Platelet storage pool deficiency
Platelet storage pool deficiency is a type of coagulopathy characterized by defects in the granules in platelets, particularly a lack of granular non-metabolic adenosine diphosphate.[3] Individuals with adenosine diphosphate deficient storage pool disease present a prolonged bleeding time due to impaired aggregation response to fibrillar collagen.
| Platelet storage pool deficiency | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Storage pool platelet disease[1] |
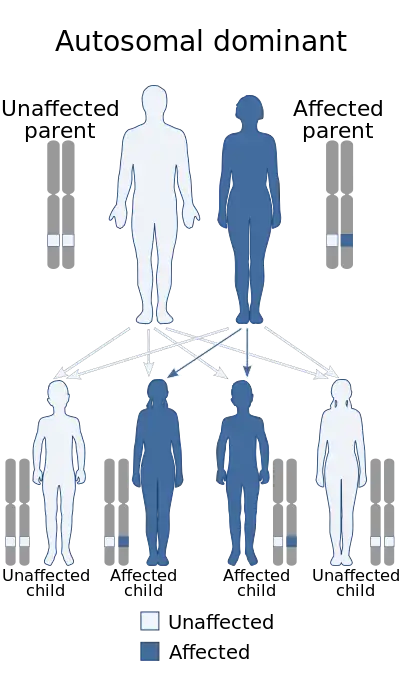 | |
| Platelet storage pool deficiency is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner | |
| Specialty | Hematology |
| Symptoms | Anemia[1] |
| Causes | Inherited or acquired[1] |
| Diagnostic method | Flow cytometry, Bleeding time analysis[1] |
| Treatment | Antifibrinolytic medications[2][1] |
Symptoms and signs
The presentation (signs/symptoms) of an individual with platelet storage pool deficiency is as follows:[1]
- Unusual bleeding(after surgical procedure)
- Anemia
- Decrease mean platelet volume
- Myelodysplasia
Cause
The condition of platelet storage pool deficiency can be acquired or inherited (genetically passed on from the individuals parents[4]).[1] Some of the causes of platelet storage pool deficiency when acquired are:[1]
Mechanism
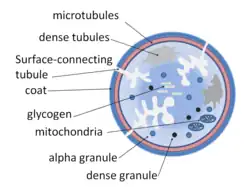
In terms of the pathophysiology of platelet storage pool deficiency one must consider several factors including the human body's normal function prior to such a deficiency, such as platelet alpha-granules one of three types of platelet secretory granule[5]
Platelet α–granules are important in platelet activity, α–granules connect with plasma membrane. This in turn increases the size of the platelet. Platelet α–granules have an important role in hemostasis as well as thrombosis. SNARE accessory proteins control the secretion of α–granule.[5]
Diagnosis

The diagnosis of this condition can be done via the following:[1]
- Flow cytometry
- Bleeding time analysis
- Platelet aggregation function study:
| ADP | Epinephrine | Collagen | Ristocetin | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P2Y receptor defect[6] (including Clopidogrel) | Decreased | Normal | Normal | Normal |
| Adrenergic receptor defect[6] | Normal | Decreased | Normal | Normal |
| Collagen receptor defect[6] | Normal | Normal | Decreased or absent | Normal |
| Normal | Normal | Normal | Decreased or absent | |
| Decreased | Decreased | Decreased | Normal or decreased | |
| Storage pool deficiency[7] | Absent second wave | Partial | ||
| Aspirin or aspirin-like disorder | Absent second wave | Absent | Normal | |
Types
This condition may involve the alpha granules or the dense granules.[8] Therefore, the following examples include:

Treatment
Platelet storage pool deficiency has no treatment however management consists of antifibrinolytic medications if the individual has unusual bleeding event, additionally caution should be taken with usage of NSAIDS[1][2]
See also
References
- "Platelet storage pool deficiency | Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD) – an NCATS Program". rarediseases.info.nih.gov. Retrieved 2017-10-28.
- Kirchmaier, Carl Maximilian; Pillitteri, Daniele (October 2010). "Diagnosis and Management of Inherited Platelet Disorders". Transfusion Medicine and Hemotherapy. 37 (5): 237–246. doi:10.1159/000320257. ISSN 1660-3796. PMC 2980508. PMID 21113246.
- Alan D. Michelson (2007). Platelets. Burlington, MA: Academic Press/Elsevier. pp. 313. ISBN 978-0-12-369367-9.
- Choices, NHS (2017-10-23). "Genetics - Genetic inheritance - NHS Choices". www.nhs.uk. Retrieved 28 October 2017.
- Blair, Price; Flaumenhaft, Robert (2009). "Platelet alpha-granules: basic biology and clinical correlates". Blood Reviews. 23 (4): 177–189. doi:10.1016/j.blre.2009.04.001. ISSN 1532-1681. PMC 2720568. PMID 19450911.
- Borhany, Munira; Pahore, Zaen; ul Qadr, Zeeshan; Rehan, Muhammad; Naz, Arshi; Khan, Asif; Ansari, Saqib; Farzana, Tasneem; Nadeem, Muhammad; Raza, Syed Amir; Shamsi, Tahir (2010). "Bleeding disorders in the tribe: result of consanguineous in breeding". Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases. 5 (1). doi:10.1186/1750-1172-5-23. ISSN 1750-1172.
- "Why Perform Platelet Aggregation?". Helena Biosciences. 2015
- William B. Coleman; Gregory J. Tsongalis (2009). Molecular pathology: the molecular basis of human disease. Academic Press. pp. 258–. ISBN 978-0-12-374419-7. Retrieved 2 November 2010.
- Reserved, Inserm US14 -- All Rights. "Orphanet: Gray platelet syndrome". www.orpha.net. Retrieved 2017-10-29.
- "OMIM Entry - # 601709 - Quebec Platelet Disorder". www.omim.org. Retrieved 29 October 2017.
- Kaushansky K, Lichtman M, Beutler E, Kipps T, Prchal J, Seligsohn U. (2010; edition 8: pages 1946–1948) Williams Hematology. McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-162151-9
- Huizing, Marjan; Malicdan, May Christine V.; Gochuico, Bernadette R.; Gahl, William A. (1993). "Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome". In Adam, Margaret P.; Ardinger, Holly H.; Pagon, Roberta A.; Wallace, Stephanie E.; Bean, Lora J.H.; Mefford, Heather C.; Stephens, Karen; Amemiya, Anne; Ledbetter, Nikki (eds.). GeneReviews. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle. PMID 20301464.update 2017
- Reserved, INSERM US14 -- All Rights. "Orphanet: Chédiak Higashi syndrome". www.orpha.net. Retrieved 29 October 2017.
Further reading
- Sandrock, Kirstin; Zieger, Barbara (2010). "Current Strategies in Diagnosis of Inherited Storage Pool Defects". Transfusion Medicine and Hemotherapy. 37 (5): 248–258. doi:10.1159/000320279. ISSN 1660-3796. PMC 2980509. PMID 21113247.
- Gresele, Paolo; Fuster, Valentin; Lopez, Jose A.; Page, Clive P.; Vermylen, Jos (2007). Platelets in Hematologic and Cardiovascular Disorders: A Clinical Handbook. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9781139468763. Retrieved 26 November 2017.