Portal:Zambia
The Zambia Portal
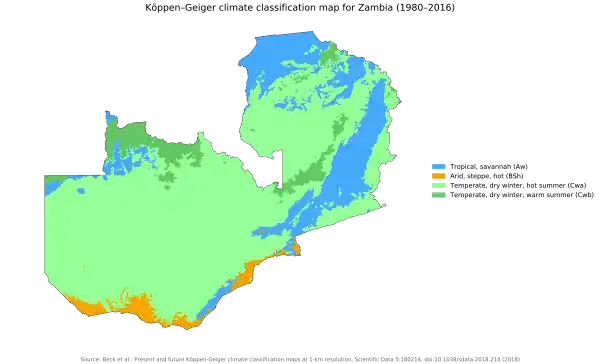
Zambia (/ˈzæmbiə, ˈzɑːm-/), officially the Republic of Zambia (Bemba: Icalo ca Zambia; Tonga: Cisi ca Zambia; Tumbuka: Chalo cha Zambia; Lozi: Naha ya Zambia; Chichewa: Dziko la Zambia), is a landlocked country at the crossroads of Central, Southern and East Africa. It is typically referred to being in South-Central Africa or Southern Africa. Its neighbours are the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the north, Tanzania to the north-east, Malawi to the east, Mozambique to the southeast, Zimbabwe and Botswana to the south, Namibia to the southwest, and Angola to the west. The capital city of Zambia is Lusaka, located in the south-central part of Zambia. The population is concentrated mainly around Lusaka in the south and the Copperbelt Province to the north, the core economic hubs of the country. Originally inhabited by Khoisan peoples, the region was affected by the Bantu expansion of the thirteenth century. Following European explorers in the 18th century, the British colonised the region into the British protectorates of Barotziland–North-Western Rhodesia and North-Eastern Rhodesia towards the end of the 19th century. These were merged in 1911 to form Northern Rhodesia. For most of the colonial period, Zambia was governed by an administration appointed from London with the advice of the British South Africa Company. On 24 October 1964, Zambia became independent of the United Kingdom and prime minister Kenneth Kaunda became the inaugural president. Kaunda's socialist United National Independence Party (UNIP) maintained power from 1964 until 1991. Kaunda played a key role in regional diplomacy, cooperating closely with the United States in search of solutions to conflicts in Southern Rhodesia (Zimbabwe), Angola, and Namibia. From 1972 to 1991 Zambia was a one-party state with UNIP as the sole legal political party under the motto "One Zambia, One Nation" coined by Kaunda. Kaunda was succeeded by Frederick Chiluba of the social-democratic Movement for Multi-Party Democracy in 1991, beginning a period of socio-economic development and government decentralisation. Zambia has since become a multi-party state and has experienced several peaceful transitions of power. Zambia contains abundant natural resources, including minerals, wildlife, forestry, freshwater and arable land. In 2010, the World Bank named Zambia one of the world's fastest economically reformed countries. The Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA) is headquartered in Lusaka. (Full article...) Selected article - Kasanka National Park is a park located in the Chitambo District of Zambia’s Central Province. At roughly 390 km2 (150 sq mi), Kasanka is one of Zambia’s smallest national parks. Kasanka was the first of Zambia’s national parks to be managed by a private-public partnership. The privately funded Kasanka Trust Ltd has been in operation since 1986 and undertakes all management responsibilities, in partnership with the Department of National Parks and Wildlife (DNPW - previously ZAWA). The park has an average elevation between 1,160 m (3,810 ft) and 1,290 m (4,230 ft) above mean sea level. It has a number permanent shallow lakes and water bodies with the largest being Wasa. There are five perennial rivers in the park, with the largest being the Luwombwa River. The Luwombwa is the only river that drains the NP, which flows out in the northwestern corner. It is a tributary of the Luapula, which further upstream also drains the Bangweulu Swamp and forms the main source of the Congo River. Although Kasanka NP is part of the Greater Bangweulu Ecosystem, there is no direct hydrological connection between the park and the Bangweulu Wetlands. A total of 114 mammal species have been recorded in the park including elephant, hippopotamus and sitatunga. A number of species have been reintroduced in the park by Kasanka Trust - the most successful of which are zebra and buffalo. Close to ten million Eidolon helvum (African straw-coloured fruit bat) migrate to the Mushitu swamp evergreen forest in the park for three months during October to December, making it the largest mammal migration in the world. Over 471 bird species have been identified in the park. An airfield (ICAO: FLKA) lies there. (Full article...)General images -The following are images from various Zambia-related articles on Wikipedia.
| ||||


.svg.png.webp)






.jpg.webp)



%252C_%25_of_world_average%252C_1960-2012%253B_Zimbabwe%252C_South_Africa%252C_Botswana%252C_Zambia%252C_Mozambique.png.webp)




.jpg.webp)






_Luba_peoples_The_Metropolitan_Museum_of_Art.png.webp)






.svg.png.webp)
