Perspicaris
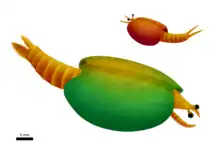
Perspicaris (from the Latin perspicax, meaning “sharp-sighted,” and caris, “crab/shrimp”) an extinct genus of bivalved arthropod from the Cambrian period. Fossils have been found in North America, primarily the Burgess Shale of British Columbia, Canada but also possibly the Wheeler Shale, Marjum Formation, Pioche Shale and Bloomington Formation. Two named species are known from the Burgess Shale Perspicaris dictynna and Perspicaris recondita, which differ in maximum size (66 millimetres (2.6 in) in P. recondita vs 29 millimetres (1.1 in) in P. dictynna), as well as proportions of the tail. Both species have a pair of stalked eyes, as well as a pair of large segmented antennae. The tail is forked and spiny. They are thought to have been active swimmers (nektonic).[2]
| Perspicaris Temporal range: | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Life restoration of Perspicaris dictynna | |
 | |
| Restoration of Perspicaris recondita | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Genus: | Perspicaris Briggs 1977 |
| Species | |
| |
Perspicaris has been identified as a member of a clade Hymenocarina close to the crown-group of Euarthropoda, which includes myriapods, chelicerates, insects and crustaceans.[3][4]
References
- Briggs, D.E.G. (1977). "Archived copy" (PDF). Palaeontology. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-08-24. Retrieved 2010-05-11.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - "Perspicaris dictynna". The Burgess Shale. Royal Ontario Museum. Retrieved 2022-10-27.
- Budd, G. (2002). "A palaeontological solution to the arthropod head problem". Nature. 417 (6886): 271–275. Bibcode:2002Natur.417..271B. doi:10.1038/417271a. PMID 12015599. S2CID 4310080.
- Izquierdo‐López, Alejandro; Caron, Jean‐Bernard (November 2021). Zhang, Xi‐Guang (ed.). "A Burgess Shale mandibulate arthropod with a pygidium: a case of convergent evolution". Papers in Palaeontology. 7 (4): 1877–1894. doi:10.1002/spp2.1366. ISSN 2056-2799. S2CID 236284813.
