01-07.
- Les McLaughlin, Legion Magazine. "Peace River Country". Archived from the original on 2006-03-02. Retrieved 2006-01-07.
- Pettit, Donald A. The Peace: A history in photographs, 2008
- Pettit, Donald A., The Peace: A history in photographs, 2008
- "Canadian Agriculture at a Glance: Bison on the comeback trail". www.statcan.gc.ca.